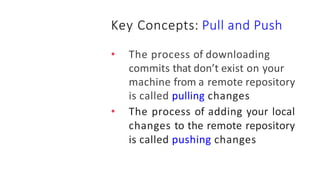
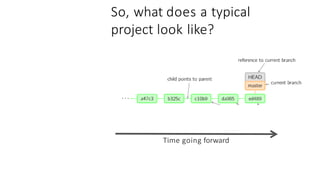
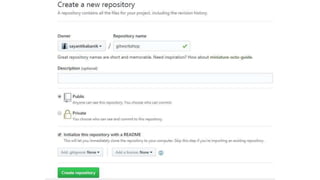
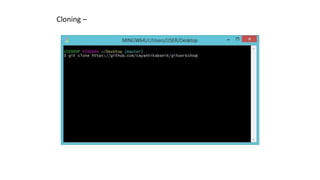
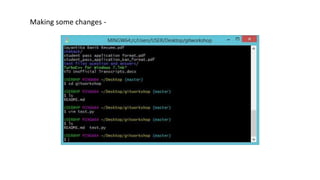
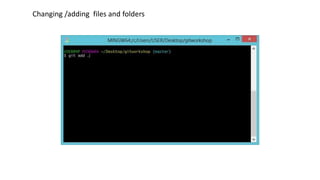
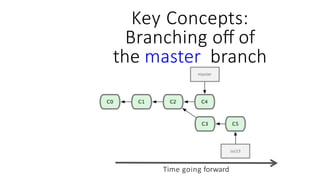
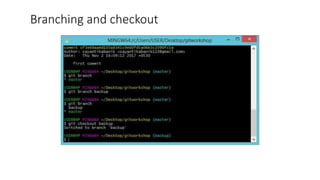
This document provides an overview of Git and GitHub. It explains that Git is a version control system that allows users to track changes to files and code over time. GitHub is a web-based hosting service for Git repositories that adds additional features like documentation and issue tracking. The document outlines key Git concepts like commits, branches, pulling and pushing changes. It provides a quick example workflow of creating a GitHub account, making a repository, cloning it locally, making commits, and pushing changes.