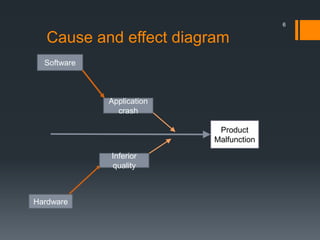
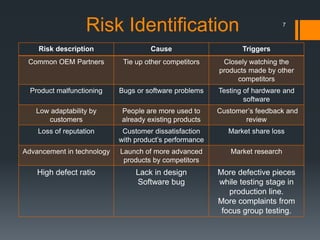
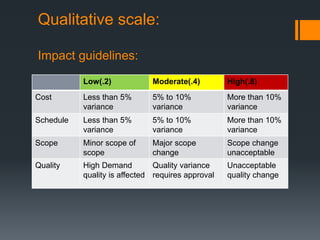
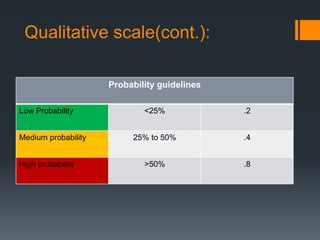
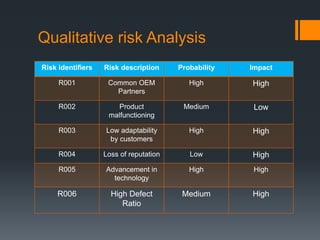
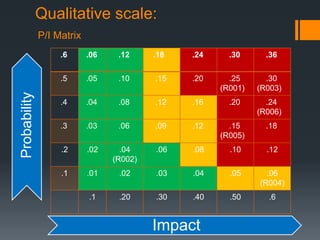
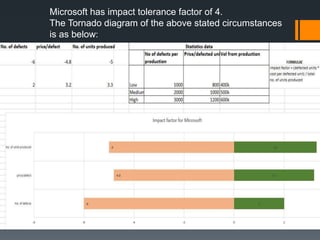
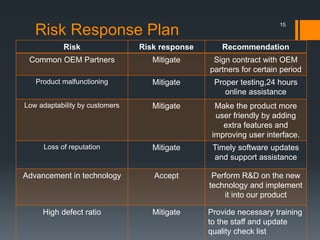
The document discusses the risks associated with the launch of the Microsoft Surface tablet in 2012 and the team's risk management plan. The team identified risks such as issues with common OEM partners, product malfunctions, low customer adoption, loss of reputation, advancing competitor technology, and high defect rates. They analyzed the risks qualitatively using a probability/impact matrix and quantitatively with an example tornado diagram. Their risk response plan was to mitigate risks through actions like signing contracts with partners, improved testing, enhancing usability, timely updates, research & development, and staff training.