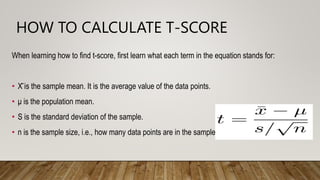
T-scores are standard scores used to describe a person's performance on a test compared to others. A score of 50 is average, with each increase or decrease of 10 representing one standard deviation. For example, a score of 60 is one standard deviation above average. T-scores allow comparison across different tests by converting raw scores to a common scale. Calculating a t-score involves taking the sample mean, subtracting the population mean, and dividing by the standard deviation of the sample, divided by the square root of the sample size.