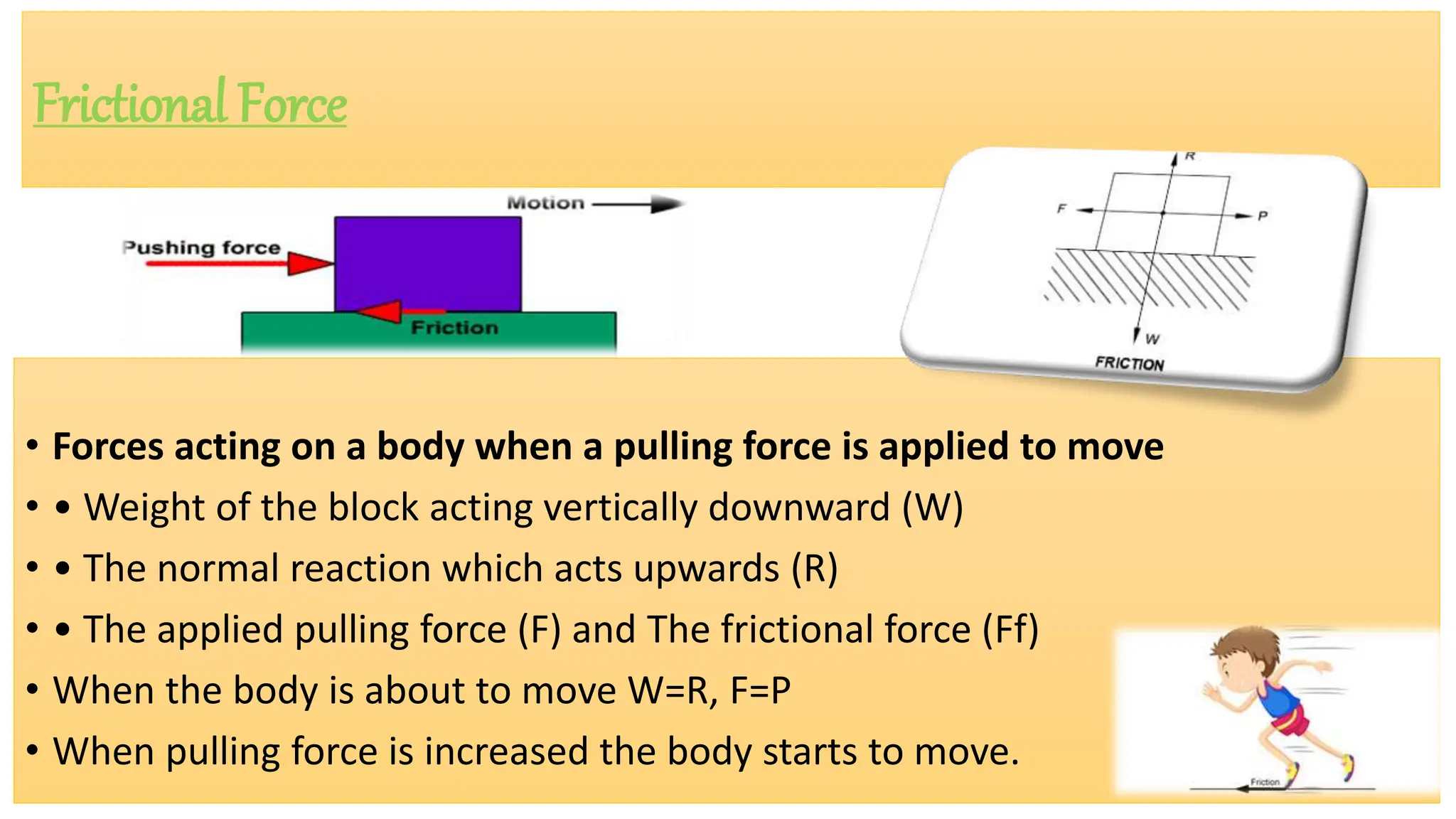
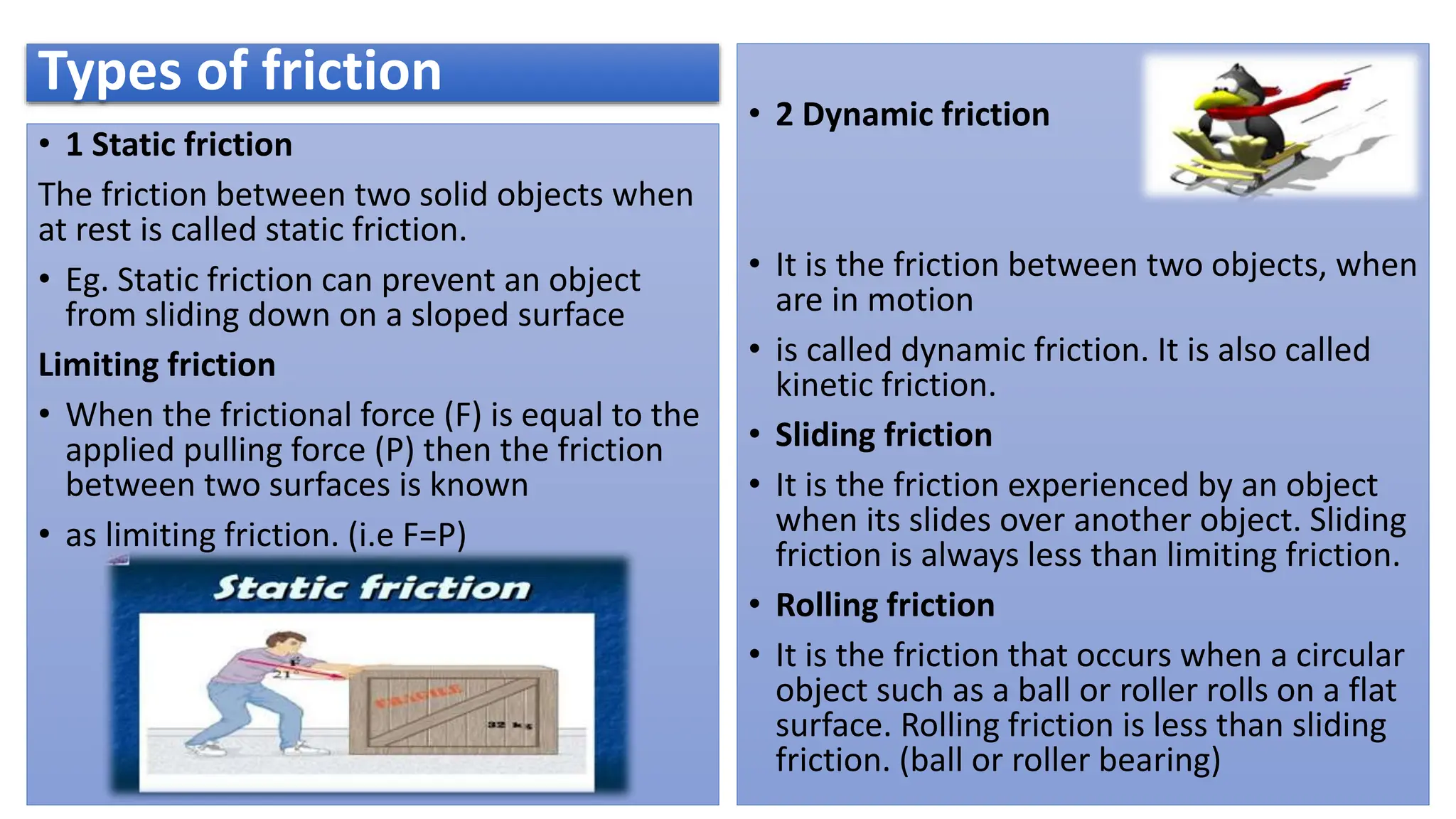
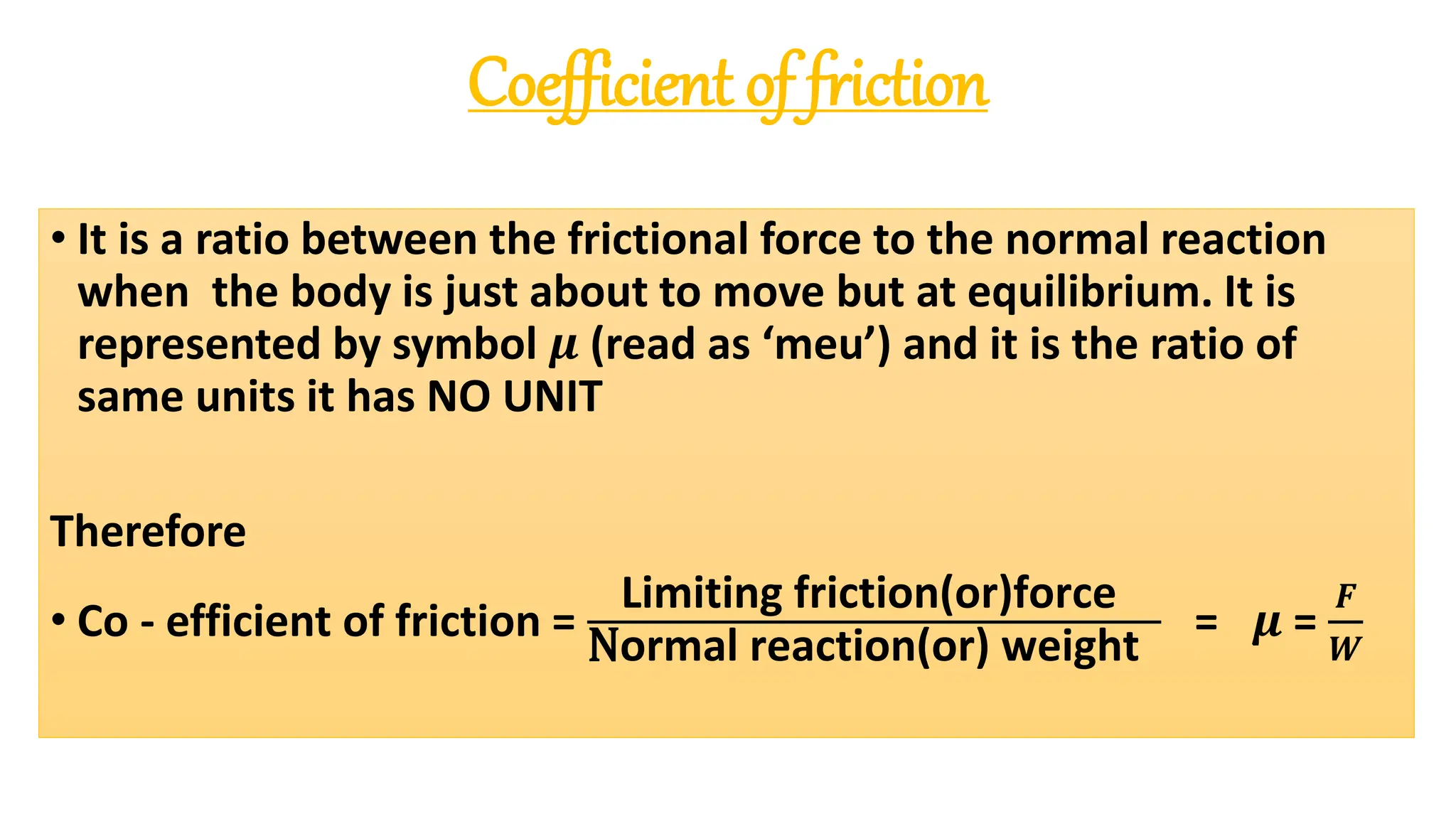
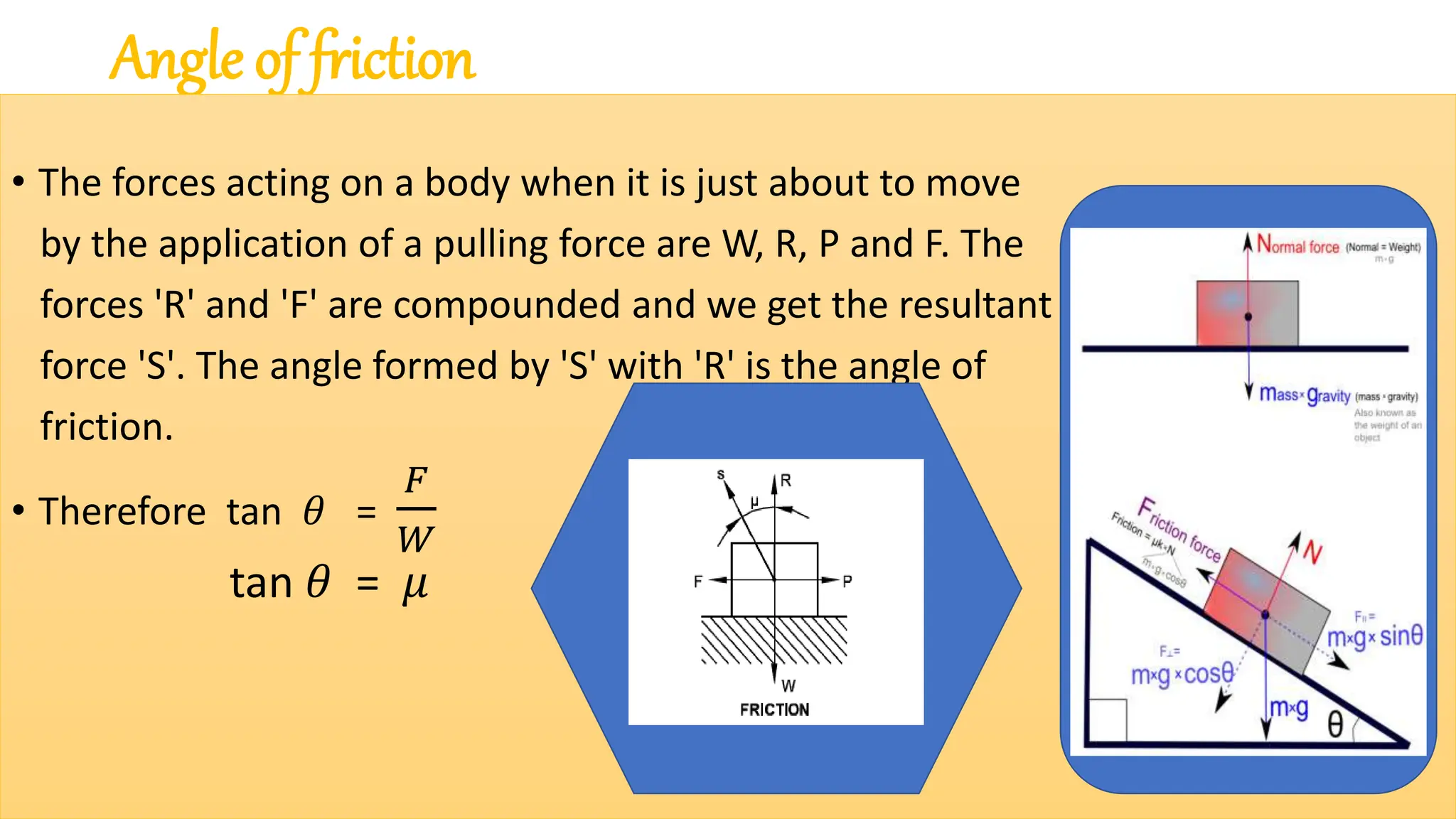
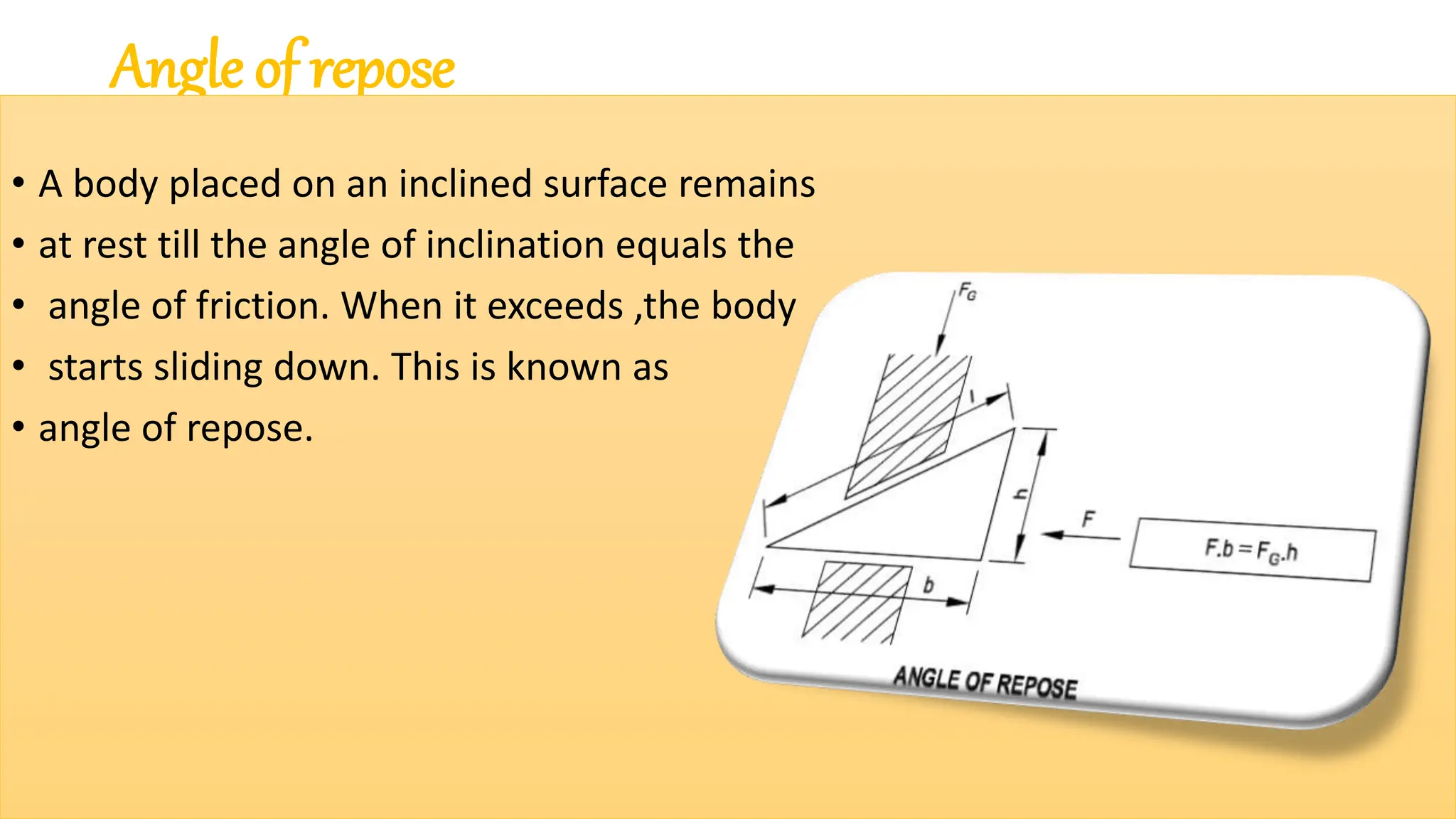
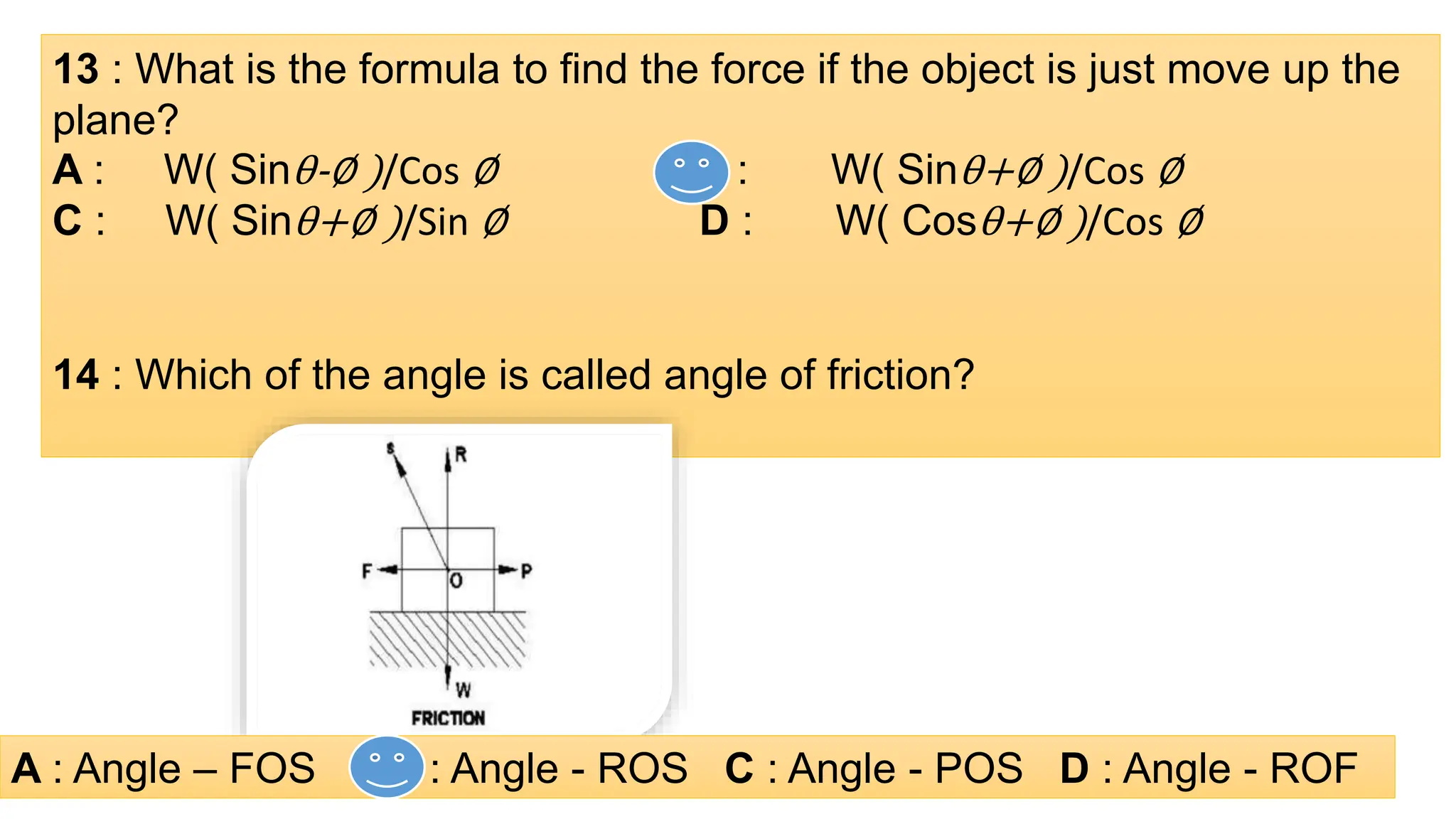
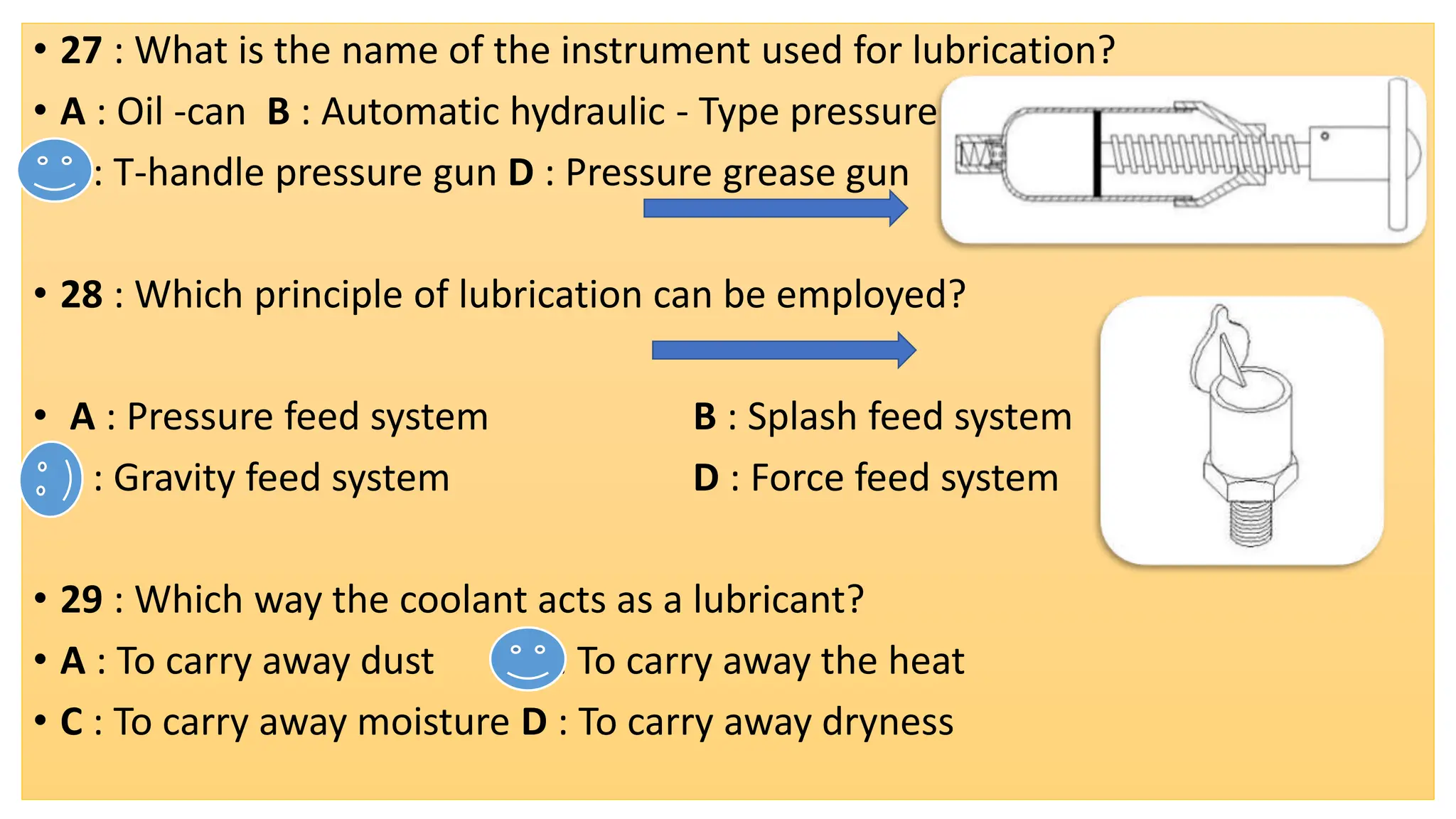
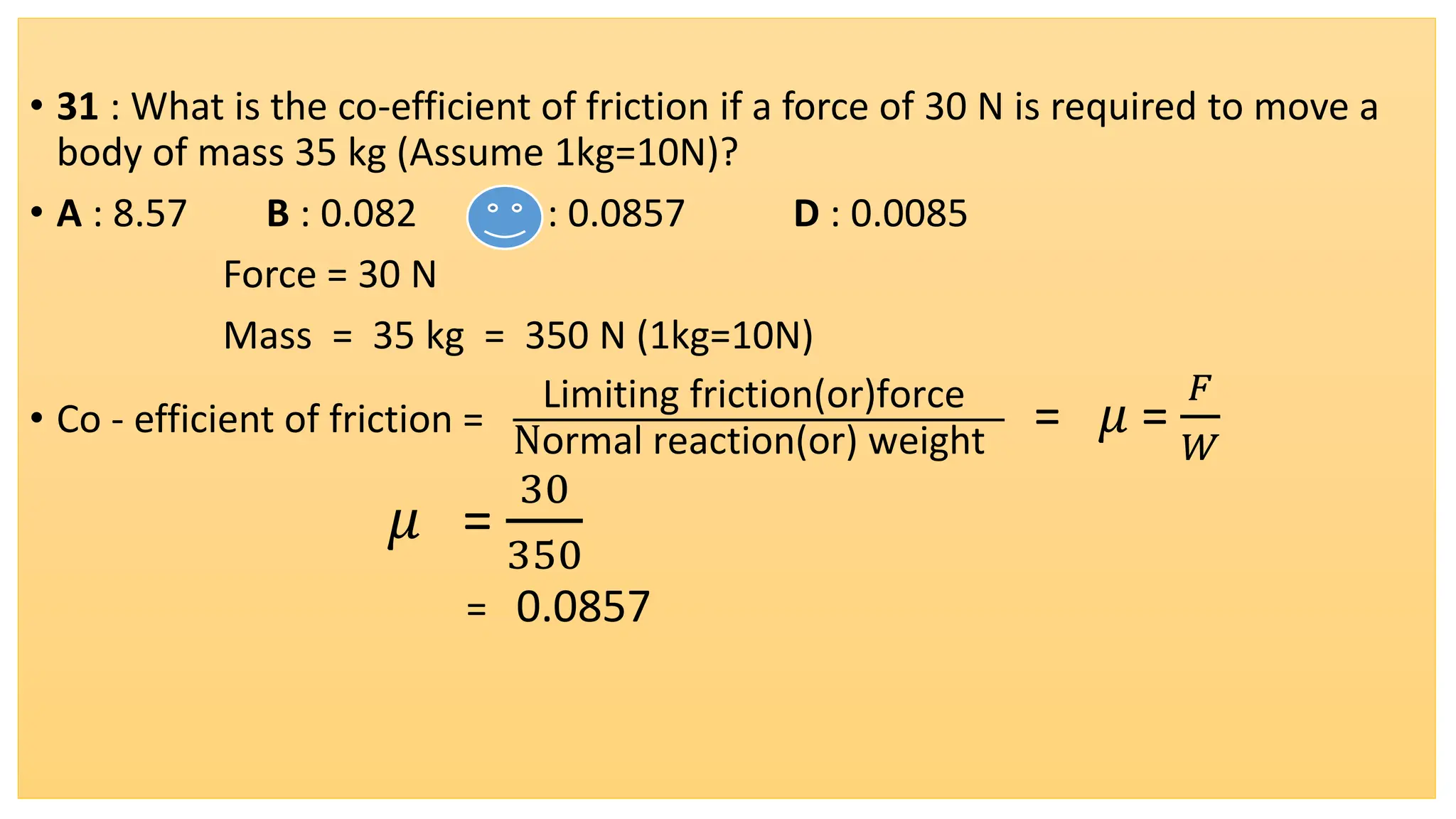
The document provides a comprehensive overview of friction, defining it as a force that resists the relative motion of solid surfaces and detailing its various types including static, dynamic, sliding, and rolling friction. It discusses the laws governing friction, its applications in engineering and daily life, measurement methods, and how friction can be beneficial or detrimental depending on the context. The document also includes multiple-choice questions (MCQs) related to the concepts of friction, coefficient of friction, and lubrication systems.