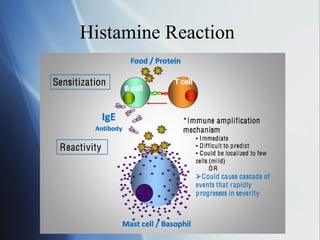
A food allergy occurs when the immune system mistakenly identifies a harmless food protein as dangerous and releases antibodies to attack it. This can trigger histamine release and cause symptoms ranging from mild to severe like anaphylaxis. Common food allergens include peanuts, tree nuts, eggs, milk, fish and shellfish. While symptoms vary, anaphylaxis affects breathing, blood pressure and could be fatal without treatment. Food allergies impact about 4% of the population so facilities need trained staff, individualized emergency plans and protocols to safely manage guests' allergies and reactions.