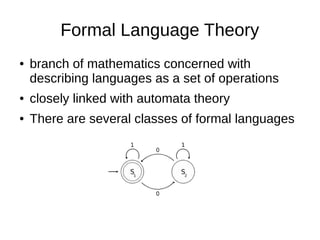
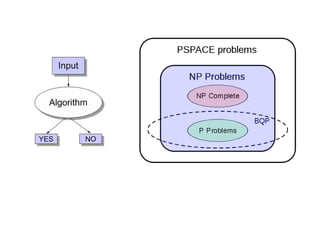
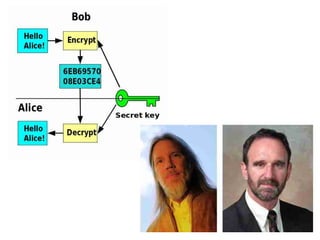
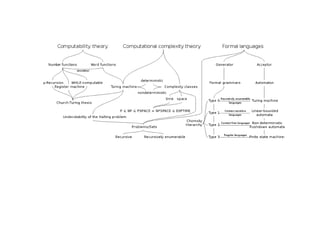
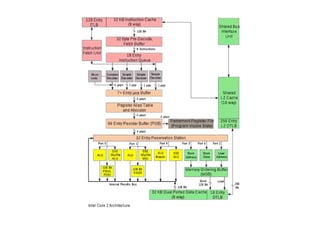
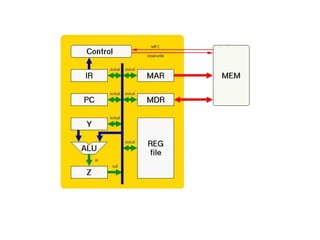
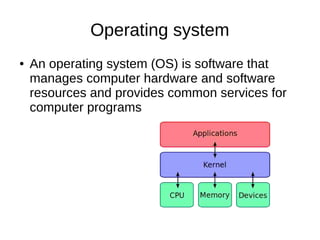
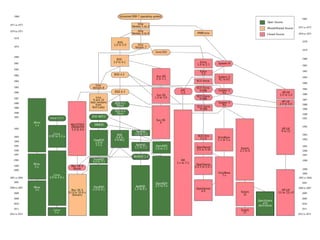
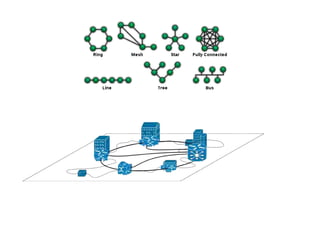
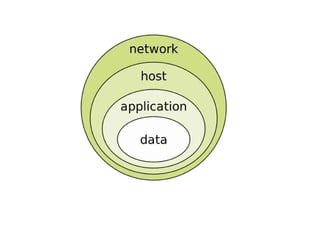
Computer science involves the theoretical and applied study of computation, algorithms, and artificial intelligence. Theoretical computer science explores computation itself and includes the study of computability, algorithms, and complexity theory. Applied computer science involves various fields including artificial intelligence, computer engineering, networking, databases, and software engineering. Computer scientists work on complex problems across many domains through the creation and analysis of computational processes and systems.