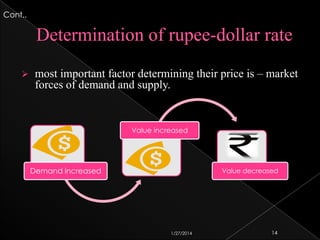
This document discusses factors that influence fluctuations in the value of the Indian rupee relative to other currencies like the US dollar. It explains that the rupee's value is determined by market forces of supply and demand. When demand for dollars is high due to imports, trade deficits, or investors taking money out of India, it puts downward pressure on the rupee. Conversely, higher exports or foreign investment inflows can strengthen the rupee by increasing its demand. The Reserve Bank of India also tries to manage volatility in the rupee's value by buying or selling dollars from its reserves.