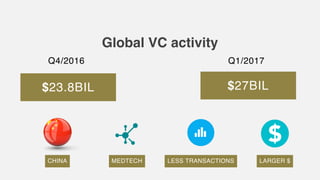
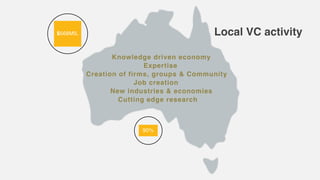
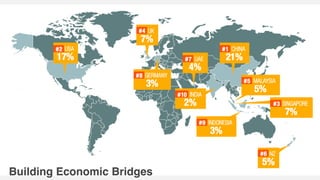
This document provides an overview of the services offered by a venture capital firm. They include providing capital and financial support, strategic support for business and sales strategies, corporate structuring support and leveraging industry networks, operational optimization and cost management support, connecting to potential customers and partners, and human capital services like coaching and talent retention. The document also lists several industries they focus on and provides statistics on global and local venture capital activity and the importance of venture capital for economic prosperity, job creation, and developing new industries.