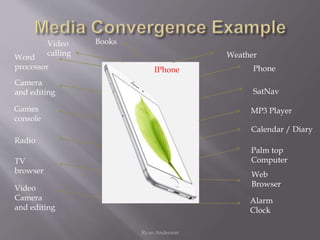
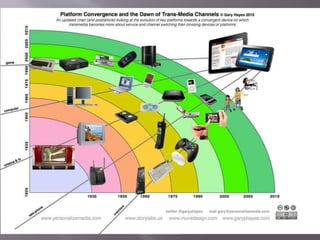
The document discusses how media institutions and audiences have changed due to technological developments and convergence. It notes that institutions now operate across multiple platforms, such as audio-visual, print, internet and interactive media. Audiences also have more choice and control over what they watch due to an increase in available content and their ability to create their own media through user-generated content online. This has resulted in audience fragmentation as groups are broken down by their individual media preferences.