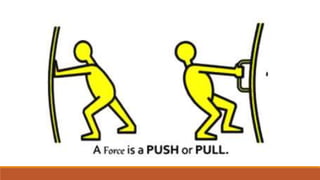
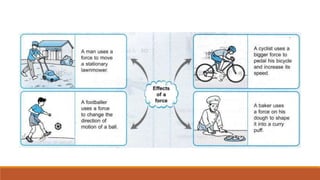
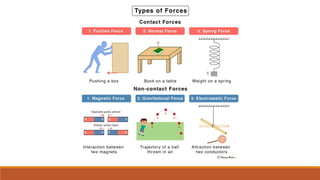
This document defines force and describes its types. It states that force is a push or pull on an object that can cause it to change its velocity or motion. There are two main types of forces: contact forces that require touching and non-contact forces that act over a distance. The document also provides the formula for calculating force as mass times acceleration and gives examples of calculating the net force required to accelerate objects with given masses and accelerations.