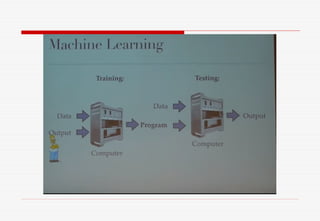
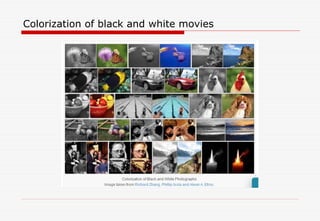
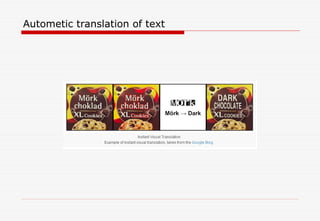
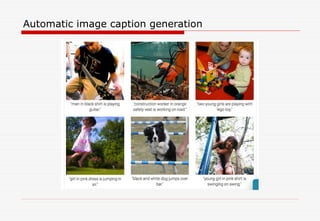
The document discusses machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI), highlighting their applications in various fields, including email categorization, ridesharing, self-driving cars, and social networking. It emphasizes the distinction between traditional programming and ML, specifically how ML models learn from data to improve performance over time. Additionally, the document mentions deep learning as an advanced ML technique and provides resources for further reading on the subject.