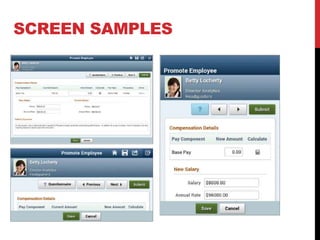
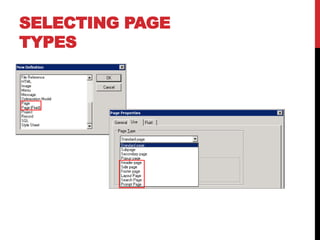
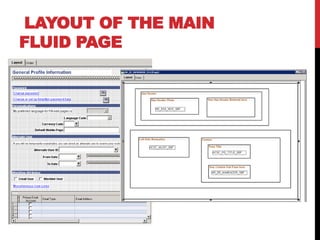
The document discusses PeopleSoft's Fluid User Interface, which enhances the classic user interface using CSS3, HTML5, and JavaScript to adjust displays based on screen size. It provides an overview of implementing the Fluid UI using tools like PeopleSoft Application Designer and considerations for selecting pages and components to convert from classic to fluid. Screenshots and descriptions of fluid page layouts, components, and search functionality are also included.