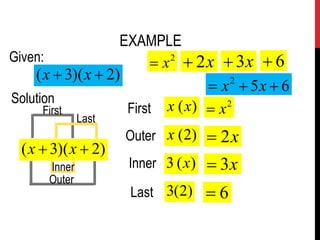
The document discusses factoring polynomials. It covers 7 techniques for factoring different types of polynomials, including those with a common monomial factor. It provides examples of finding the greatest common factor and using it to factor polynomials. Key steps involve finding the greatest common monomial factor, dividing each term by the factor, and combining the results into a factored form. Methods like factoring quadratics using FOIL and box multiplication are also reviewed.