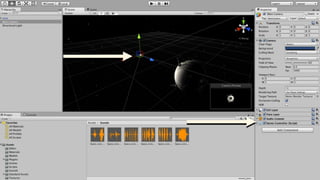
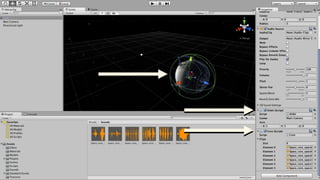
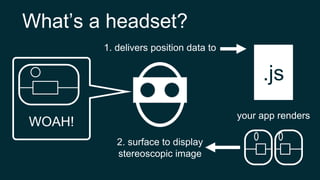
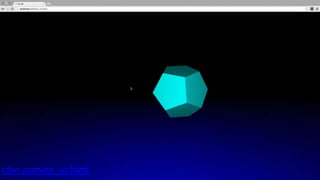
The document provides an introduction to using WebVR with JavaScript, emphasizing the importance of libraries like three.js for rendering 3D graphics in virtual reality. It outlines how to set up a basic VR app, including handling device input and rendering environments, while noting the challenges such as performance and compatibility with mobile browsers. Additionally, it mentions interactive elements and tools like Leap Motion for enhanced VR experiences.











































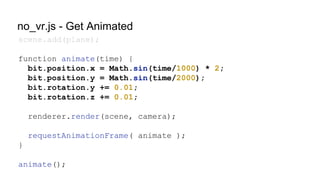
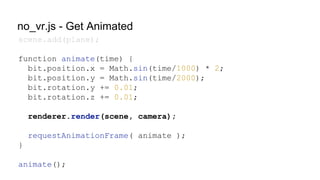
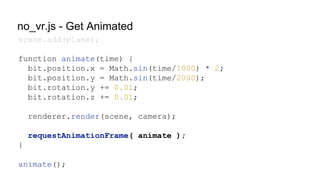













![VRControl.js - Initialization
function gotVRDevices( devices )
devices = filterInvalidDevices( devices );
for ( var i = 0; i < devices.length; i ++ ) {
if ( devices[ i ] instanceof PositionSensorVRDevice ) {
vrInputs.push( devices[ i ] );
}
}
if ( onError ) onError( 'HMD not available' );
}
if ( navigator.getVRDevices ) {
navigator.getVRDevices().then( gotVRDevices );
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/getting-started-in-vr-with-js-150426154412-conversion-gate02/85/Getting-Started-in-VR-with-JS-69-320.jpg)


![VREffect.js - Initialization
function gotVRDevices( devices ) {
for ( var i = 0; i < devices.length; i ++ ) {
if ( devices[ i ] instanceof HMDVRDevice ) {
///…
}
if ( vrHMD === undefined ) {
if ( onError ) onError( 'HMD not available' );
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/getting-started-in-vr-with-js-150426154412-conversion-gate02/85/Getting-Started-in-VR-with-JS-72-320.jpg)




![VRControls.js - Get State from VR Device
this.update = function () {
for ( var i = 0; i < vrInputs.length; i ++ ) {
var vrInput = vrInputs[ i ];
var state = vrInput.getState();
if ( state.orientation !== null ) {
object.quaternion.copy( state.orientation );
}
if ( state.position !== null ) {
object.position.copy( state.position )
.multiplyScalar( scope.scale );
}
}
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/getting-started-in-vr-with-js-150426154412-conversion-gate02/85/Getting-Started-in-VR-with-JS-77-320.jpg)



























![raycast.js - Gaze
var raycaster = new THREE.Raycaster();
var center = new THREE.Vector2();
function gaze() {
if(!audioPlaying) {
raycaster.setFromCamera(center, camera);
var intersects = raycaster.intersectObjects([bit]);
if (intersects.length > 0) {
audioPlaying = true;
if (Math.random() < 0.5) {
switchBitTo(1);
yes.play();
} else {
switchBitTo(0);
no.play();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/getting-started-in-vr-with-js-150426154412-conversion-gate02/85/Getting-Started-in-VR-with-JS-107-320.jpg)