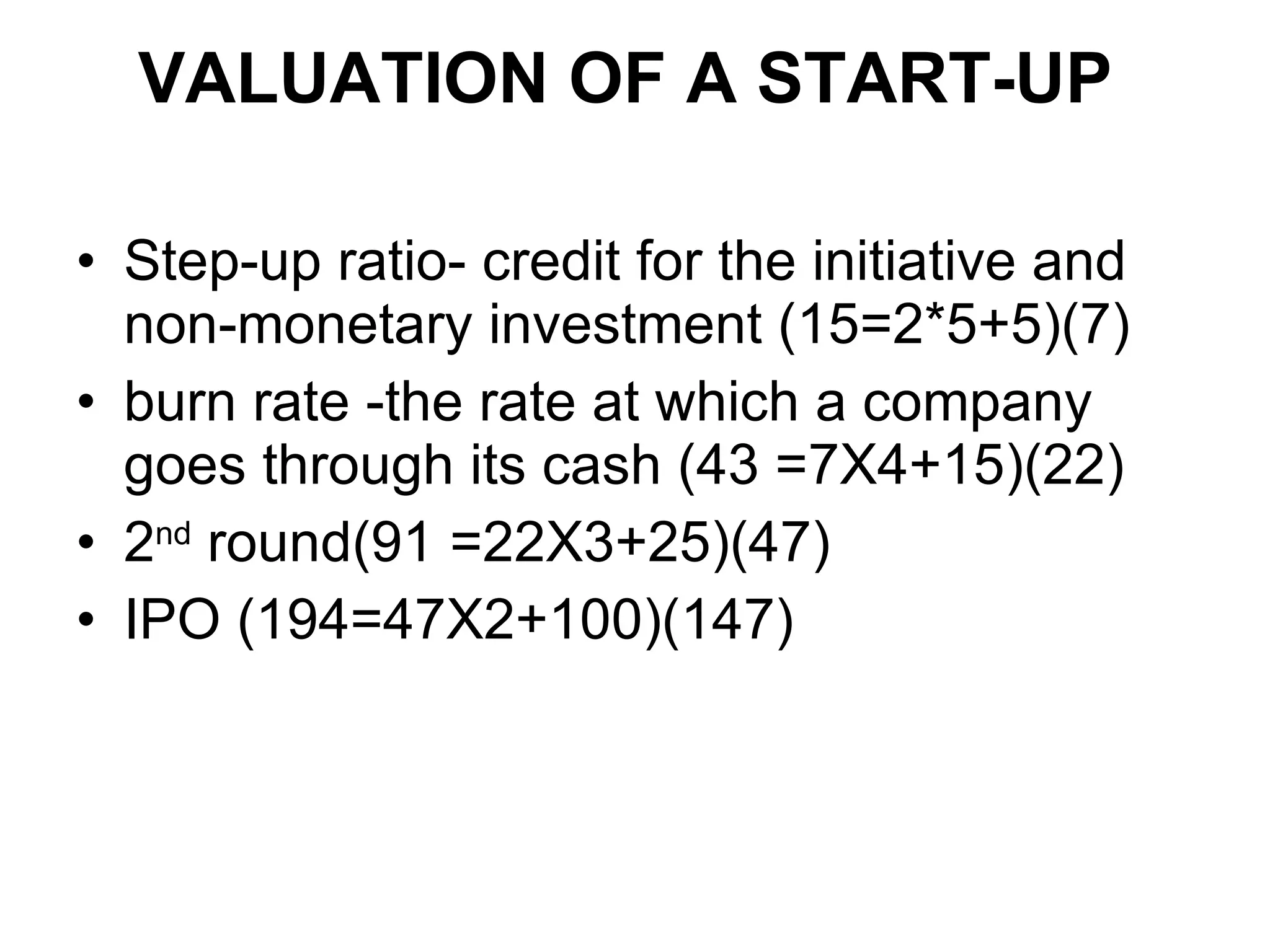
Angel investors provide capital and guidance to startups. Venture capital funds (VCFs) join entrepreneurs as co-promoters and share risks and rewards. VCFs expect high growth and do not require collateral. They provide financing, mentoring, and help with exits. Startups go through seed, early, and expansion stages of funding. VCFs appraise startups through business plans, due diligence, and setting terms like board seats and investment structure. Valuing startups is complex and considers factors like burn rate and growth potential. Risks include changes in markets, technology, management, and regulations. To attract VCFs, startups need strong teams, financials showing high growth, and plans