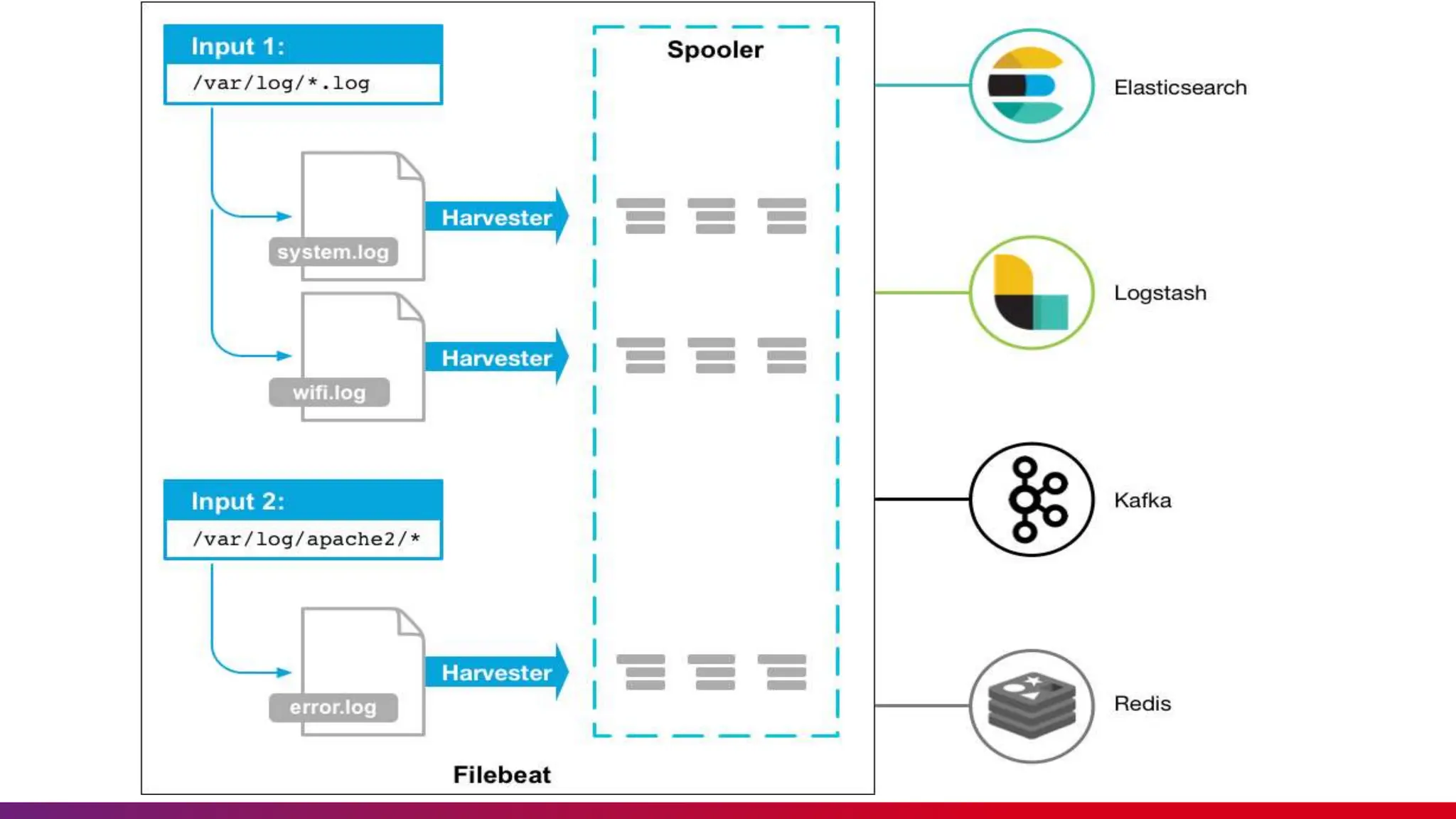
The document outlines the etiquette expected during a session on Elasticsearch, including punctuality, feedback, and minimizing disturbances. It offers an overview of Elasticsearch, Kibana, and Filebeat, detailing their functionalities and benefits, such as high performance, scalability, and data visualization. Additionally, it highlights the operational aspects of Filebeat as a log data shipper that forwards and centralizes logs for processing.