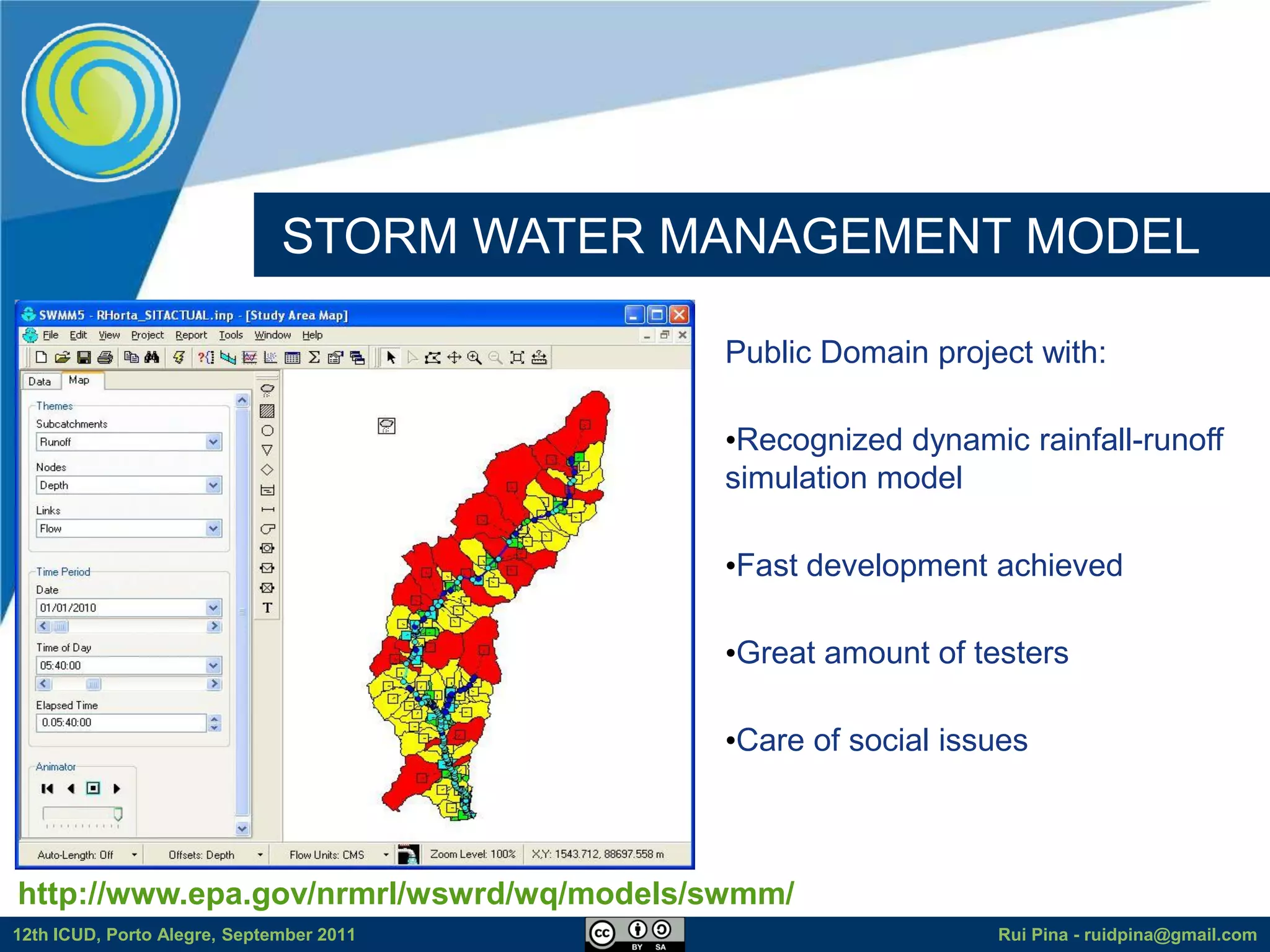
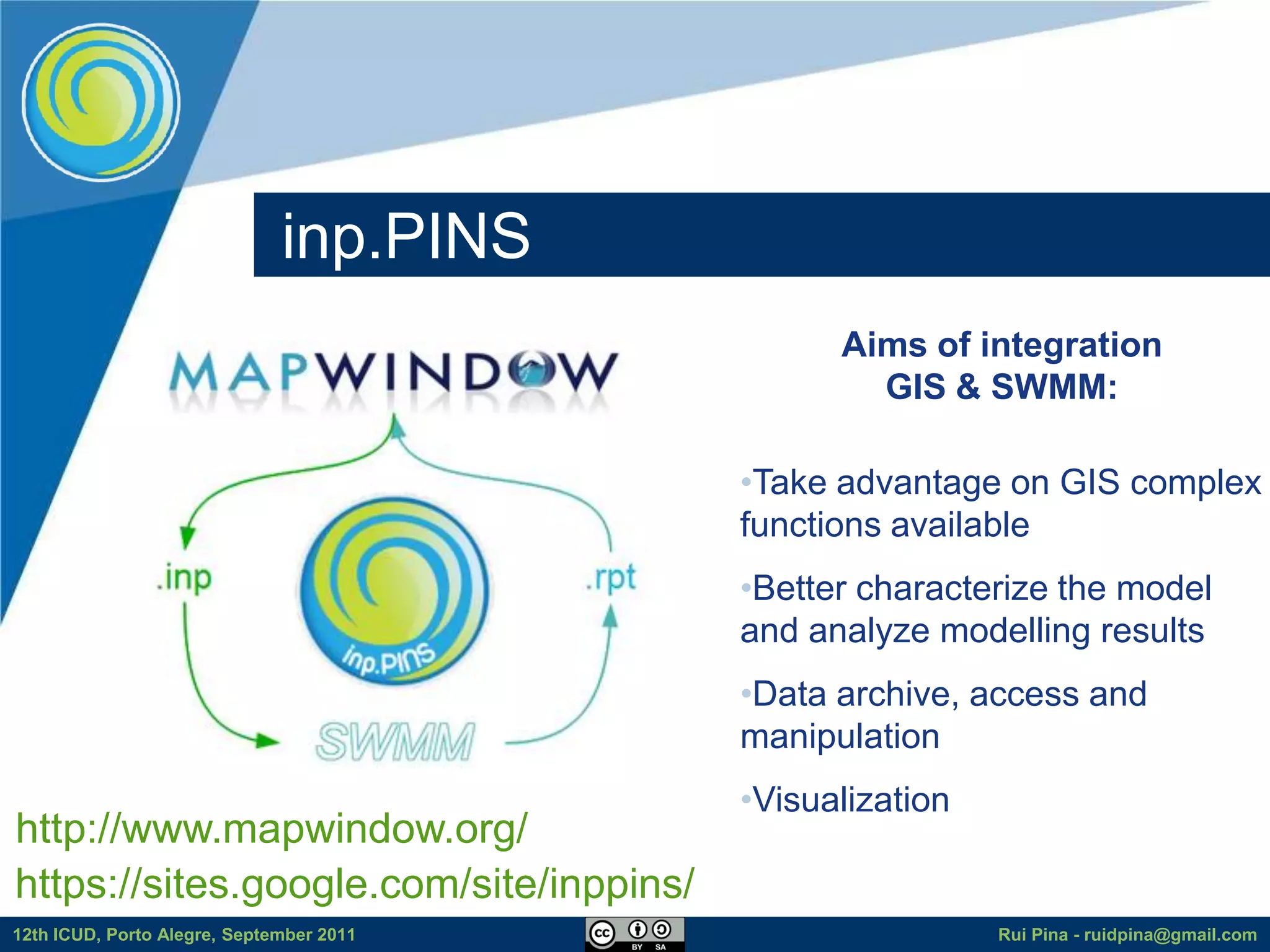
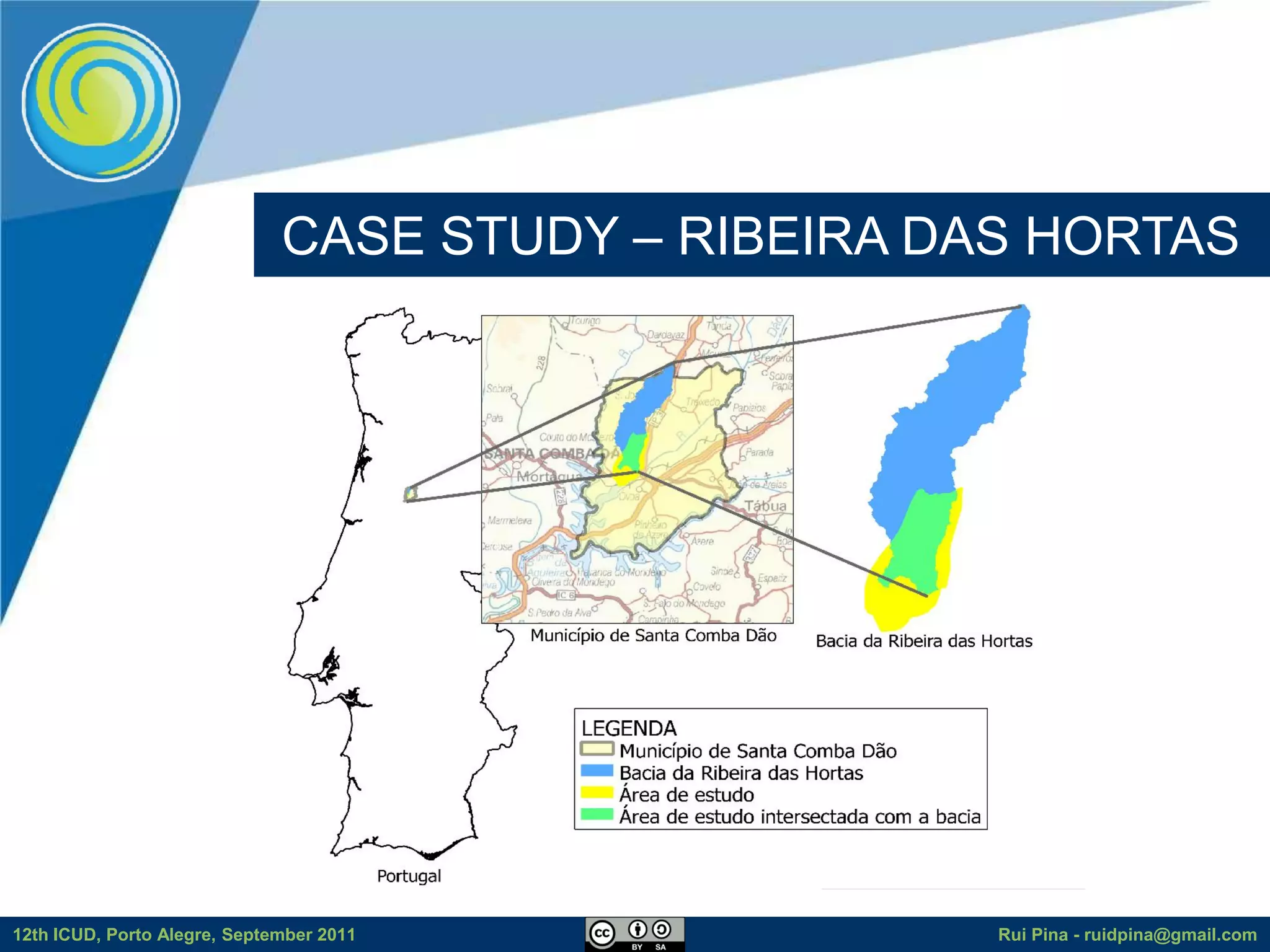
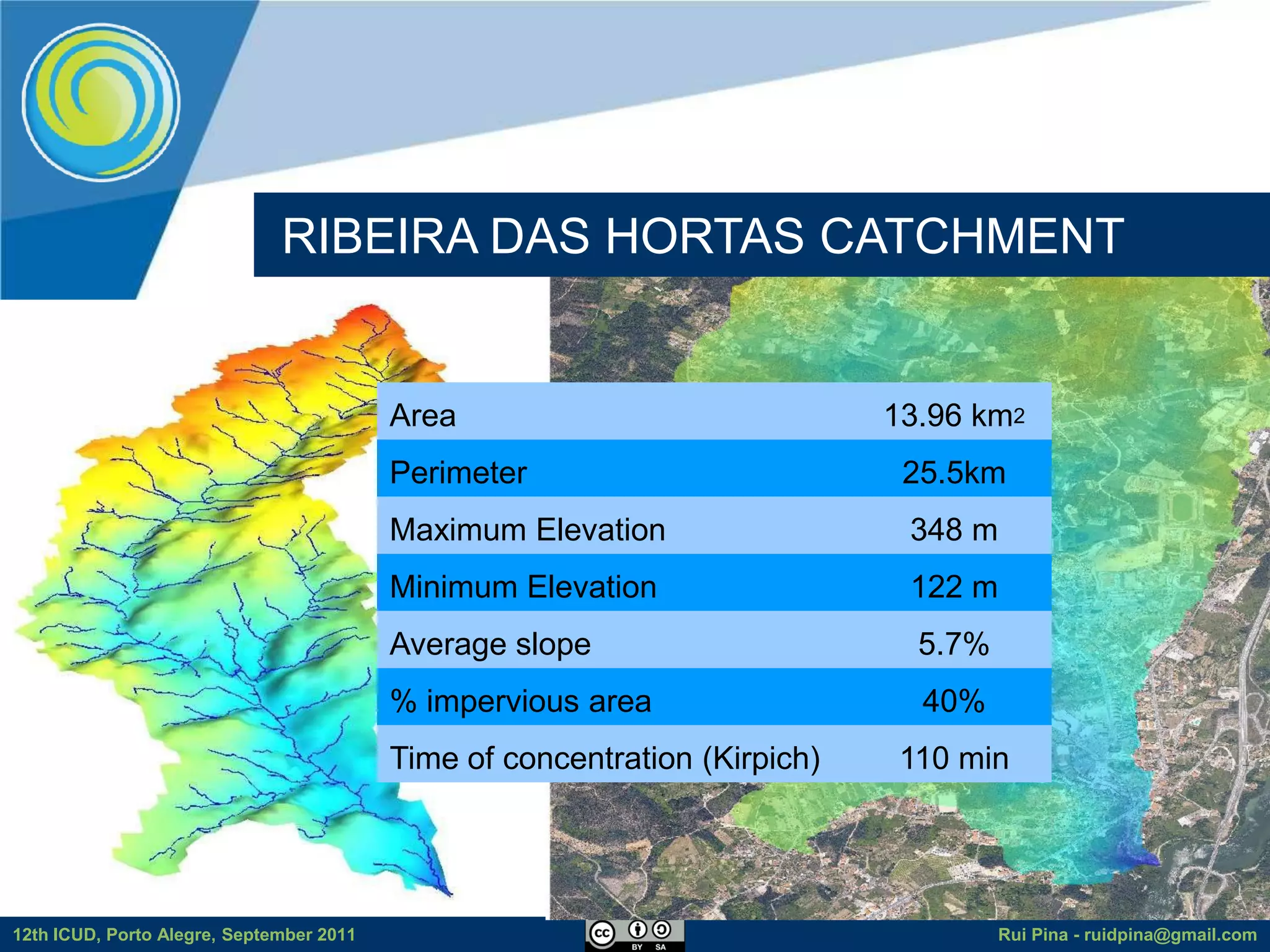
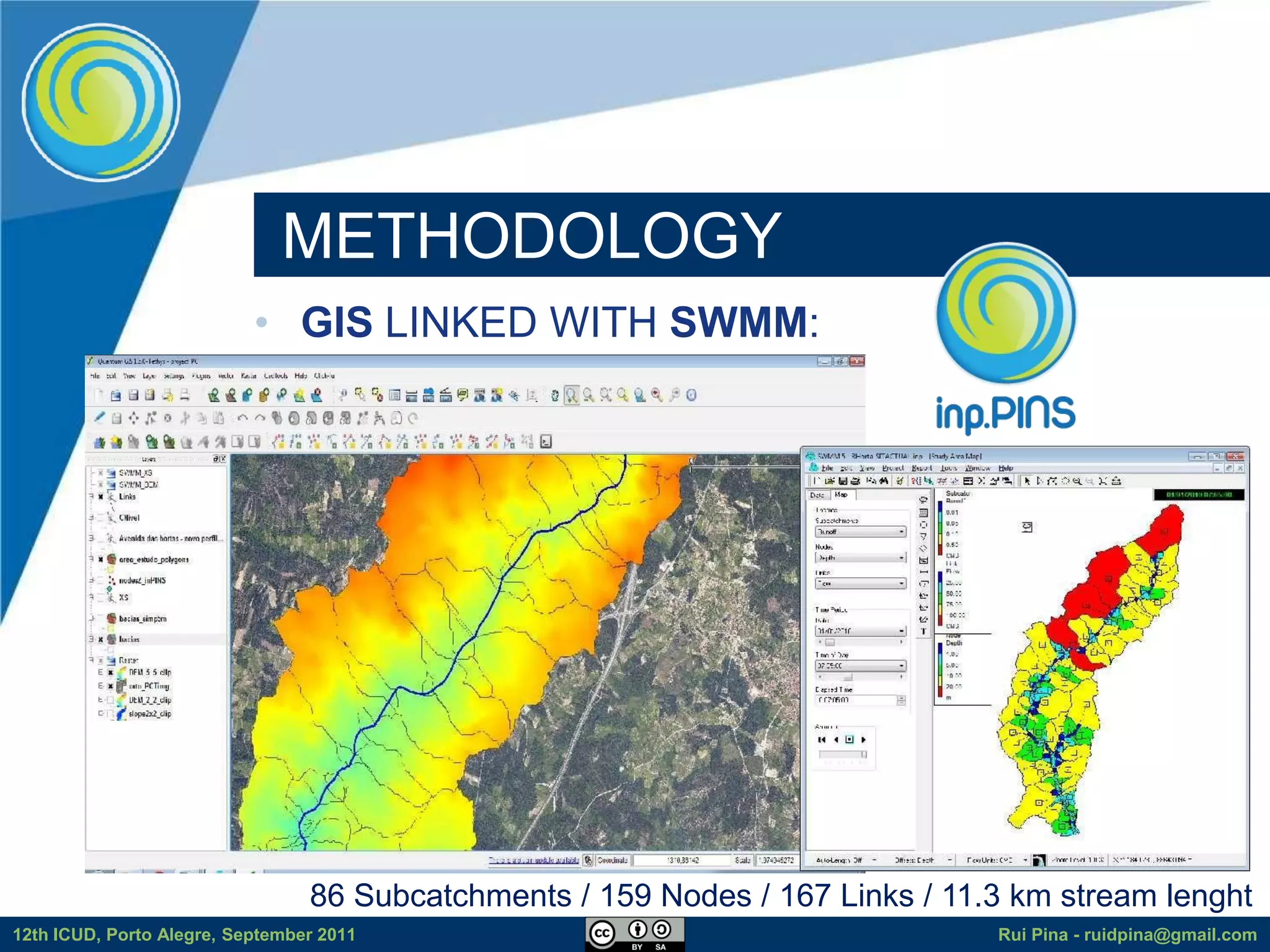
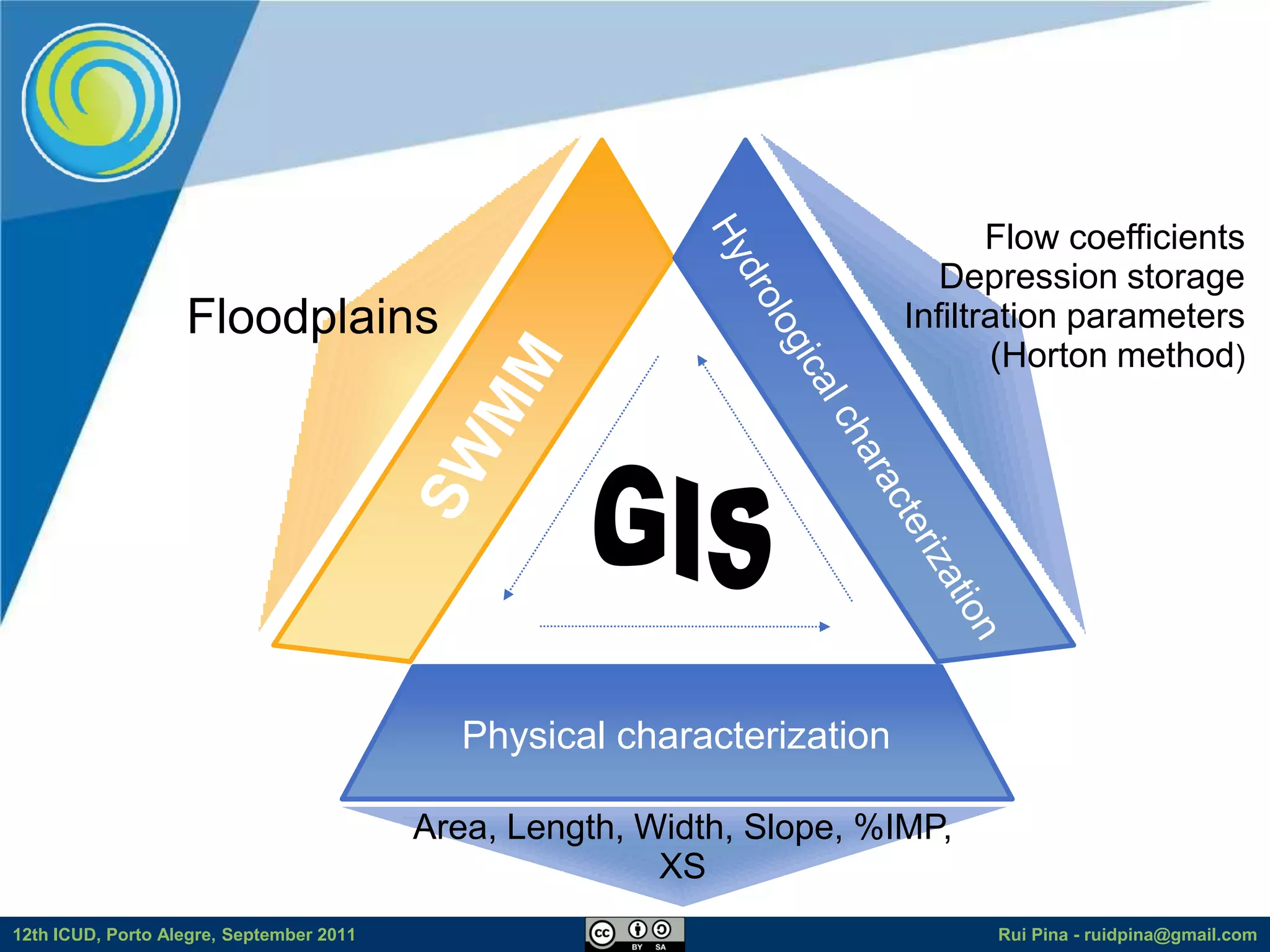
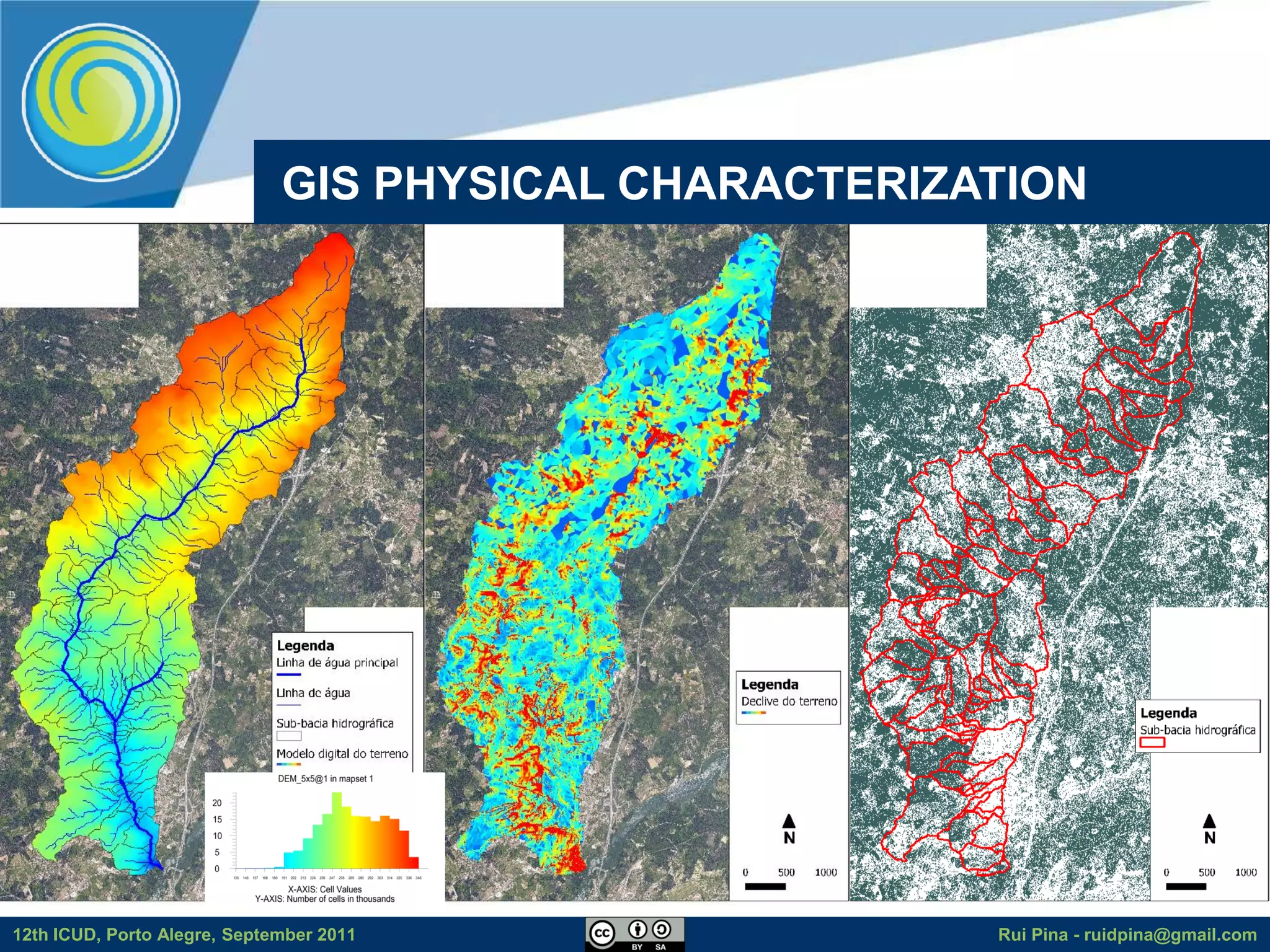
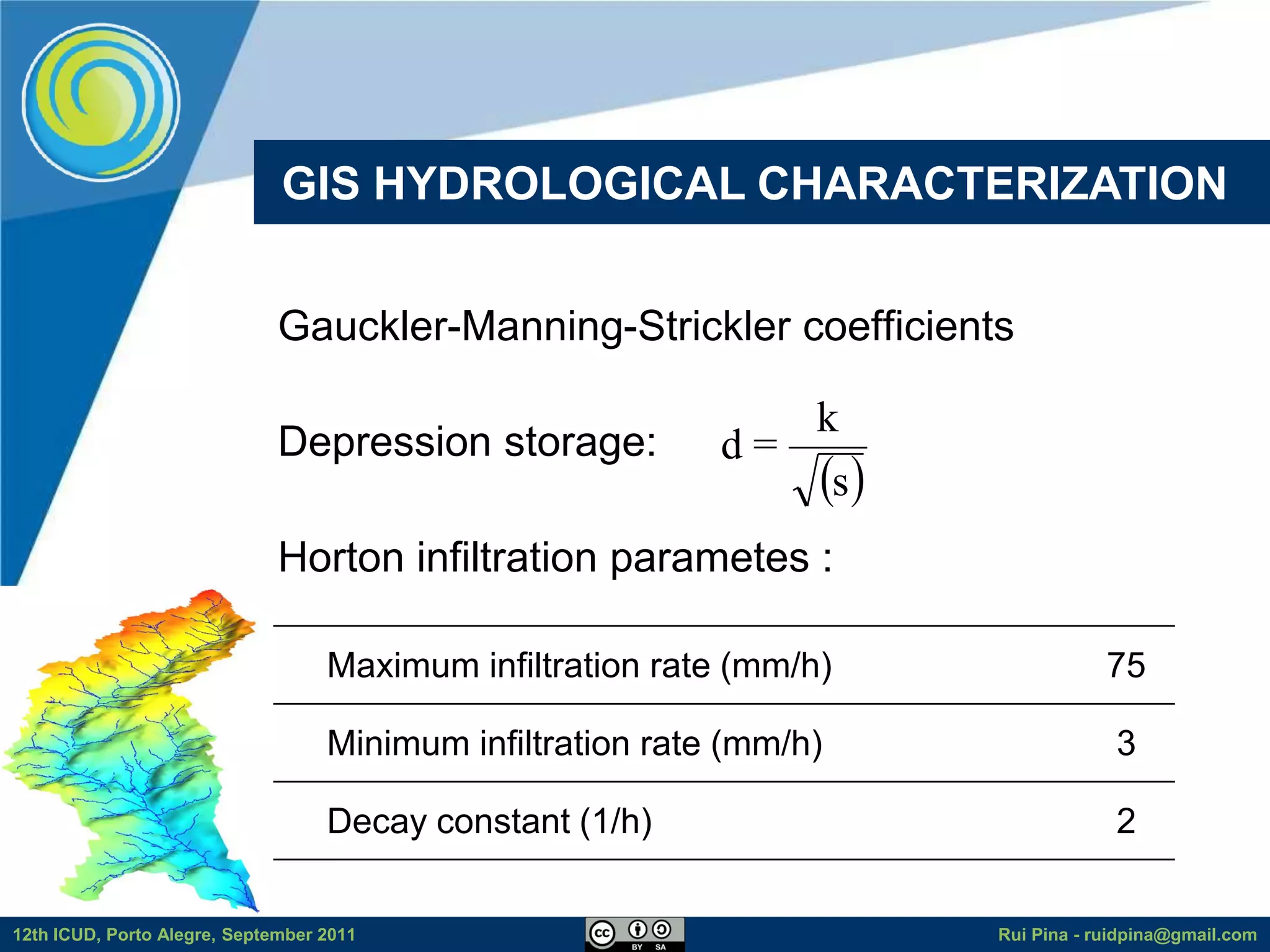
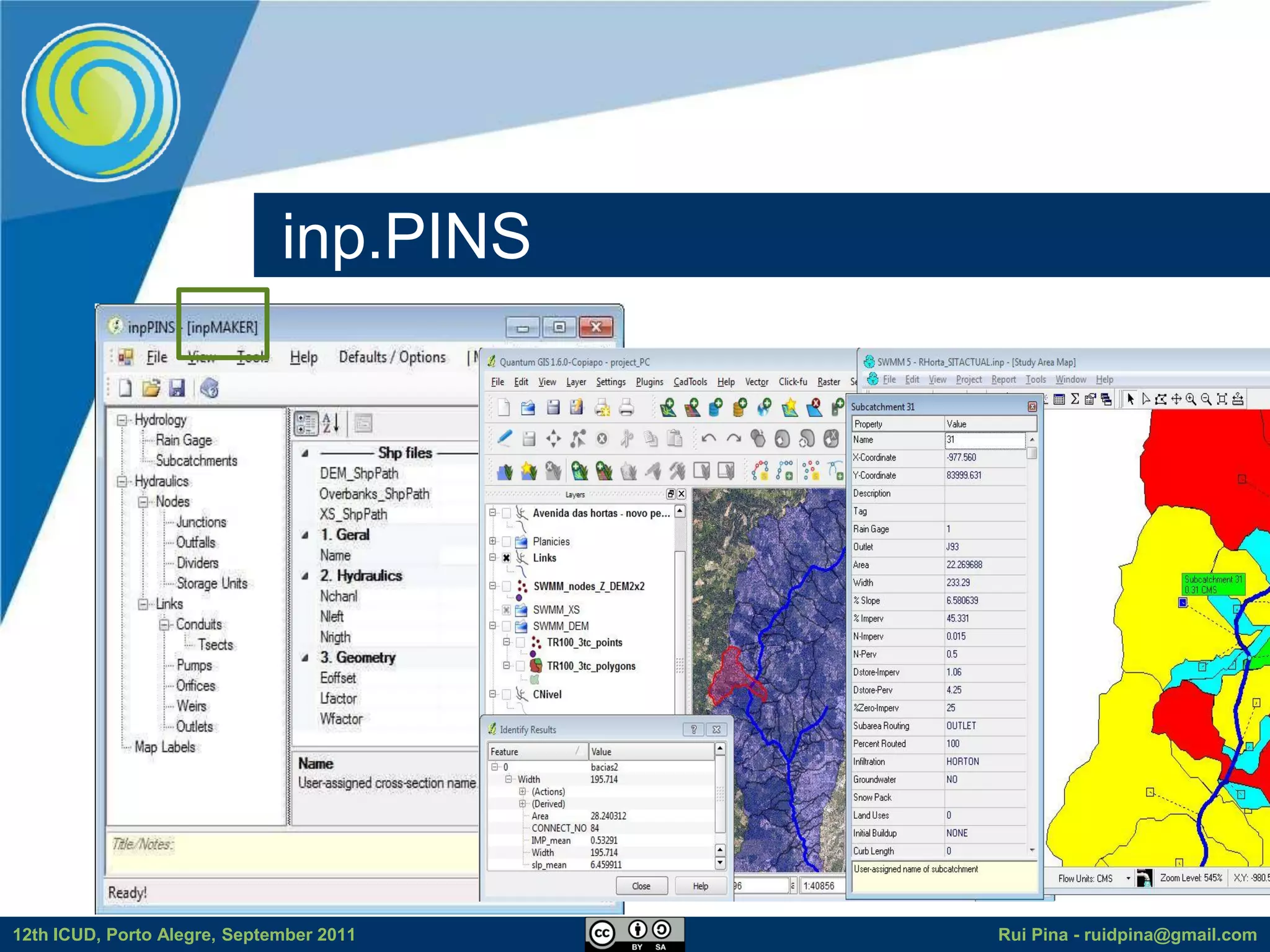
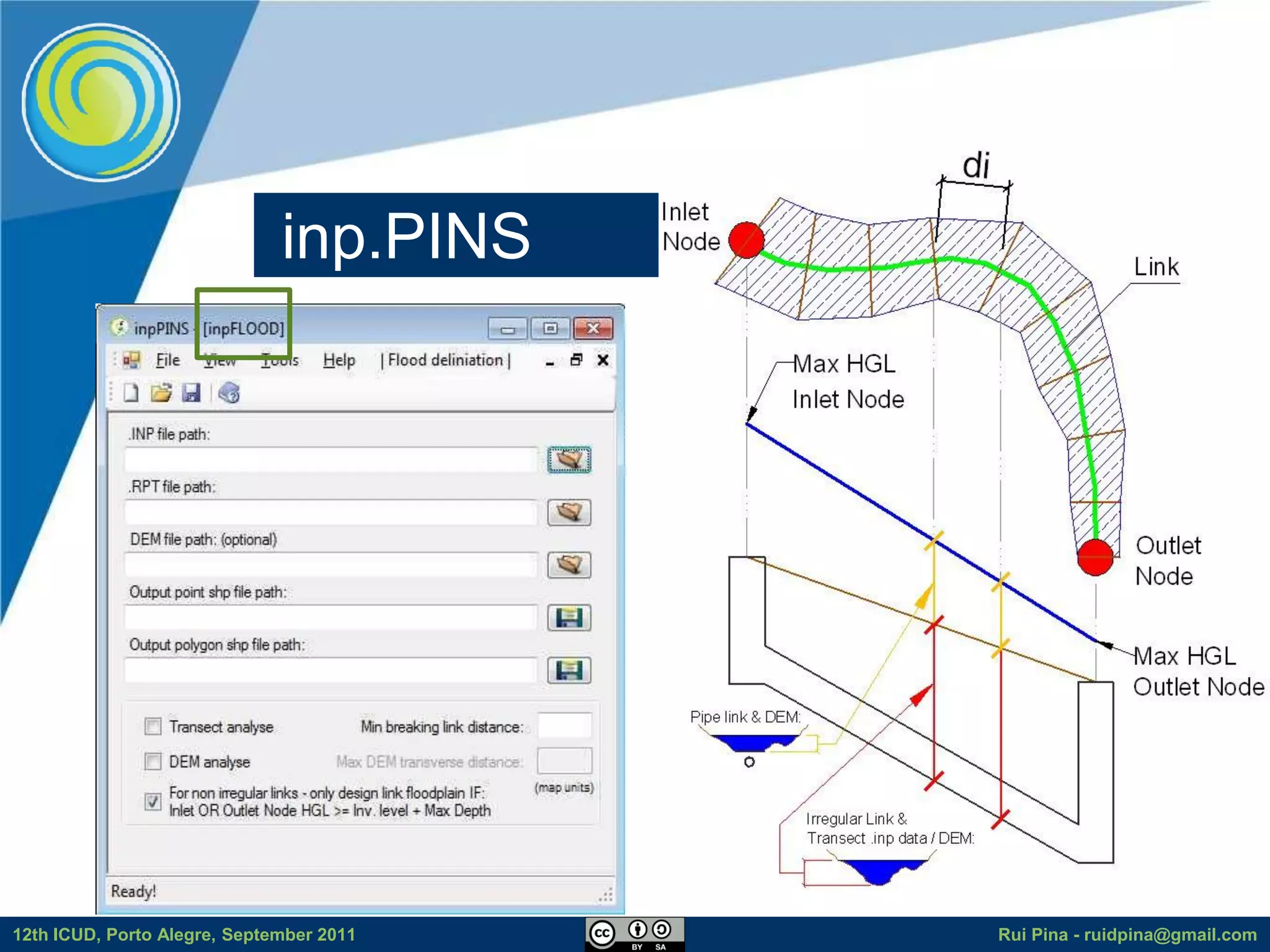
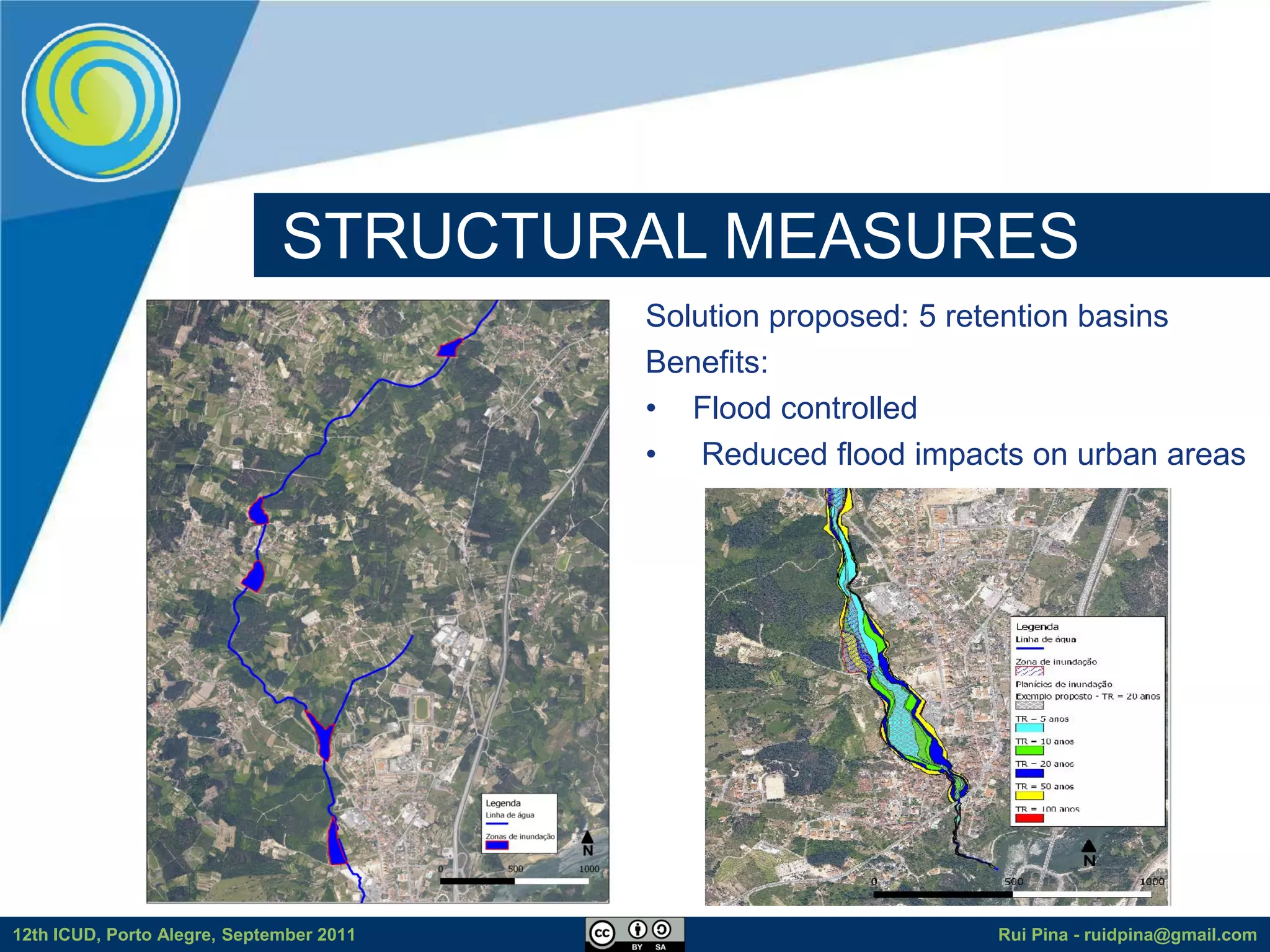
The document discusses using free and open source software (FOSS) for floodplain delineation. It presents inp.PINS, a tool that integrates GIS and the Storm Water Management Model (SWMM) to characterize watersheds and drainage systems. A case study applying inp.PINS to the Ribeira das Hortas catchment in Portugal is described. The document concludes that inp.PINS provides interoperability benefits and cost advantages over proprietary software for flood risk analysis.