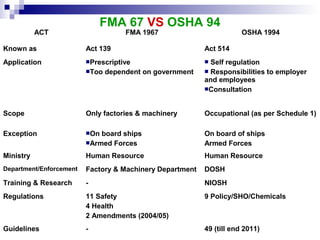
The document discusses the Factory and Machinery Act 1967 (FMA 1967) and associated regulations in Malaysia. The key points are:
1) FMA 1967 aimed to control factory operations regarding safety, health and welfare, and register machinery.
2) It specified requirements for machinery, duties of employees and occupiers, and required written approval and inspections.
3) Numerous regulations were gazetted to provide detailed provisions on specific safety and health matters.
4) The Occupational Safety and Health Act 1994 (OSHA 1994) later superseded the FMA 1967 in the event of conflicts and had a broader scope of application.