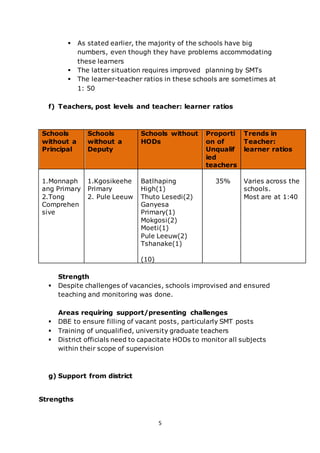
This document presents a baseline study report on school functionality trends across 20 schools in the Dr Ruth Segomotsi Mompati District of North West Province, South Africa. It finds that the schools generally have strengths in areas like teaching taking place according to timetables, cleanliness, and teacher preparation. However, it also identifies several areas needing support, such as low teacher morale, large class sizes, weak reading skills among learners, and underperformance in intermediate and senior grades. The report proposes a three-year school support program to address challenges in leadership, teaching, learning, resources, and learner performance.