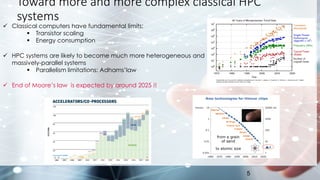
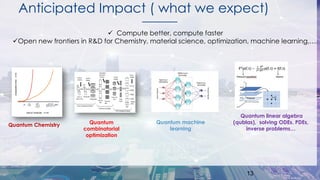
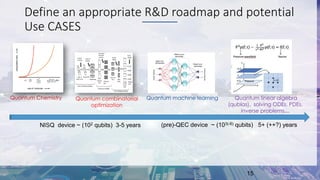
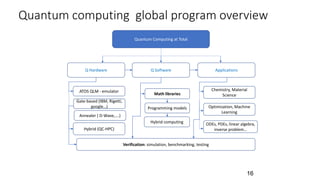
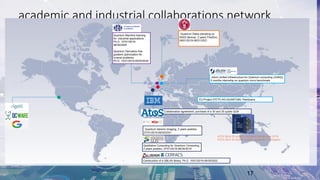
This document summarizes Total's exploration of quantum computing technology. It discusses how classical computing is reaching its limits and how quantum computing may provide new opportunities. Total's objectives are to understand quantum computer evolution, build competencies through research partnerships, and develop algorithms for business uses. Total has collaborated with several academic and industrial partners, purchased a 30-qubit quantum emulator, and has ongoing work in areas like quantum machine learning and optimization. The conclusion states that quantum computing is a major shift that could open new research frontiers, and Total aims to build skills to develop algorithms for its applications.