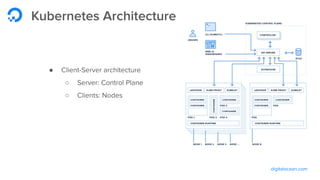
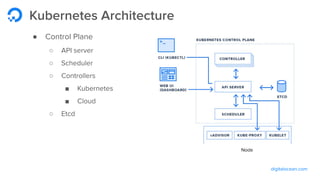
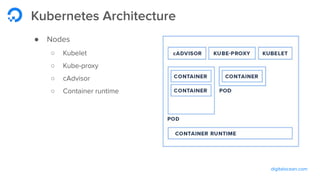
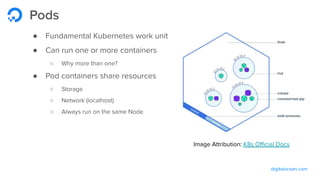
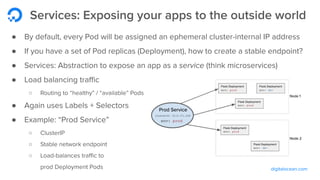
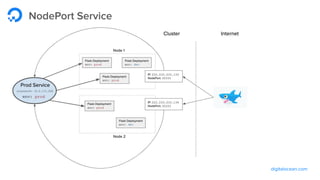
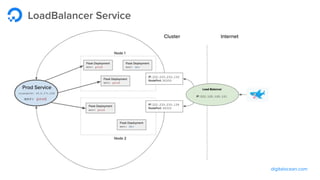
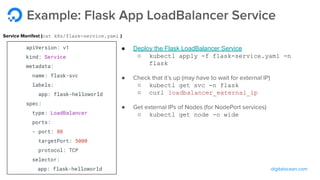
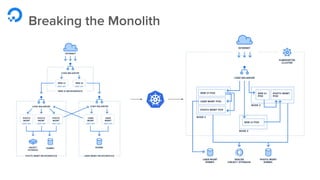
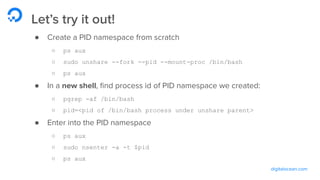
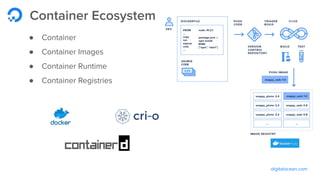
The document outlines a webinar by Wayne Warren from DigitalOcean on containers and Kubernetes, focusing on app design and deployment. It provides a high-level overview of containers, their architecture, and Kubernetes features, including live demonstrations of building a containerized Flask app and deploying it on a Kubernetes cluster. Key topics include namespaces, pods, workloads, services, management of containers, and resources like ConfigMaps and Secrets.









![digitalocean.com
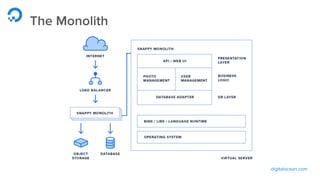
Example: Containerized Flask App
FROM python:3-alpine
WORKDIR /app
COPY requirements.txt .
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
COPY . .
EXPOSE 5000
CMD ["python", "app.py"]
Dockerfile (cat app/Dockerfile)
● Build & tag image
○ docker build -t flask:v0 .
○ docker images
● Run container / test
○ docker run -p 5000:5000
flask:v0
○ docker ps
○ curl http://localhost:5000
● Push to Docker Hub repo (optional)
● What would this look like in VM world?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/getting-started-with-containers-and-kubernetes-march-2020-cncf-webinar-240422165828-e9bff4f4/85/Getting-Started-with-Containers-and-Kubernetes_-March-2020-CNCF-Webinar-pdf-14-320.jpg)