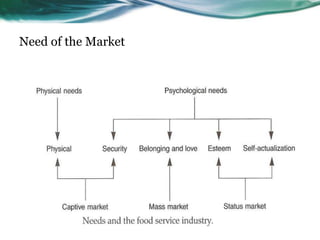
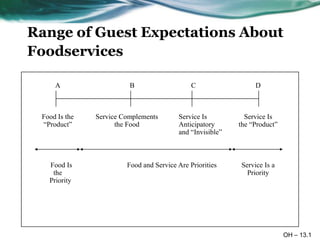
The document discusses different types of customers in foodservice markets including captive, mass, and status markets. It examines factors that influence customer choices such as convenience, social occasions, and lifestyle. Various customer segments are also analyzed including repeat customers, families, seniors, and their specific needs and expectations from foodservice establishments.