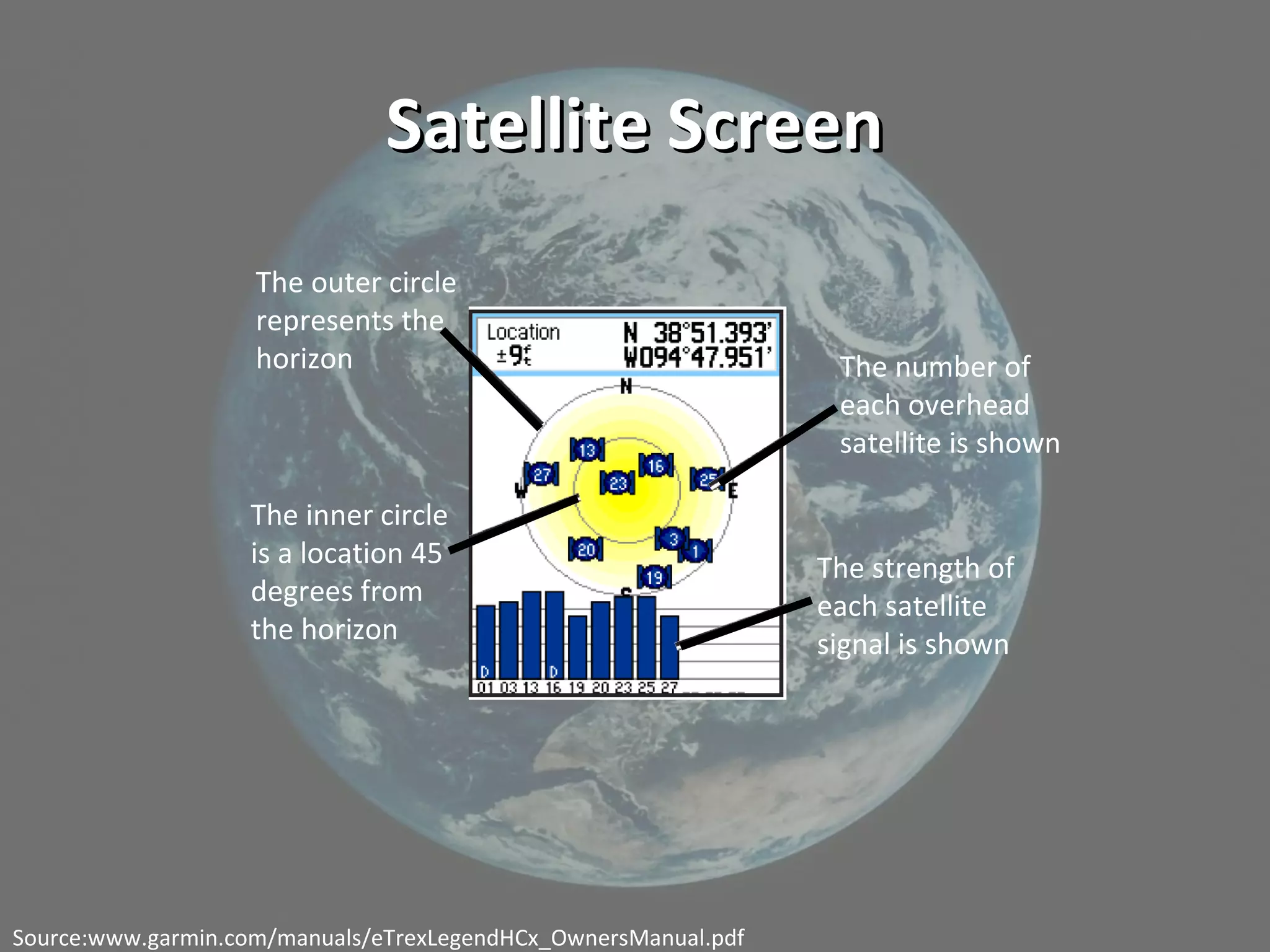
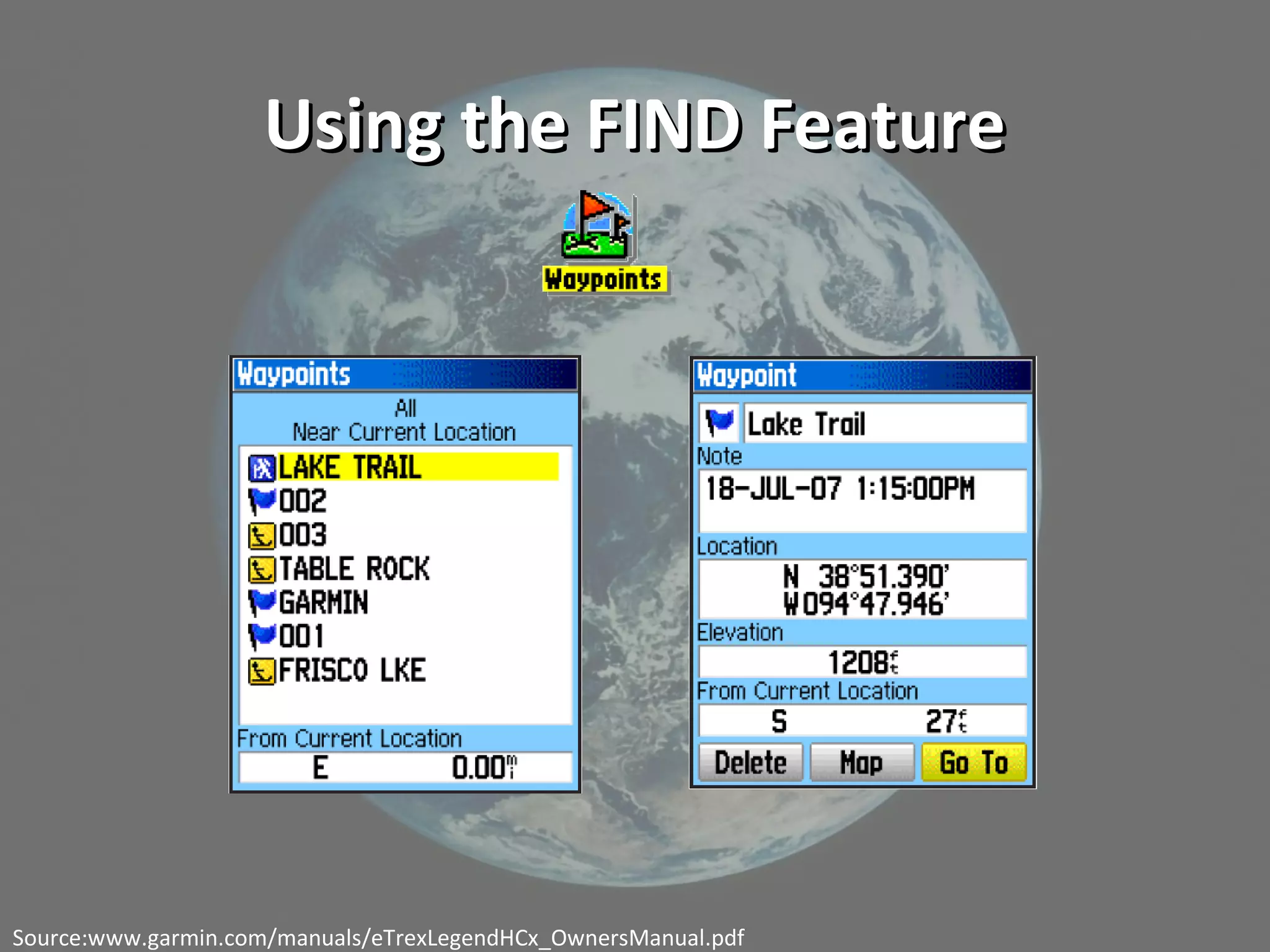
This document discusses geolocation technology and its applications. It begins with definitions of key terms like geolocation, GPS, satellites, waypoints and geocaching. It then demonstrates how to use a GPS receiver to find locations, mark waypoints and view coordinate data. The document discusses using geotagged photos and sharing locations online. It emphasizes that geolocation provides new ways to organize and search information, with implications for research and learning like observing patterns and gaining deeper insights when location data is incorporated.