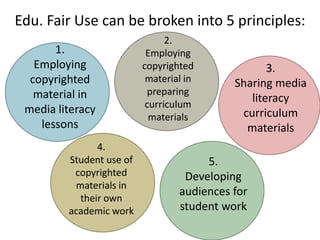
Educational fair use allows the use of copyrighted materials for educational purposes, including in lessons, curriculum materials, and student work. It has five key principles: 1) using copyrighted works in media literacy lessons, 2) incorporating them into curriculum materials, 3) sharing curriculum materials, 4) allowing student use in academic work, and 5) developing audiences for student work. Creative Commons licenses provide legal means to share, remix, and reuse digital content, aiming to realize the full potential of the internet through universal access to research, education, and culture. They allow simple selection of license terms that both protect content and fit creators' needs. Major organizations and websites use Creative Commons licenses.