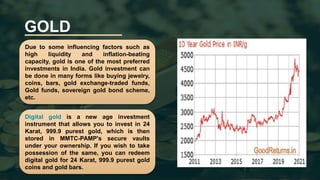
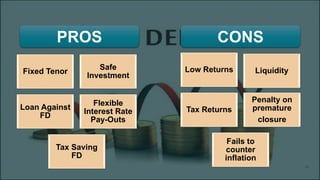
The document summarizes various financial sectors available for investment in India, including their pros and cons. It discusses share markets, mutual funds, gold, bank fixed deposits, provident funds, post office savings schemes, and insurance. The share market allows trading of publicly listed company shares but carries risks like losses from company failures. Mutual funds provide diversified, professionally managed portfolios at low cost but have annual fees. Gold is seen as a hedge against inflation but does not generate income. Bank deposits are seen as safe but offer low returns. Provident funds help save for retirement through mandatory contributions. Post office schemes offer government-backed guaranteed returns but have lower interest rates than some other options.