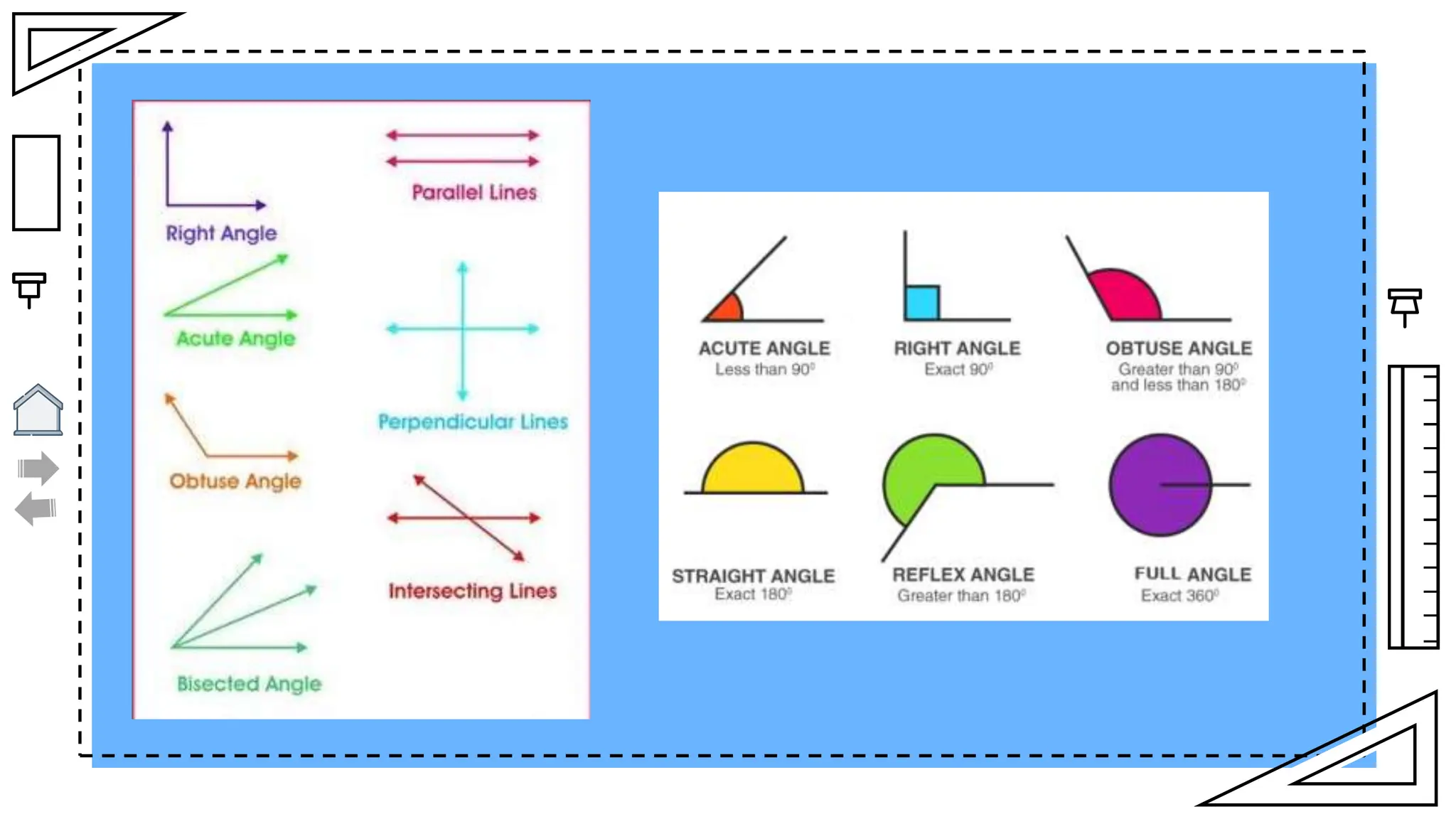
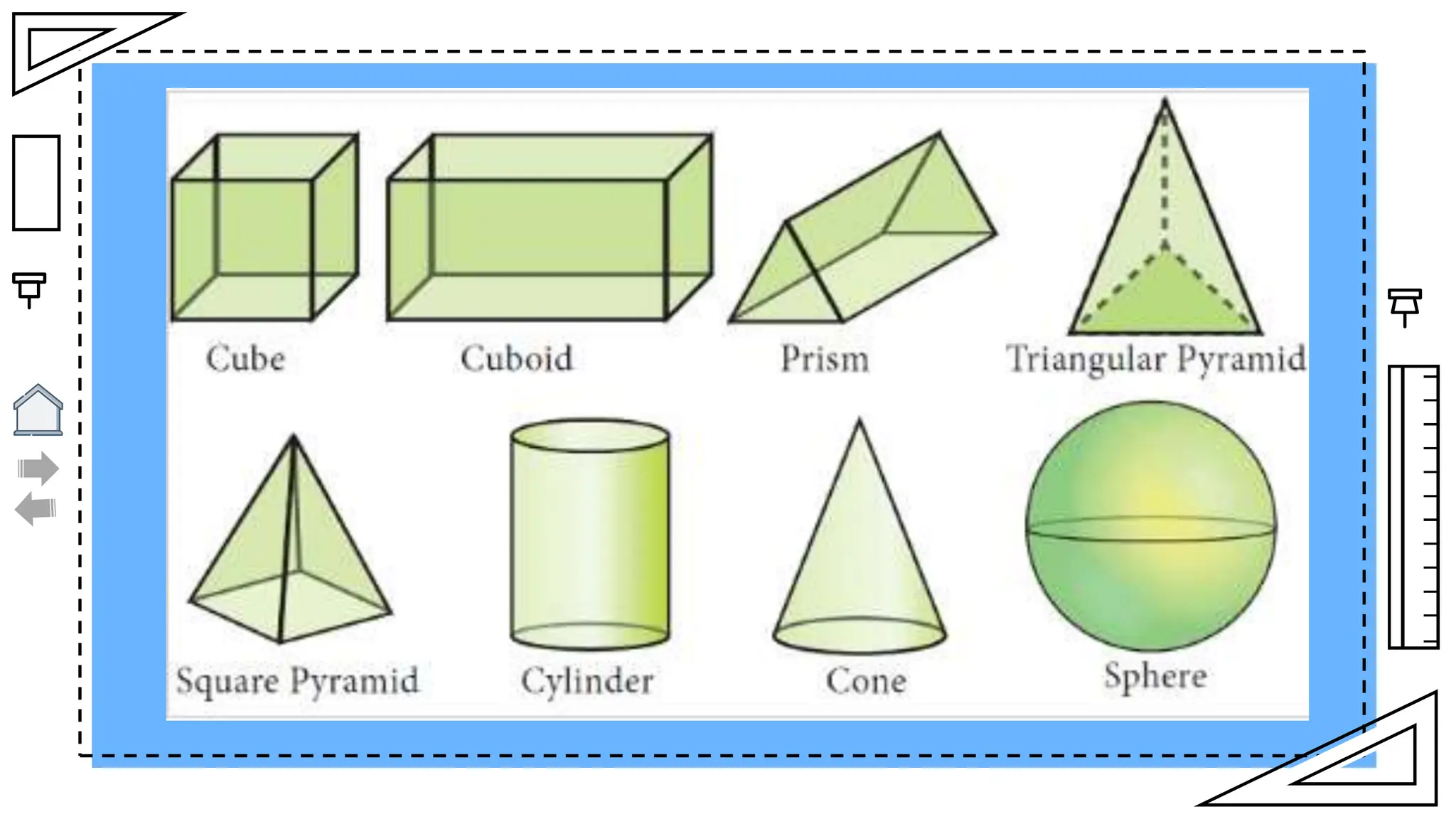
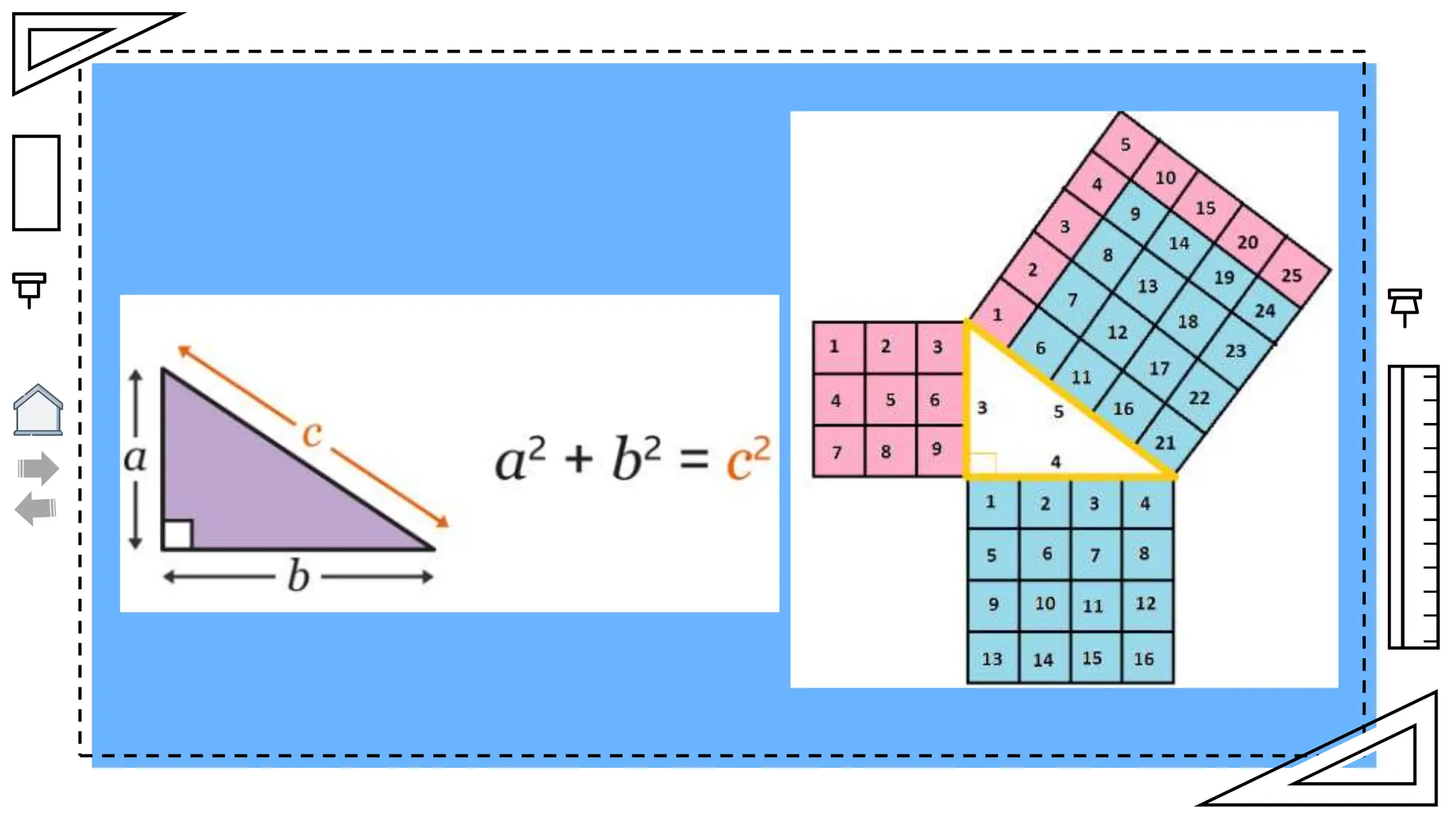
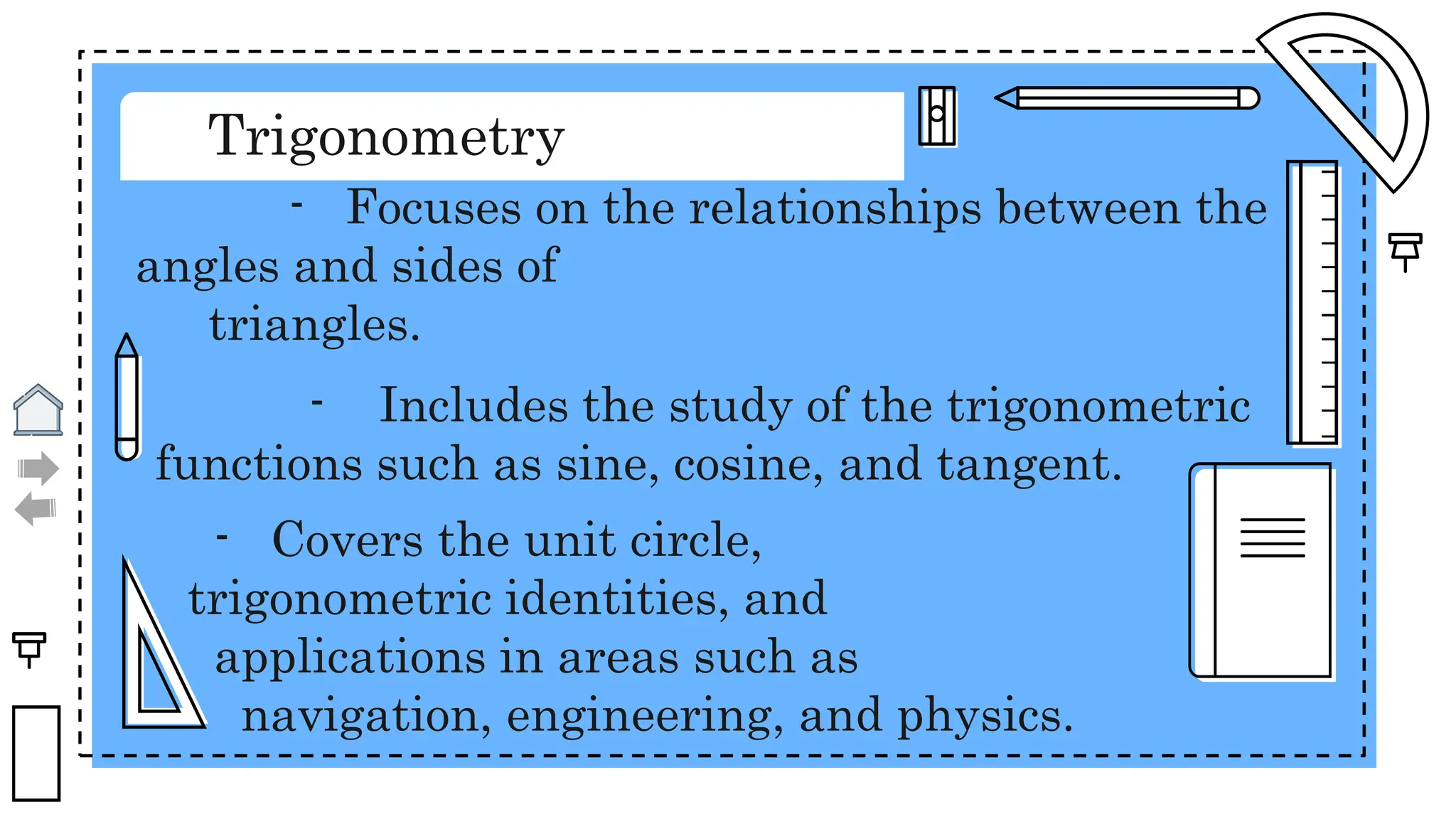
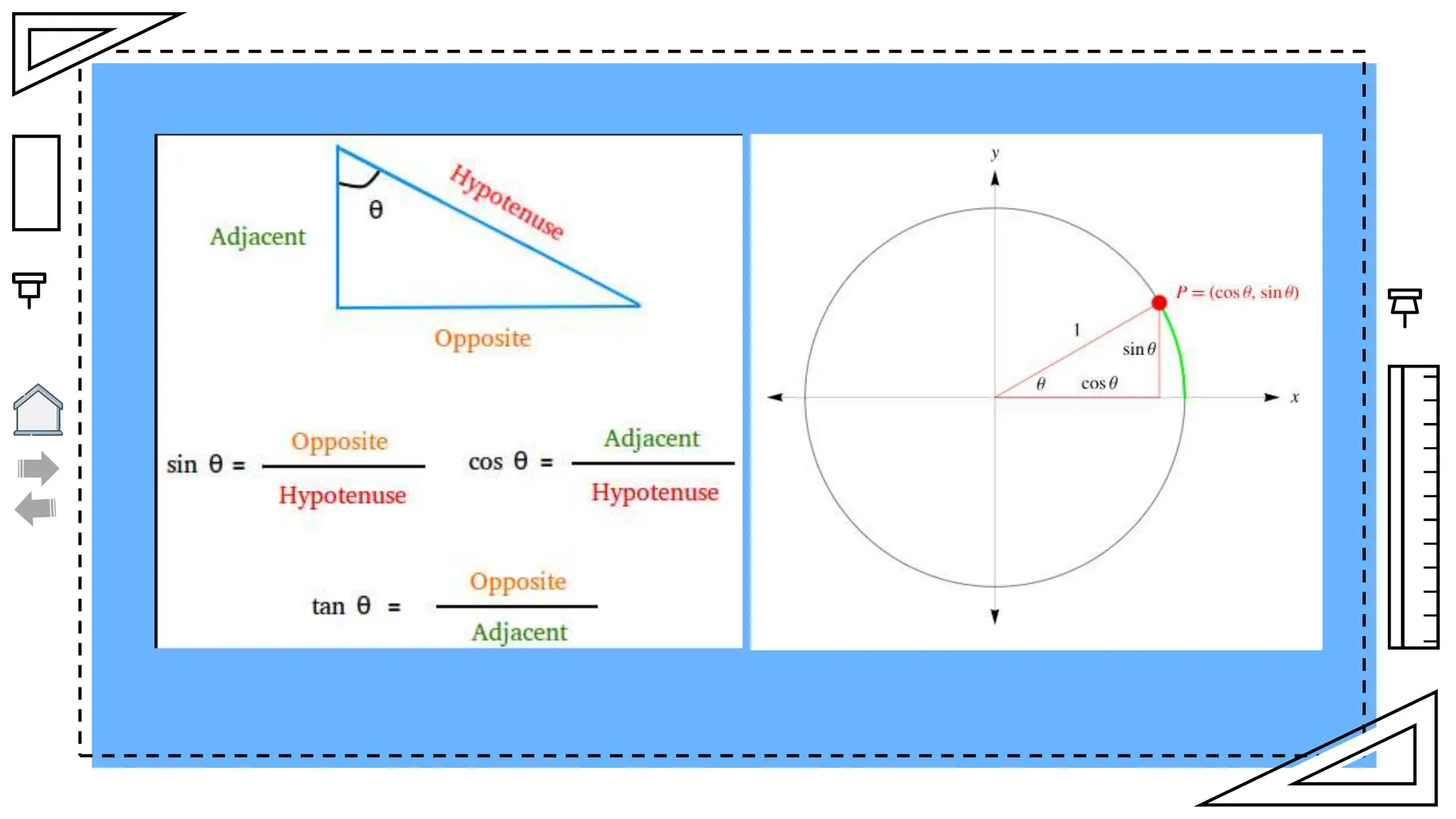
The document outlines essential principles of geometry, including concepts of lines, angles, volume, surface area, equations, and the Pythagorean theorem. It emphasizes the interrelationships of angles and sides in triangles through trigonometry, covering critical functions and applications. The information is presented with credits to various sources for images and icons used in the template.