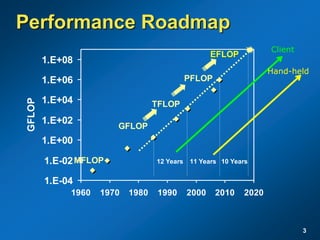
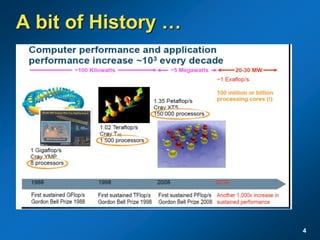
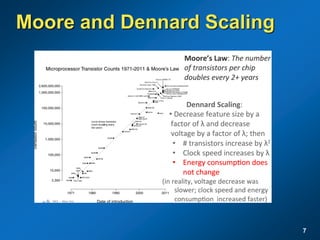
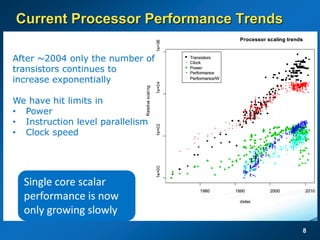
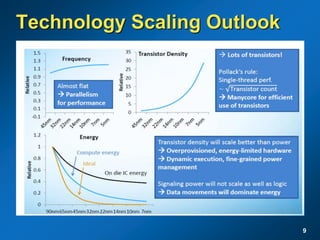
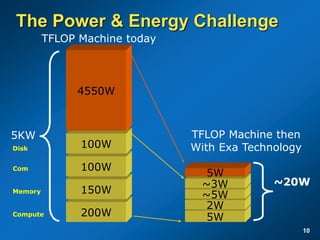
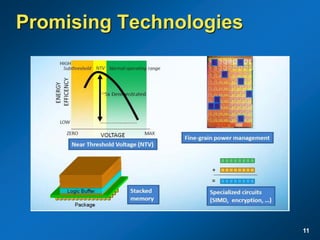
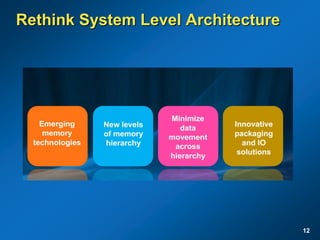
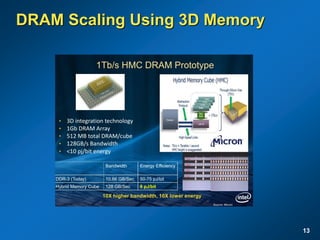
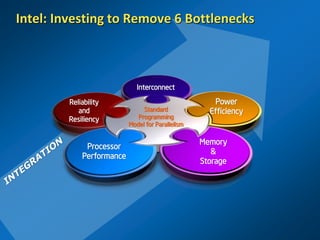
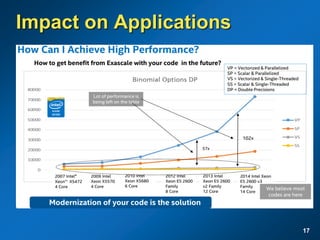
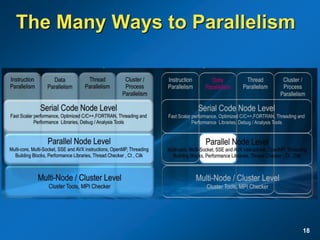
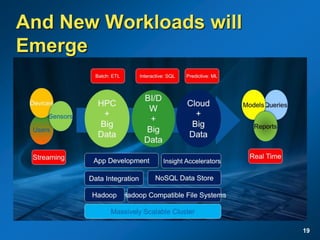
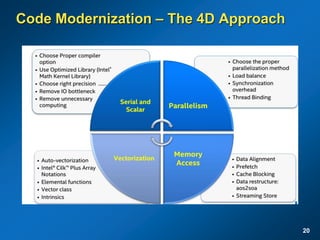
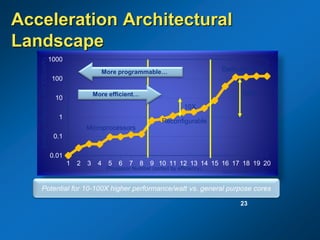
The document discusses the path to exascale computing and the challenges involved. It outlines existing trends like the end of Moore's law and major technology challenges. Technologies being developed to overcome issues include more efficient interconnects, memory, storage, and processors. The development of exascale systems will also require rethinking architectures and a paradigm shift in priorities like power efficiency. Significant code modernization efforts will be needed to effectively utilize exascale systems and harness massively parallel computing.