Embed presentation
Downloaded 16 times

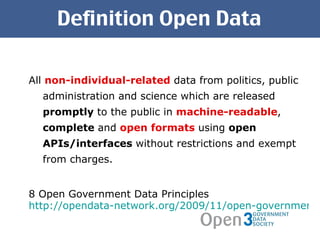



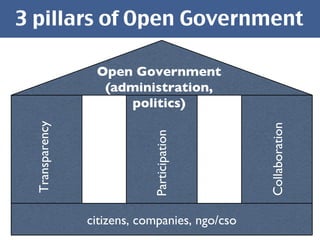
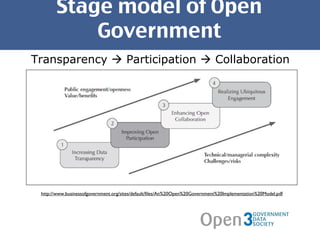
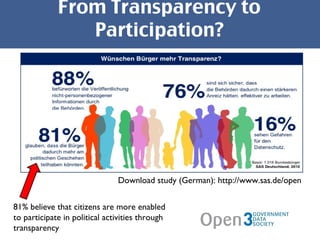
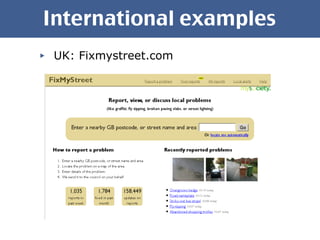



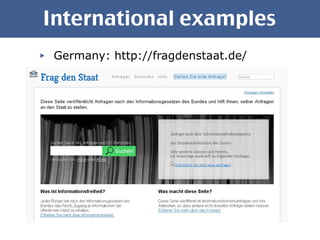

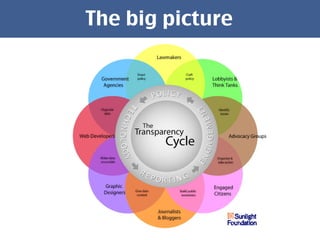

The document discusses open government data and its potential benefits. It defines open data as non-individual data from politics, public administration, and science that is publicly and freely available without restrictions. Open data can make politics and government more transparent and enable better decision making. The document outlines stages of open government from transparency to participation to collaboration. It provides examples from the UK, Germany, and Austria of open data projects and tools that increase civic engagement and oversight of elected representatives.















