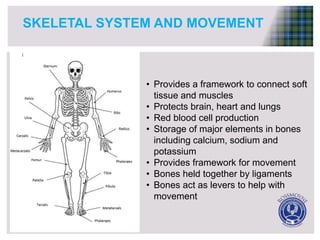
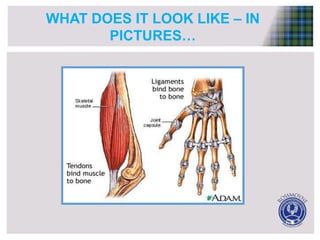
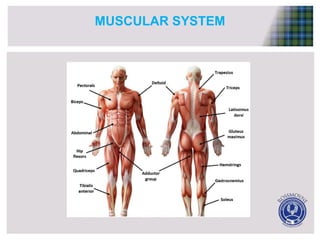
Skeletal muscle has several key functional anatomy characteristics. It attaches to bones via tendons and crosses joints, allowing bones to act as levers and produce movement when muscles contract. Muscles are attached to both sides of joints and work antagonistically in pairs - when one muscle contracts to move a bone in one direction, its counterpart relaxes to allow the motion. Together, the coordinated actions of muscles pulling on bones via tendons enable the skeleton to produce a wide range of movements.