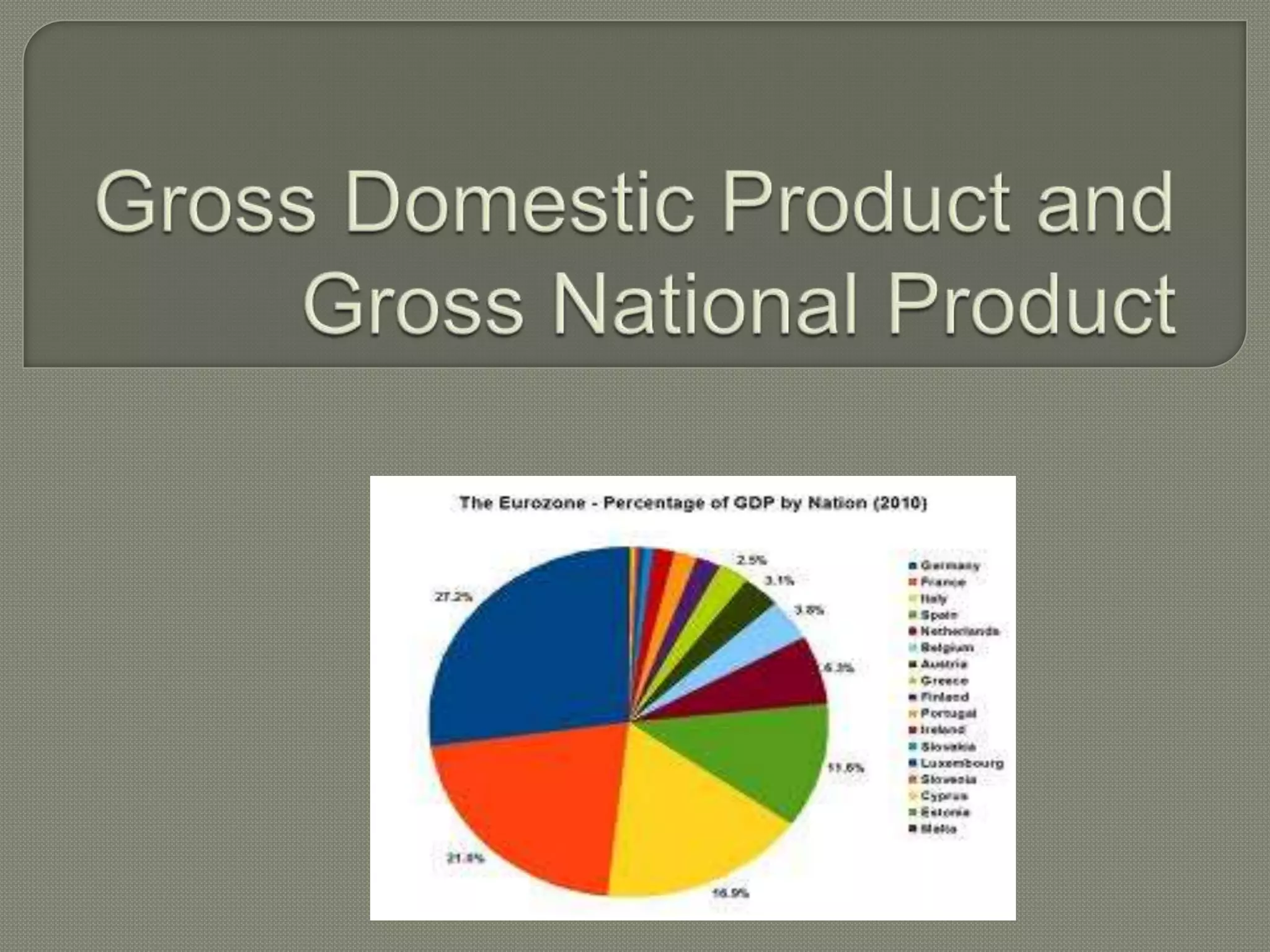
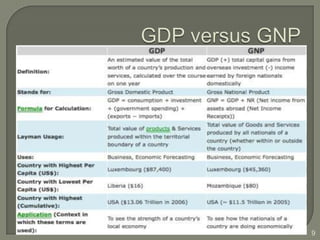
GDP is the total market value of all final goods and services produced in a country in a given period. It is a key indicator of the size and health of a country's economy. GDP per capita is also used to compare standards of living between countries. Economists and investors rely on GDP data to analyze economic growth and determine where to invest resources. While GDP measures production within a country, GNP includes the total output of a country's citizens wherever in the world they may be located. Both GDP and GNP help evaluate a country's economic conditions and guide policymaking around issues like saving, investment, consumption and sectoral contributions to the economy.