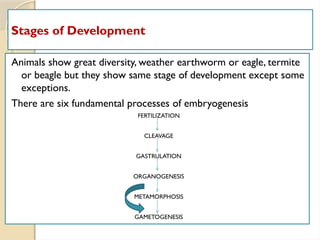
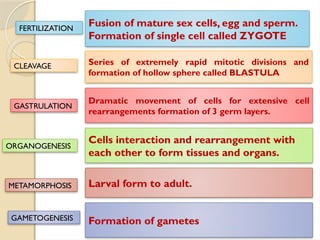
This document outlines a syllabus for a developmental biology course, covering historical perspectives, fundamental processes of embryogenesis, and stages of development in animals. It includes units on gametogenesis, fertilization, cleavage, cell interactions, and the formation of fetal membranes. The course emphasizes key concepts such as induction, differentiation, and metamorphosis in various species.