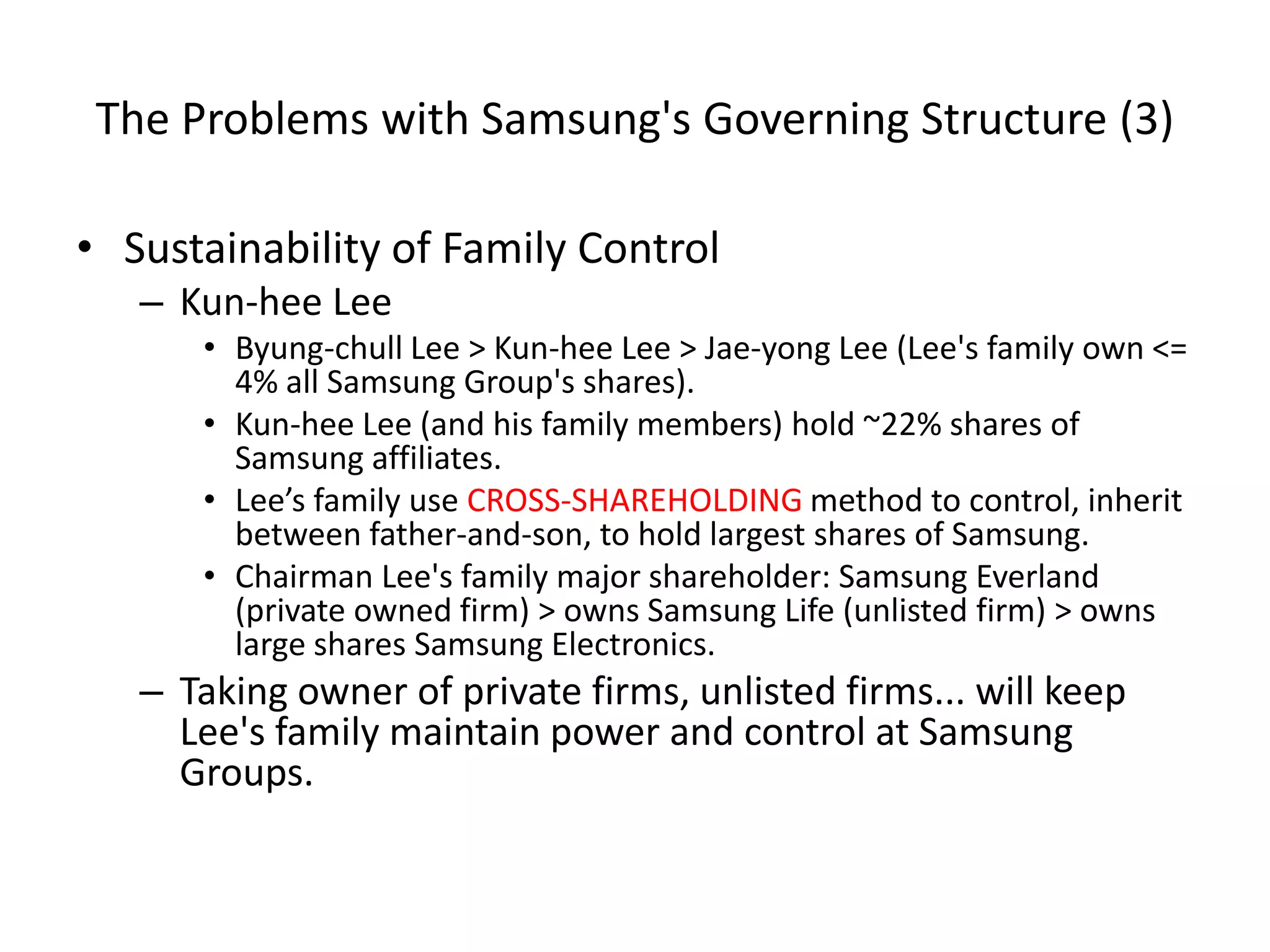
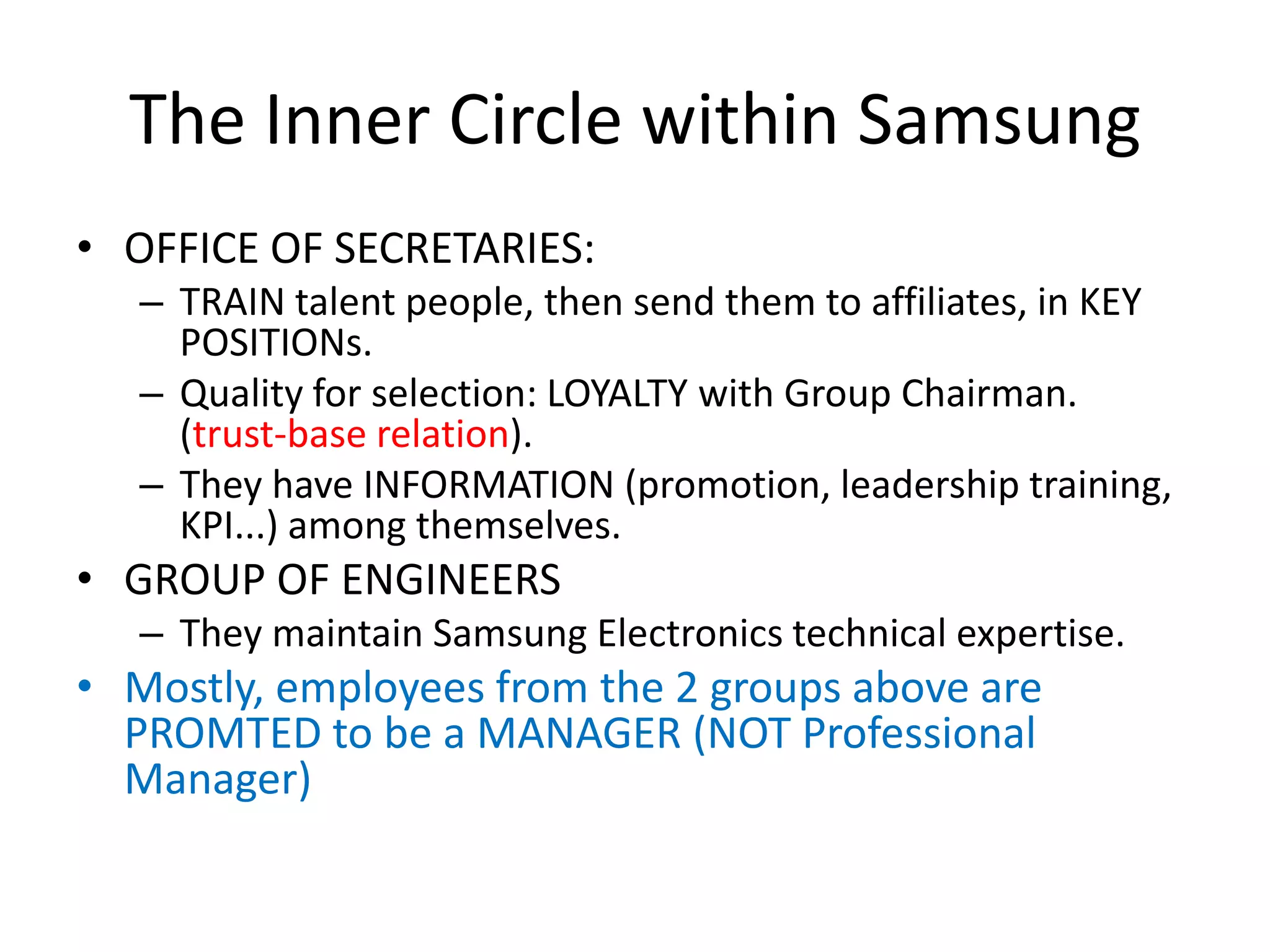
This document summarizes and compares the governing structures of Sony and Samsung. It describes Sony's transition from founder-led management to a more Western-style structure with professional managers and boards, which created issues with succession, internal politics, and applicability. Samsung has a powerful owner-centered structure under Chairman Lee, which allows quick decisions but risks from one-man decision making and sustainability concerns with family control. Both companies faced challenges transitioning to leadership from professional managers rather than founders.