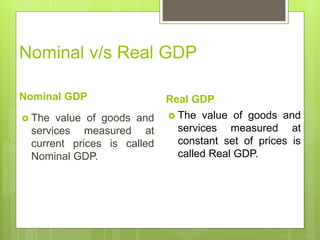
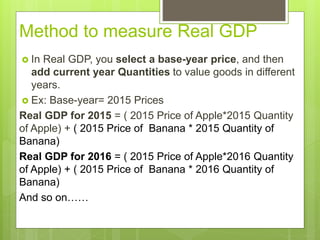
GDP measures the total value of goods and services produced in an economy over a period of time. There are rules for computing GDP, such as only including the value of final goods and services and using imputed values for non-market goods and services. GDP can be measured nominally, using current prices, or realistically, using fixed base year prices to adjust for inflation. Real GDP is a better measure of economic activity as it accounts for changes in quantity rather than just price level changes. The GDP deflator shows the inflation rate by dividing nominal GDP by real GDP.