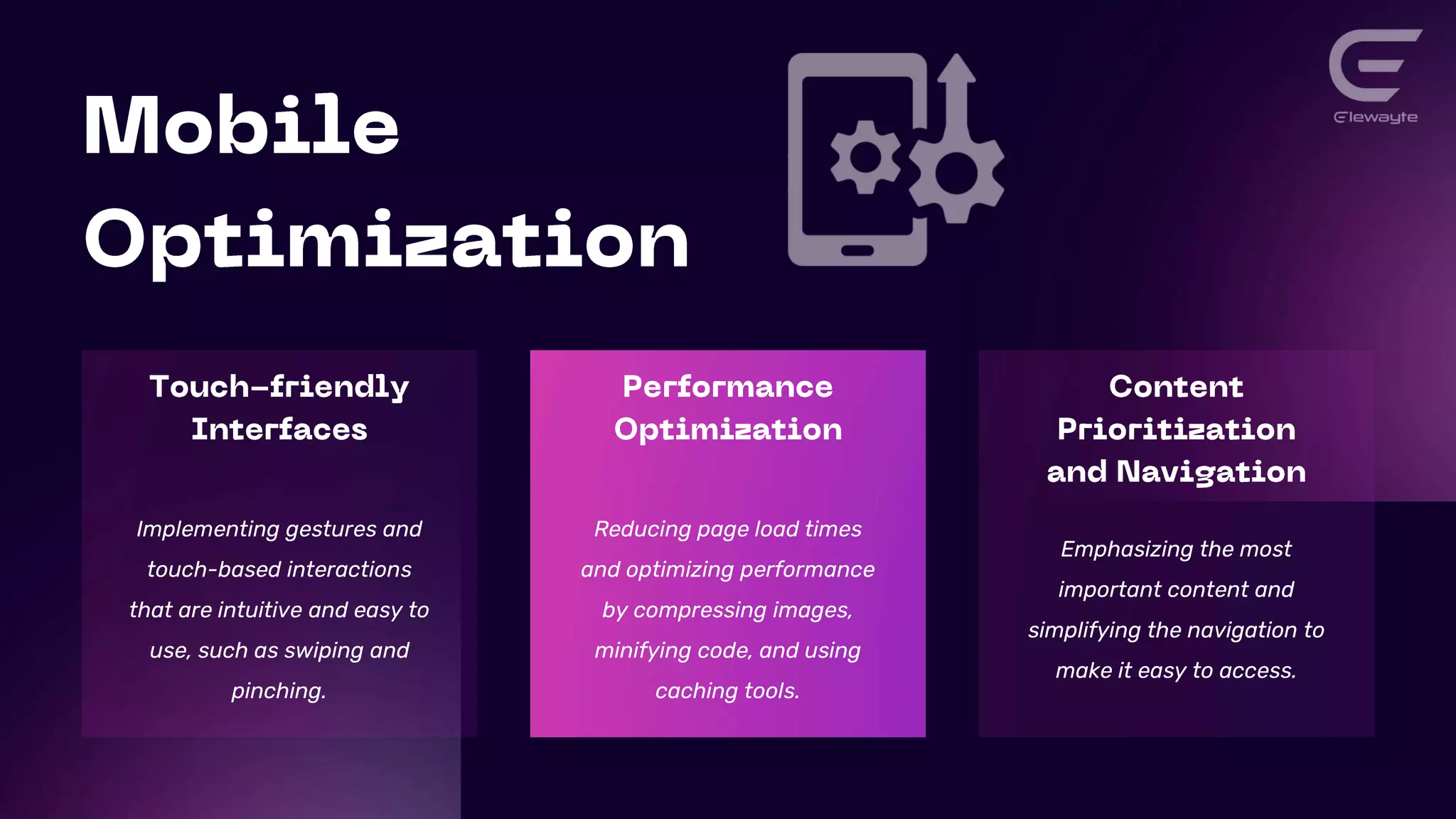
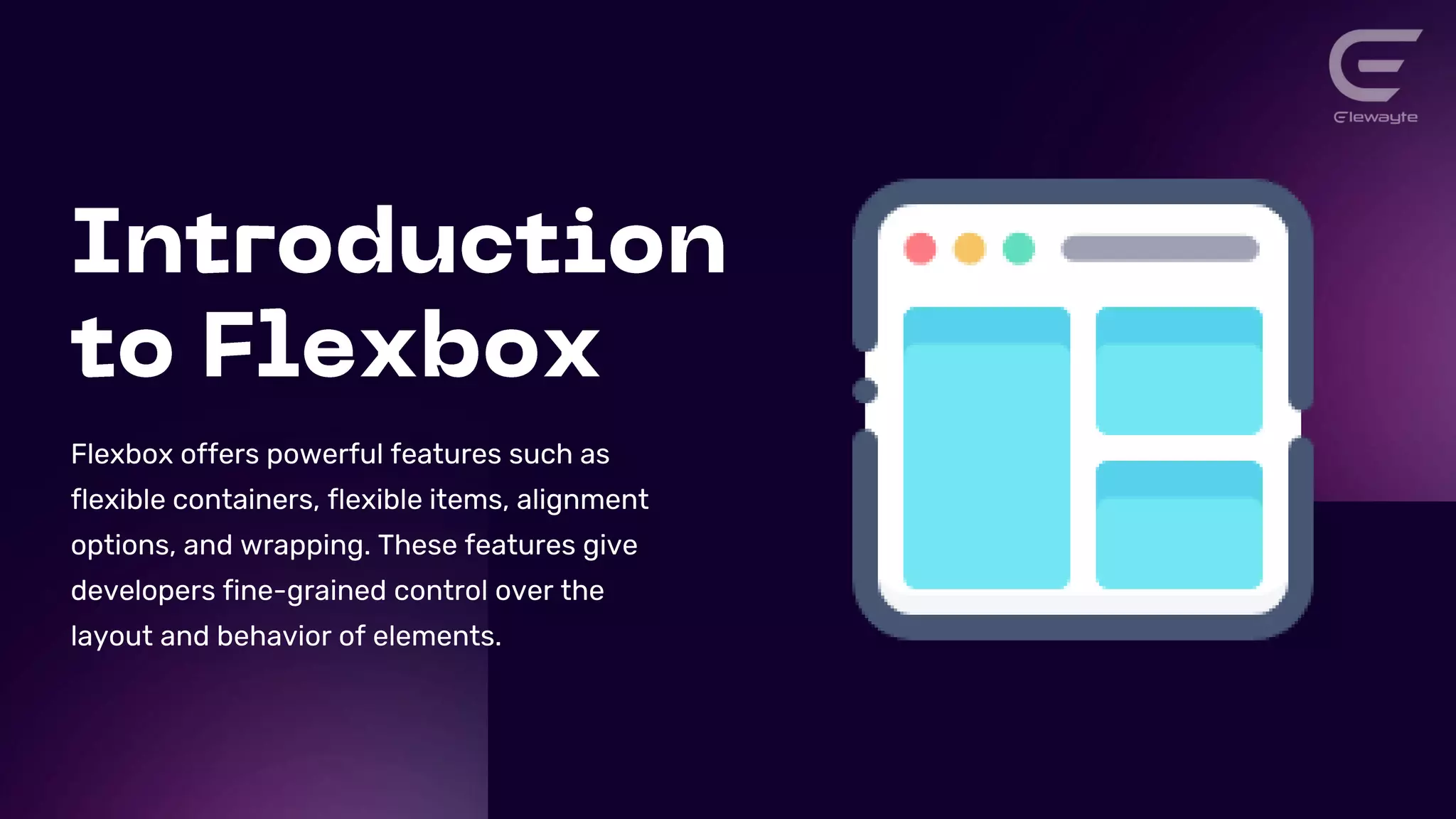
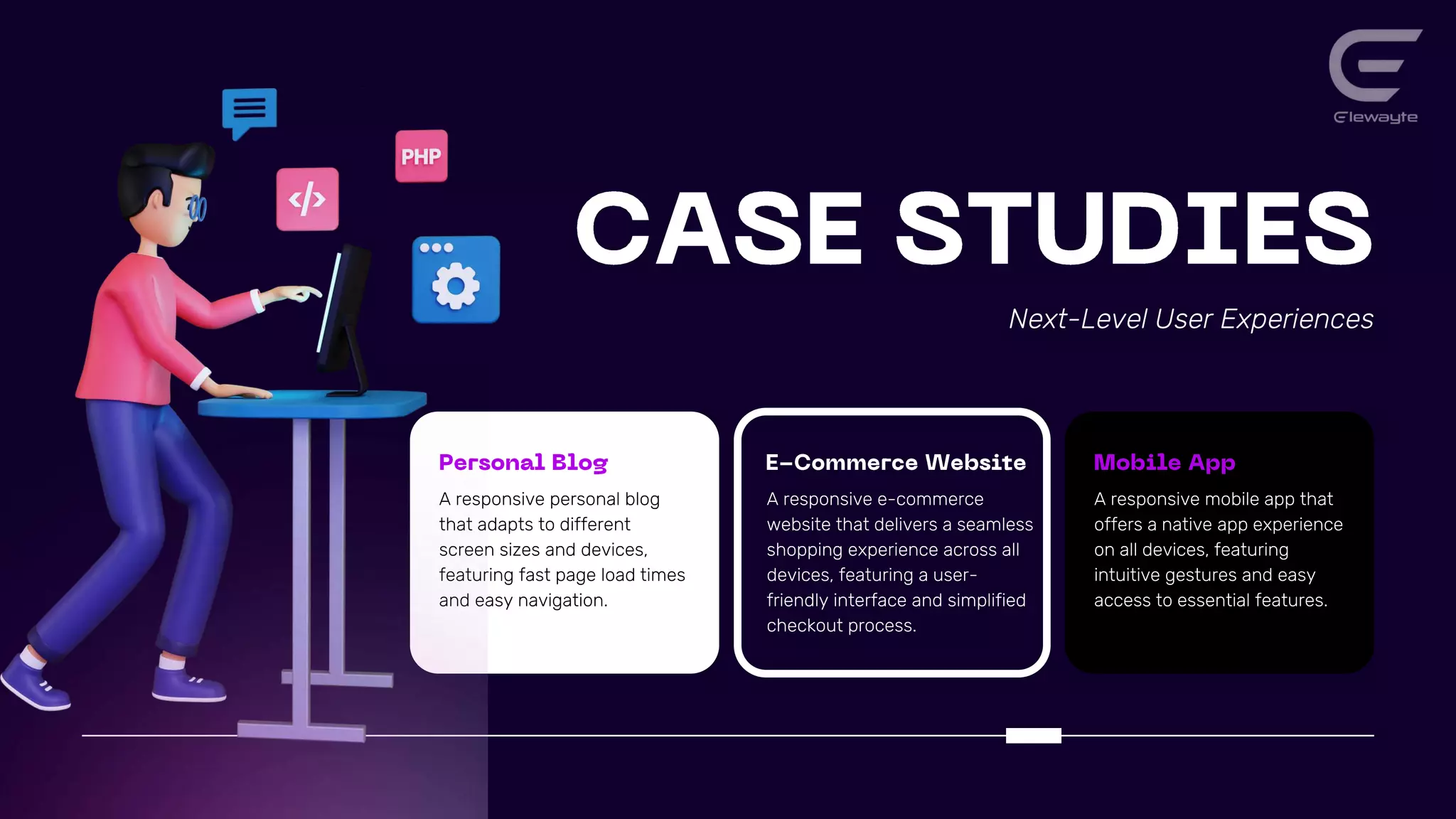
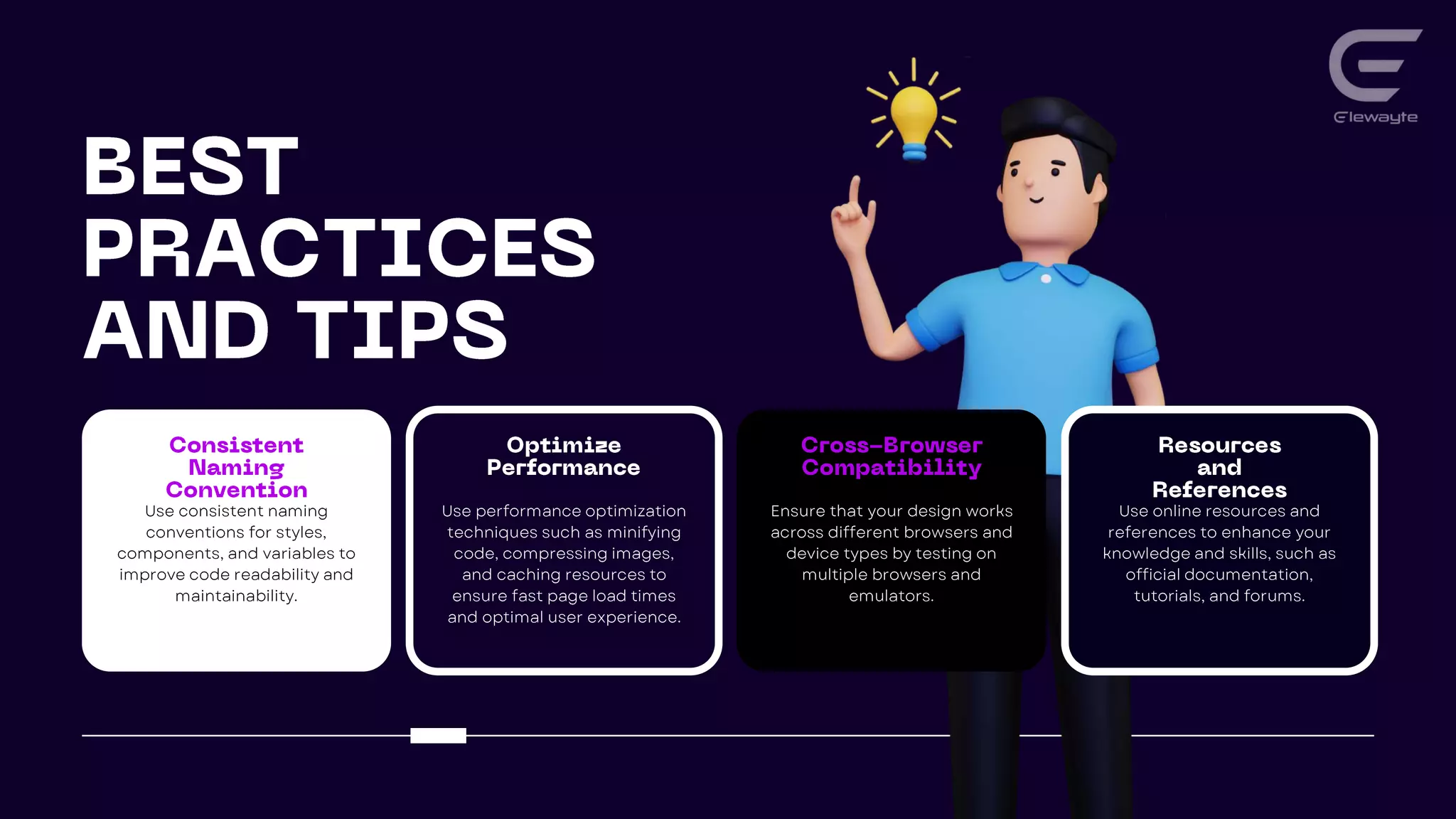
This document discusses responsive web design principles and techniques for creating next-level user experiences. It covers fluid grids, flexible images, media queries, and responsive typography. It also discusses optimizing performance, emphasizing important content, and simplifying navigation. Flexbox layout and React Hooks are introduced as tools for building responsive interfaces. Examples of using these techniques to create responsive blogs, ecommerce sites, and mobile apps are provided.