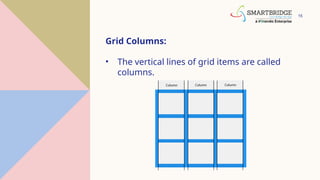
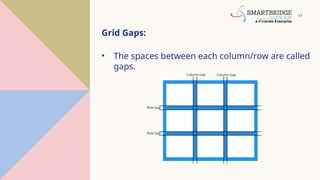
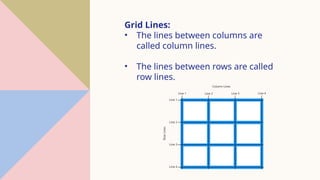
The document is a comprehensive overview of CSS layout techniques, focusing on the position property, CSS Grid, and Flexbox. It details various positioning methods (static, relative, fixed, absolute, and sticky) and explains how to construct a grid layout with grid properties and flex container structures. Additionally, it discusses responsive design with media queries and how these CSS tools can facilitate layout designs without floats or explicit positioning.