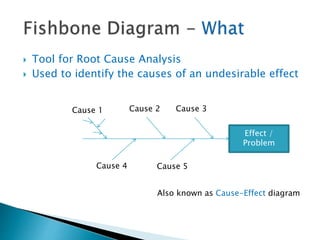
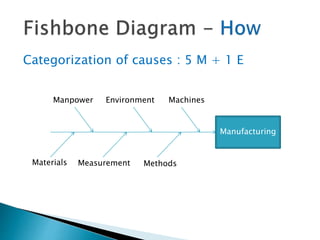
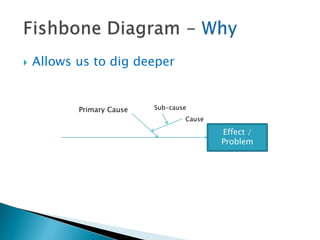
The document outlines a continuous improvement toolkit developed by Shilpa Singhal, which serves as a tool for root cause analysis using a cause-effect diagram to identify and organize causes of business problems. It categorizes causes into six areas: manpower, environment, machines, measurement, methods, and materials, and provides steps for constructing the analysis. The toolkit aims to optimize processes, identify potential issues, and support product design and planning.