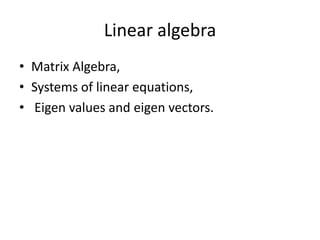
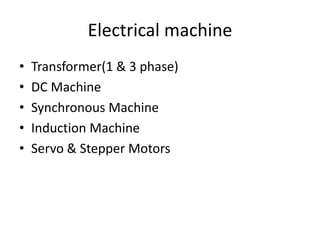
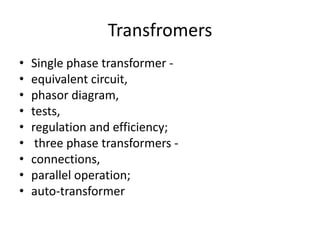
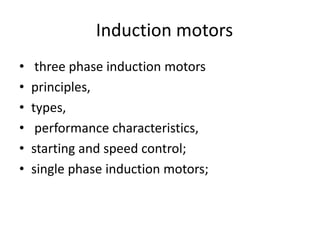
The document provides information about the GATE 2012 exam for electrical engineering, including the breakdown of marks between general aptitude, engineering mathematics, and subjects. It also lists the main topics covered in the engineering mathematics, electrical machines, power systems, control systems, and other electrical engineering subjects on the exam. The topics include concepts like linear algebra, calculus, differential equations, transformers, DC machines, induction motors, power generation, transmission lines, and feedback control systems.