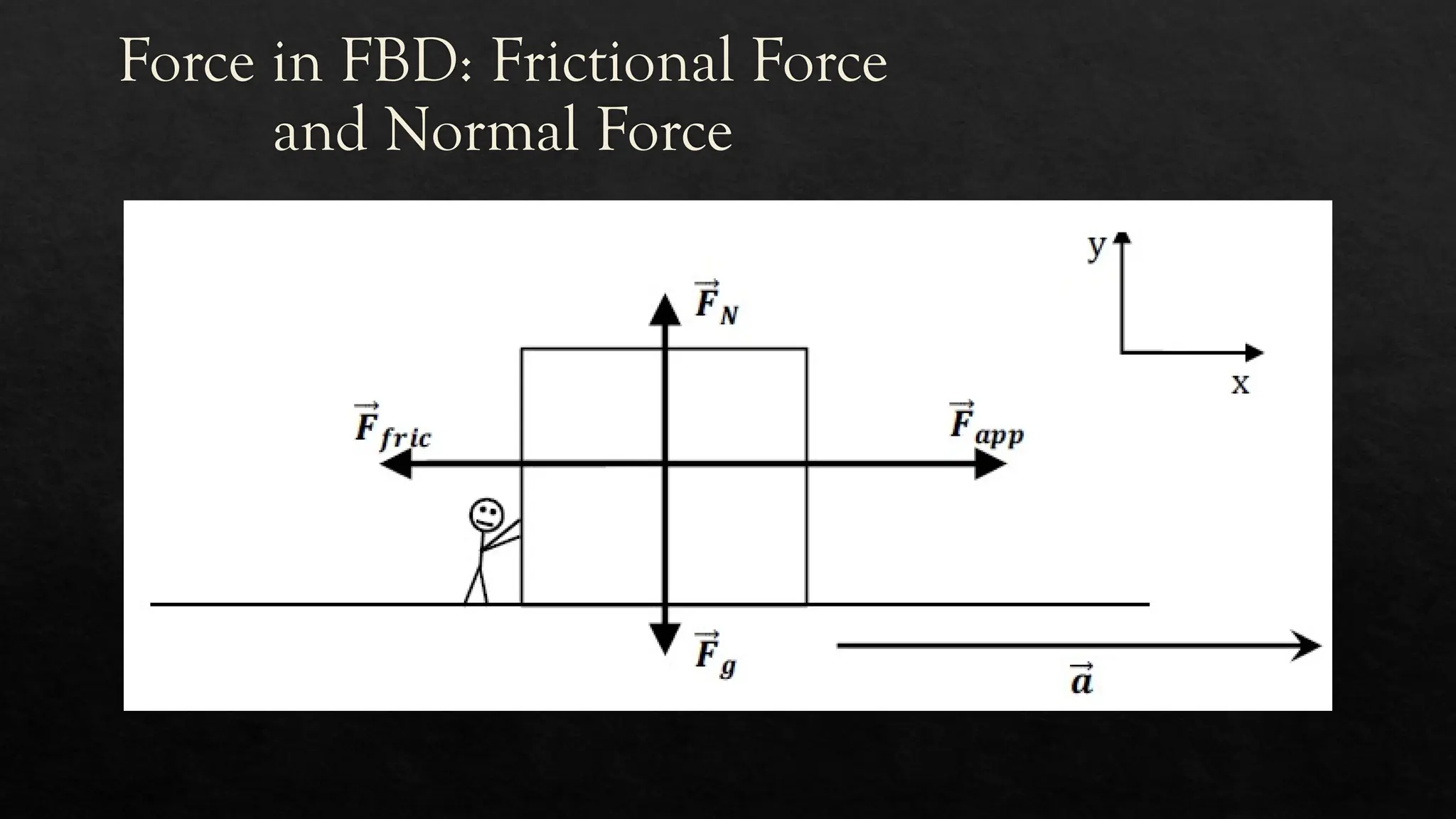
The document discusses free-body diagrams (FBDs) as a tool to visualize forces acting on an object, highlighting the magnitude and direction of these forces through arrows. It explains the concepts of frictional forces, normal forces, and how they relate to static and kinetic friction, along with distinguishing balanced and unbalanced forces. Essential points include the relationship between normal force and weight, as well as the characteristics of stationary and moving objects in terms of friction.