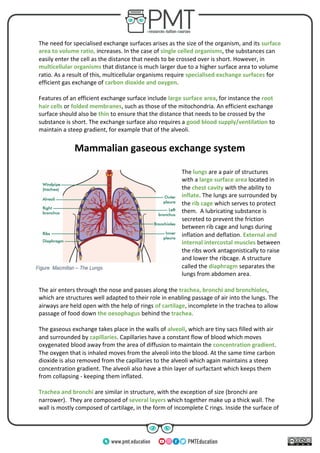
This document summarizes gas exchange and the mammalian respiratory system. It explains that multicellular organisms require specialized exchange surfaces due to their higher surface area to volume ratio compared to single-celled organisms. It then describes the key features of the lungs and respiratory system that facilitate efficient gas exchange in mammals, including the large surface area of the alveoli where oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between the air and blood. The roles of structures like cartilage, ciliated cells, and smooth muscle in supporting breathing and airflow throughout the respiratory tract are also outlined.