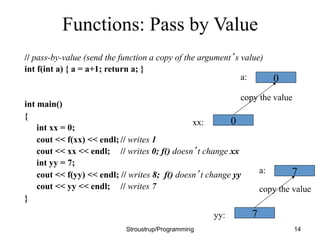
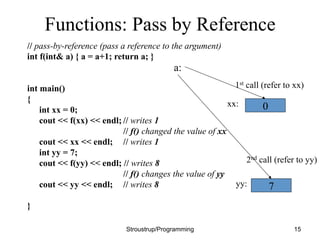
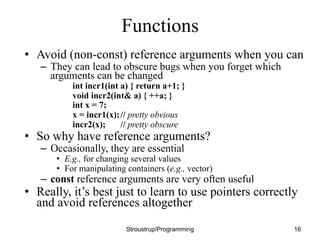
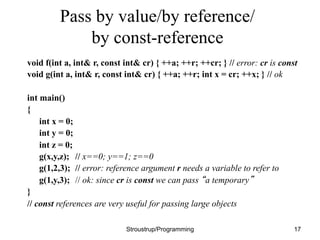
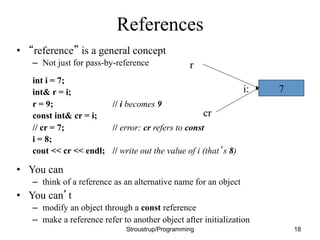
This document discusses functions and header/source files in C++. It covers declarations, definitions, and the differences between them. Declarations introduce names and specify types, while definitions also fully specify the entity. Declarations allow interfaces to be specified. Headers contain declarations to share interfaces between parts of a program. Functions are described as units of operation that can take parameters and return values. The document also discusses scopes, namespaces, and storage classes like static.














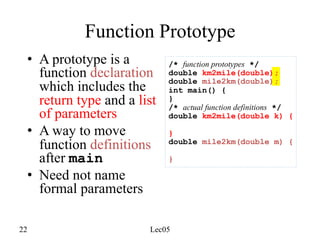



![Scope
#include "std_lib_facilities.h" // get max and abs from here
// no r, i, or v here
class My_vector {
vector<int> v; // v is in class scope
public:
int largest() // largest is in class scope
{
int r = 0; // r is local
for (int i = 0; i<v.size(); ++i) // i is in statement scope
r = max(r,abs(v[i]));
// no i here
return r;
}
// no r here
};
// no v here
Stroustrup/Programming 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04functionsandheaderfiles-240222161224-1c2b6881/85/Functions-And-Header-Files-In-C-Bjarne-stroustrup-26-320.jpg)











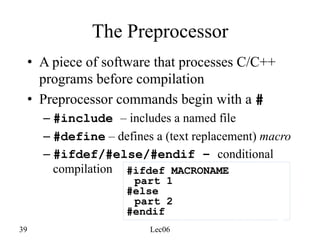




![44 Lec06
Defining a Macro for #ifdef
• #define DEBUG
• #define DEBUG 0
• #define DEBUG 1
• The –Dmacro[=def] flag of g++
– g++ –DDEBUG hw1.cpp –o hw1
– g++ –DDEBUG=1 hw1.cpp –o hw1
– g++ –DDEBUG=0 hw1.cpp –o hw1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04functionsandheaderfiles-240222161224-1c2b6881/85/Functions-And-Header-Files-In-C-Bjarne-stroustrup-44-320.jpg)