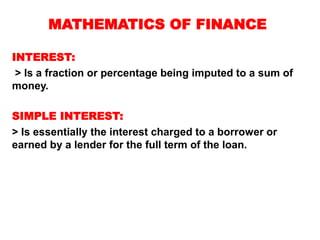
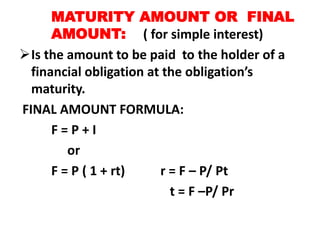
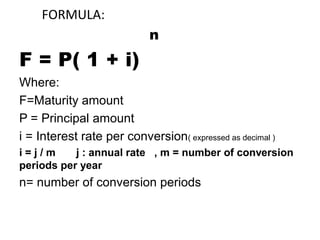
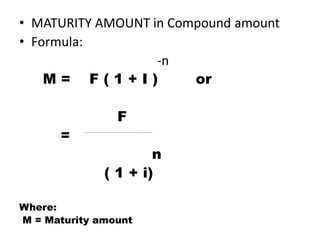
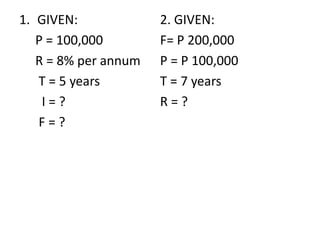This document discusses the mathematics of finance, including simple and compound interest calculations. Simple interest is calculated as Interest = Principal x Rate x Time. Compound interest calculates interest on prior interest amounts over multiple compounding periods. Formulas are provided to calculate interest, principal, maturity/final amounts, and rates for both simple and compound interest scenarios. Examples demonstrate applying the formulas to solve for unknown values.