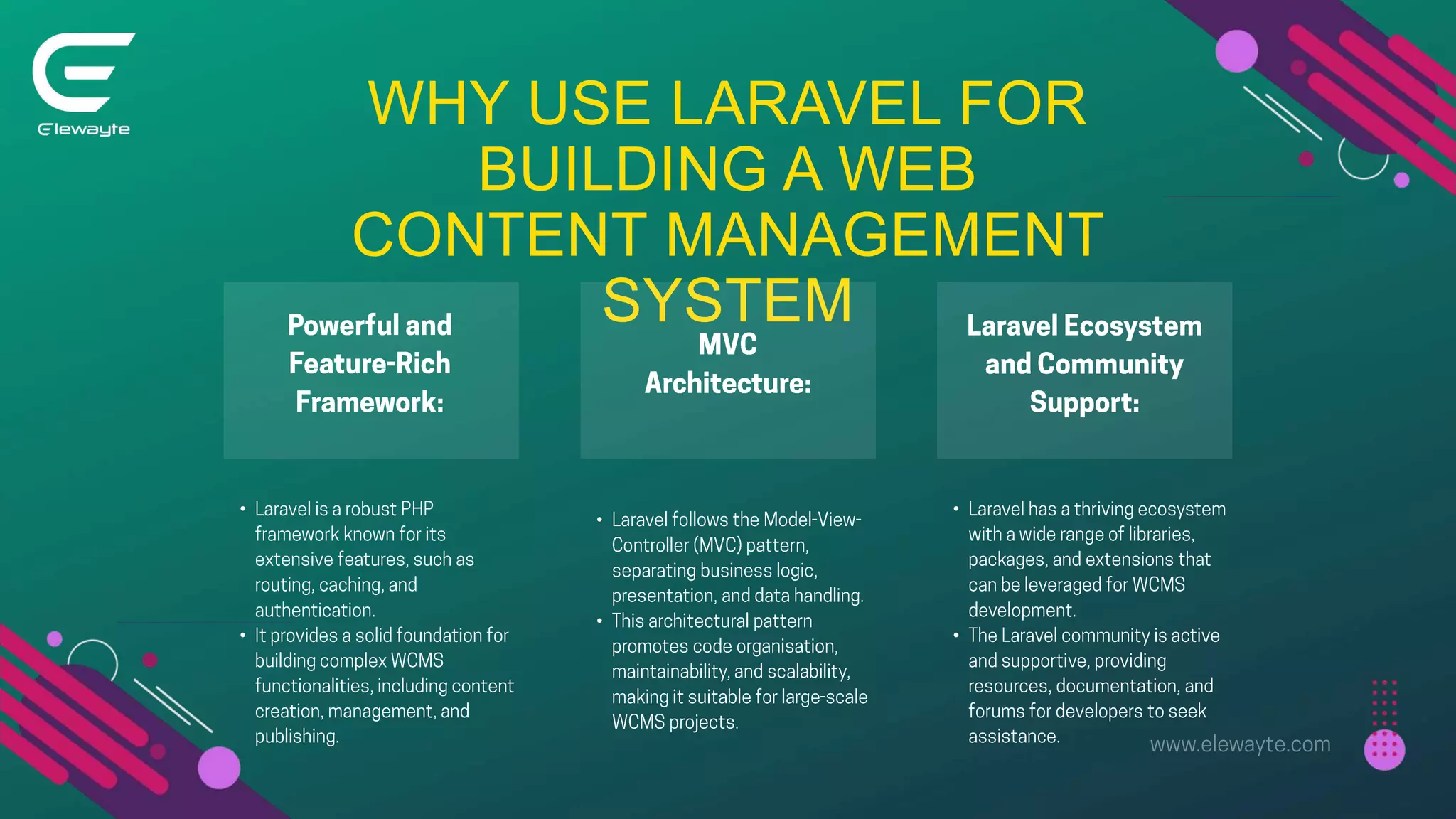
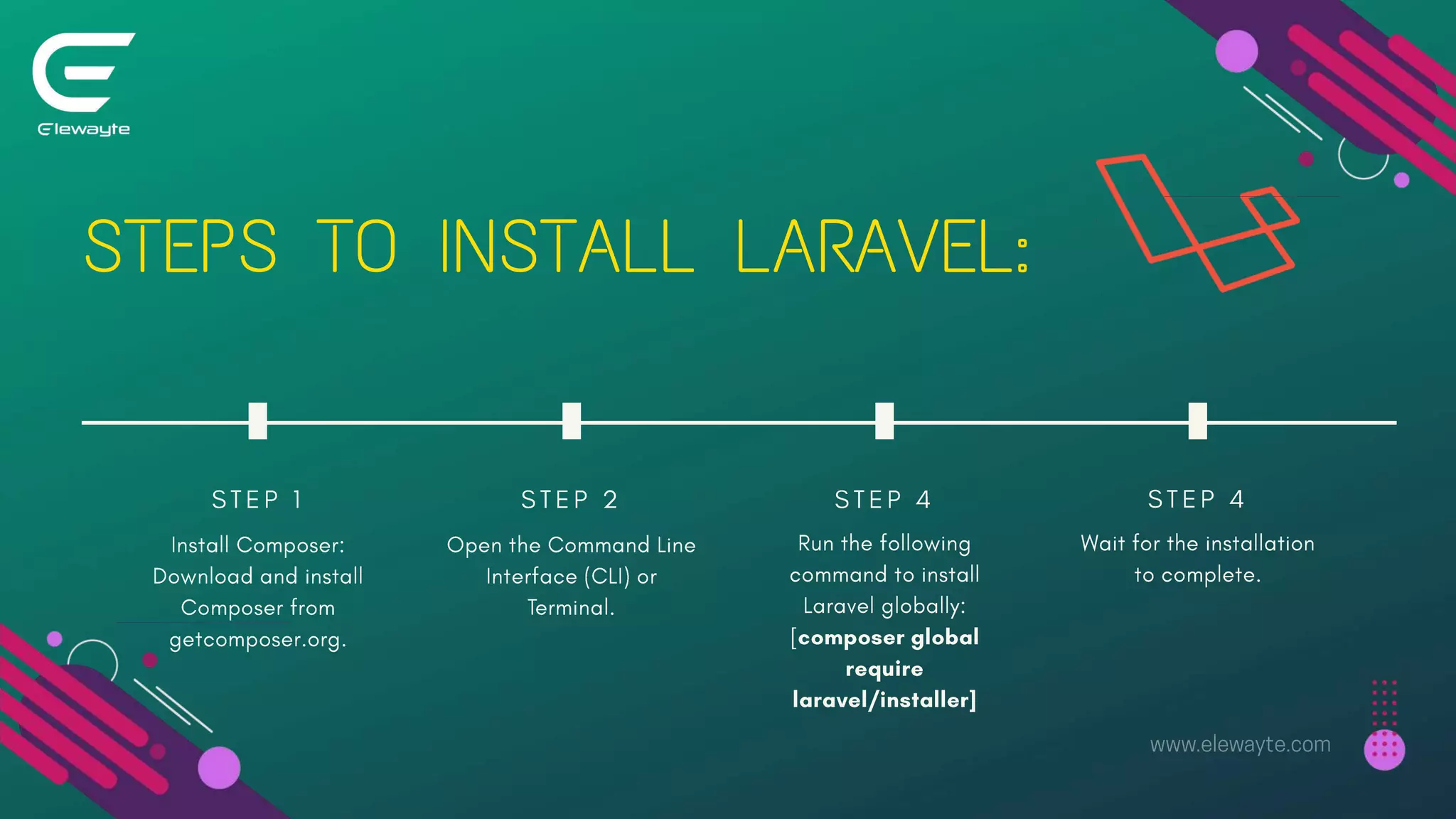
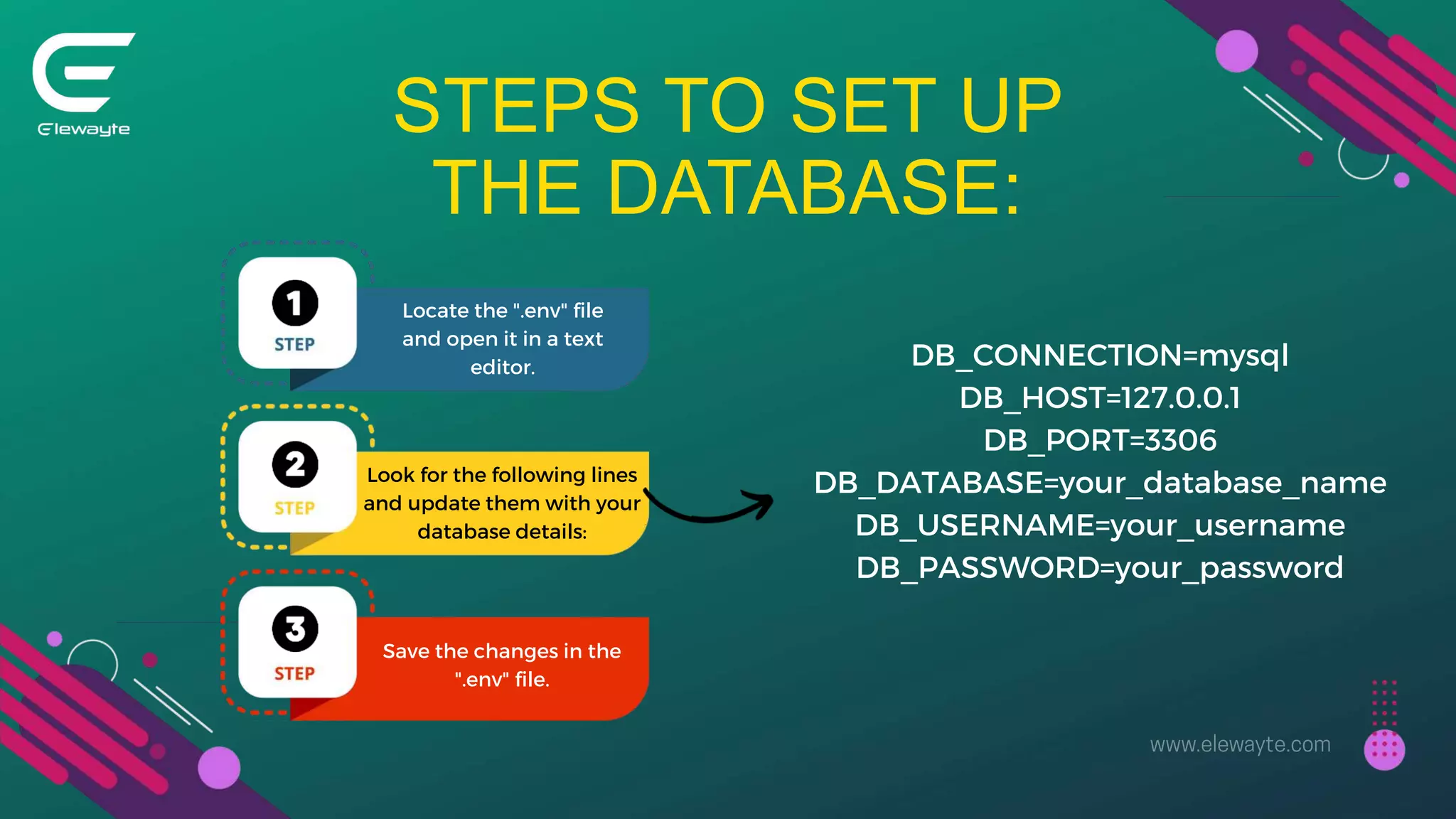
The document serves as a comprehensive guide for setting up a web content management system using Laravel, detailing the benefits, installation steps, and essential functionalities like CRUD operations and user authentication. It also highlights the importance of search functionality, file uploads, and SEO best practices for enhancing visibility and user experience. Overall, it provides a step-by-step approach to creating a robust and user-friendly web content management system.