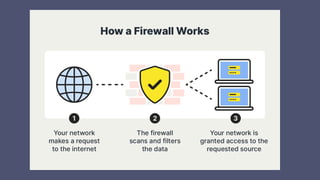
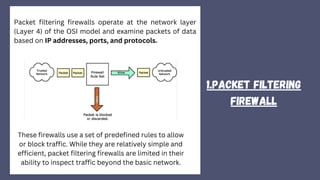
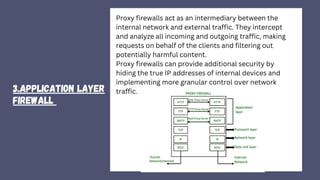
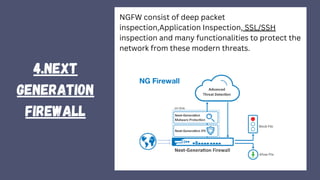
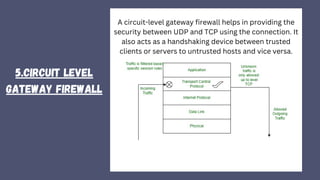
A firewall is a crucial network security device that monitors and filters incoming and outgoing traffic to prevent unauthorized access and potential threats. It operates based on security policies and can be hardware or software-based, evolving from simple access control lists to more advanced types like stateful inspection and next-generation firewalls. While effective in securing networks and logging activities, firewalls can be costly and may slow down network efficiency.