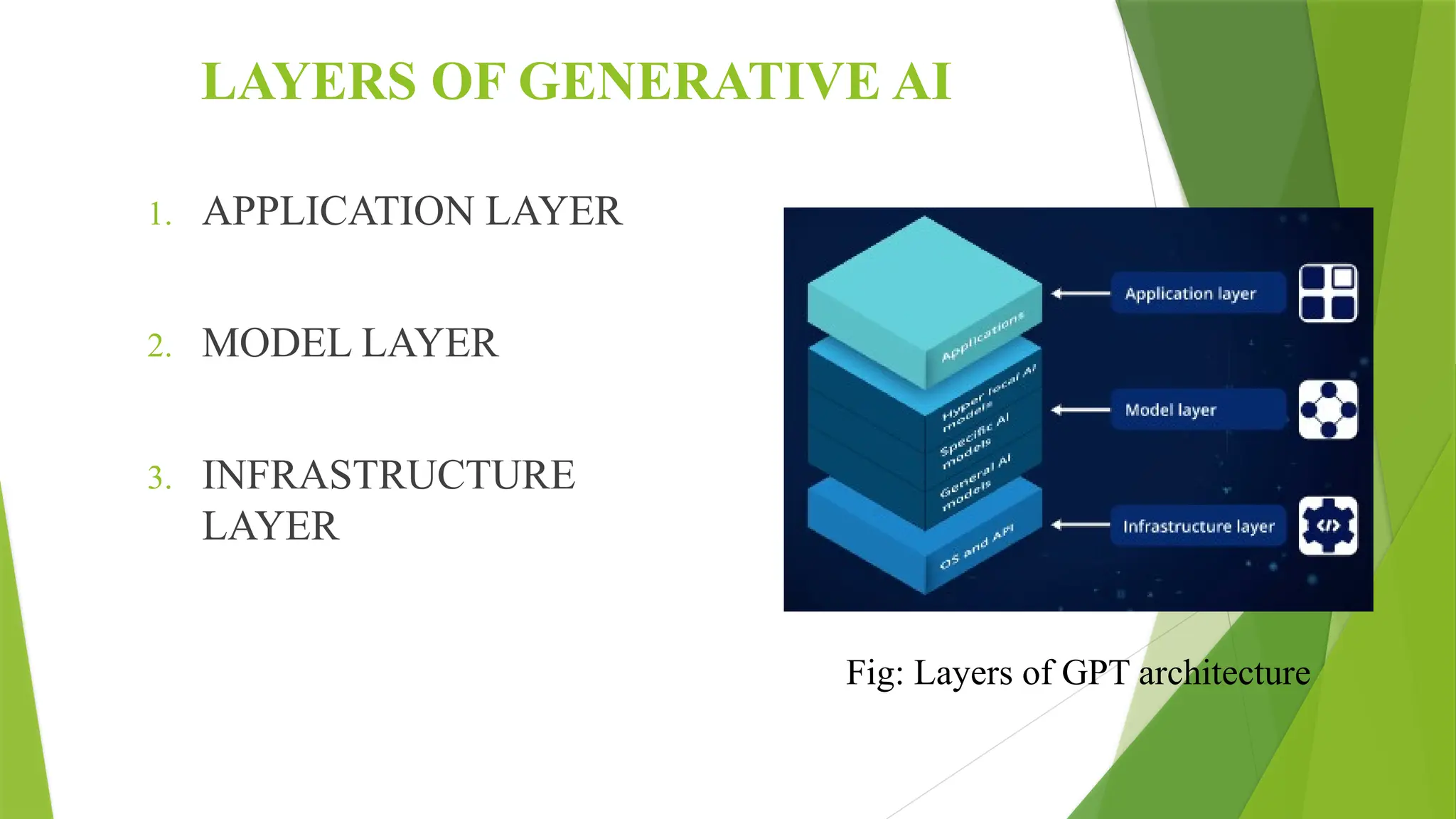
The document presents an overview of Generative AI, detailing its introduction, objectives, applications, and associated advantages and disadvantages. Key elements include various types of large language models (LLMs), their layers, and how generative systems generate content using algorithms like GANs and VAEs. While Generative AI enhances creativity and personalization, it also raises ethical concerns related to misinformation and quality control.