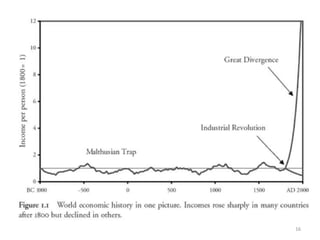
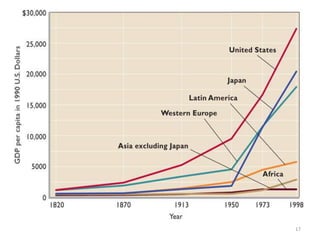
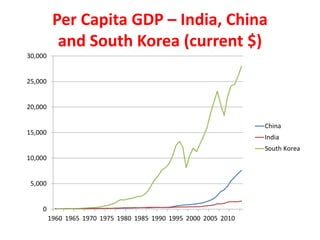
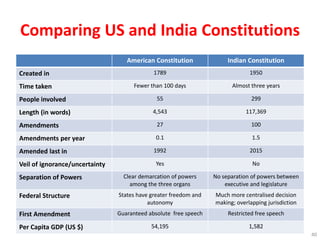
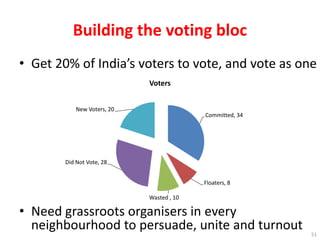
The document argues that India's constitution is flawed and needs to be rewritten to enable prosperity and freedom for its citizens. It discusses the structure and limitations of the current government and calls for collective action to create a new voting bloc aimed at electing representatives who will support a new constitution by 2020. The author emphasizes the need for a rules revolution to change India's trajectory and address the issues of poverty and governance.