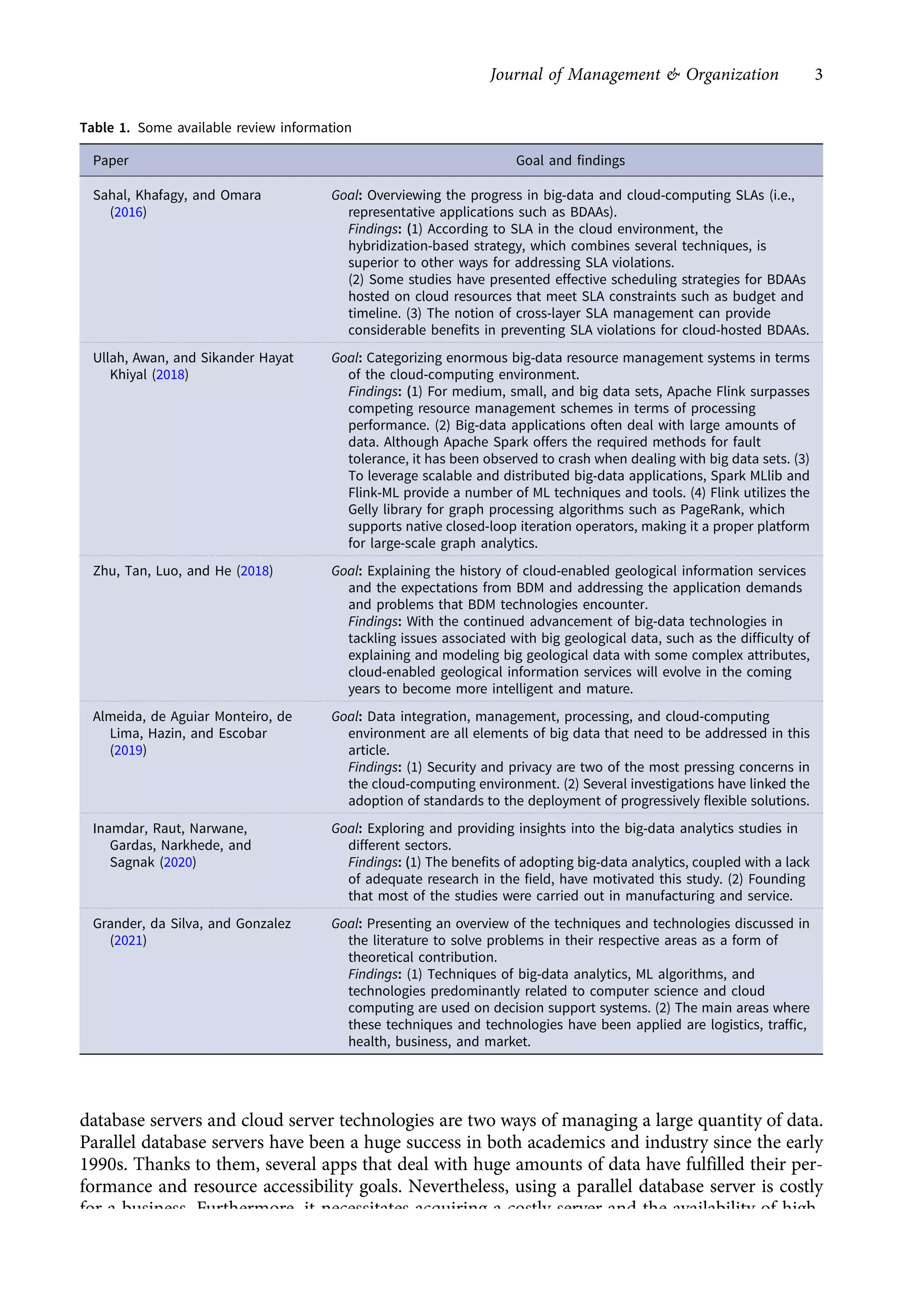
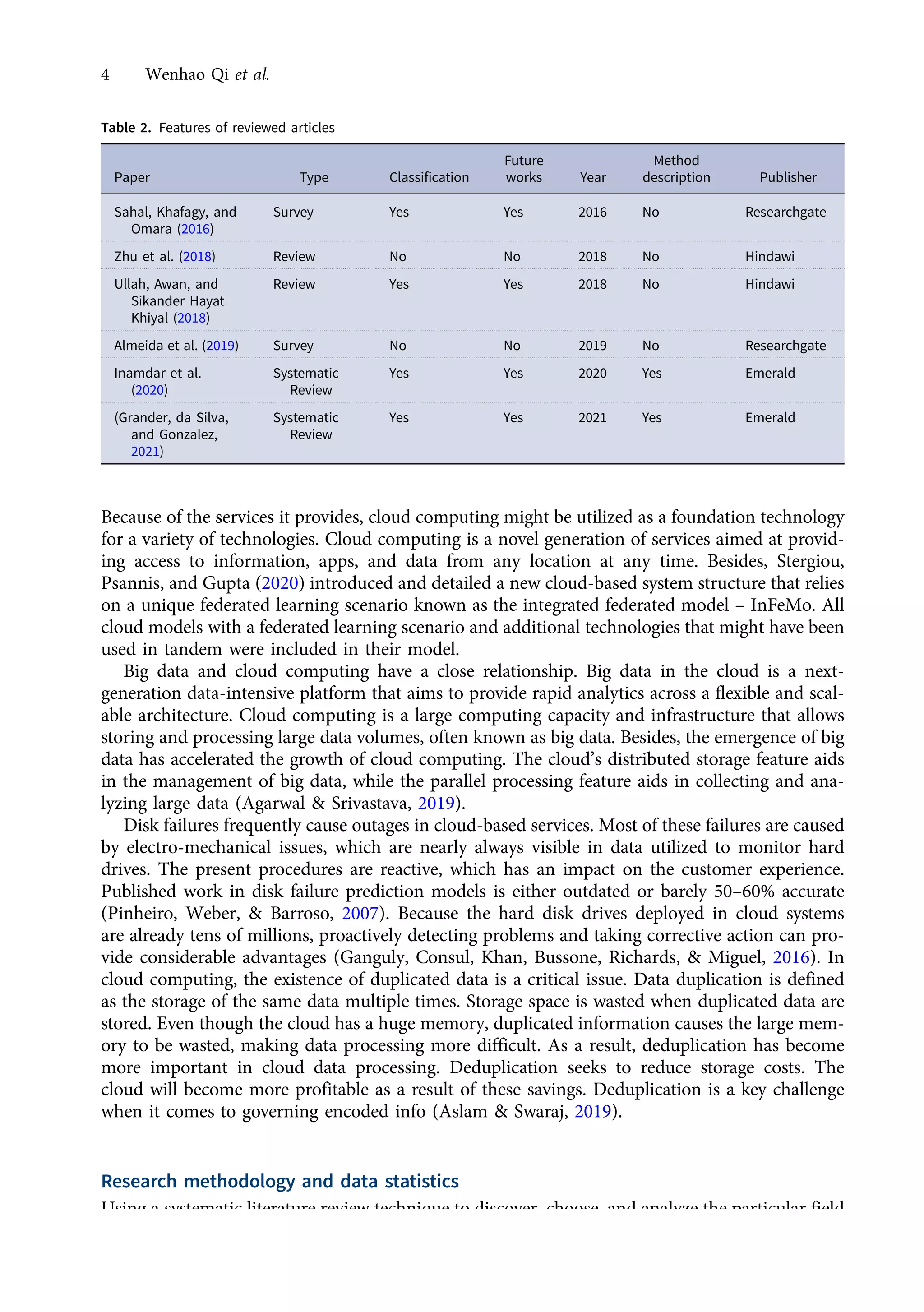
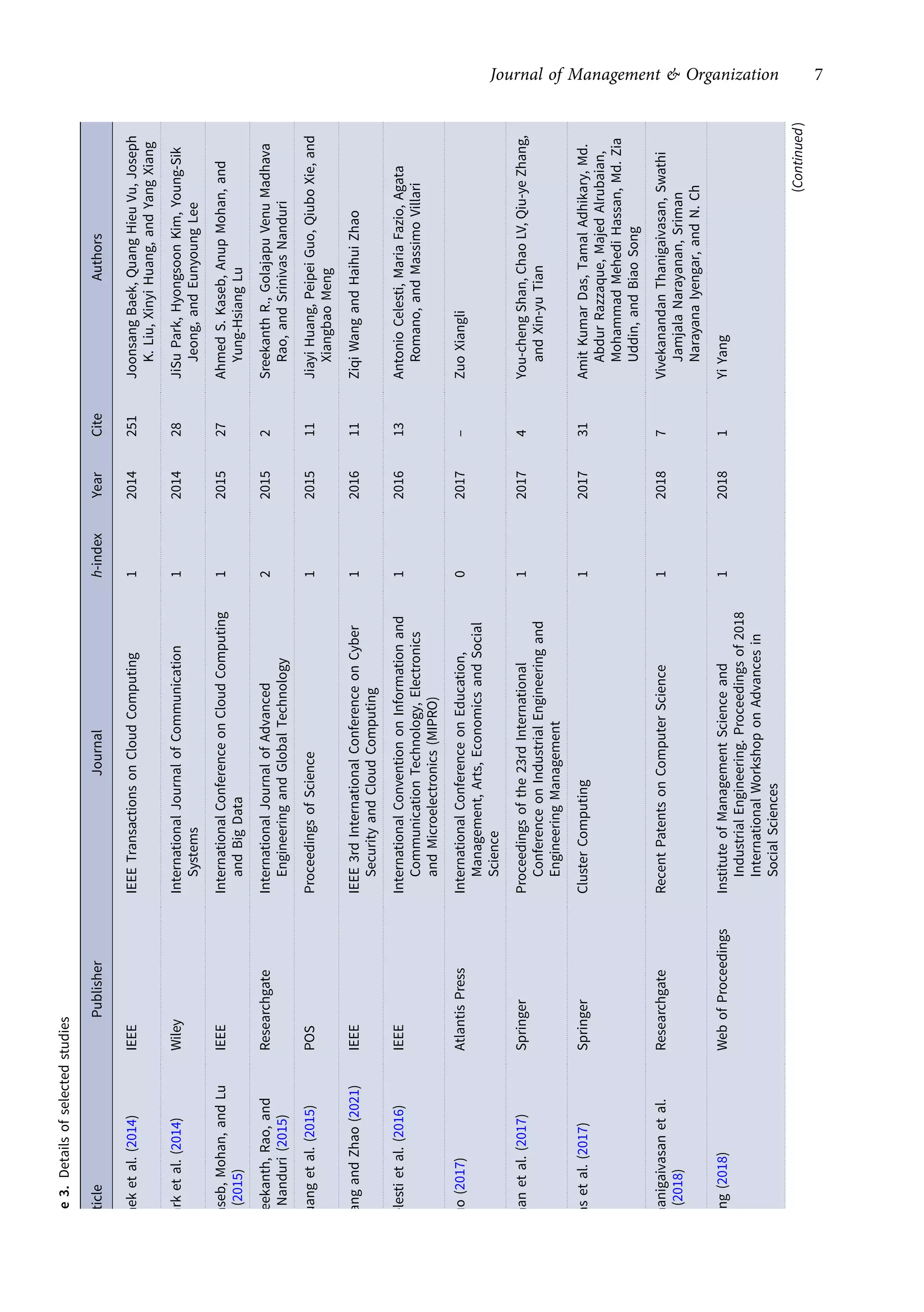
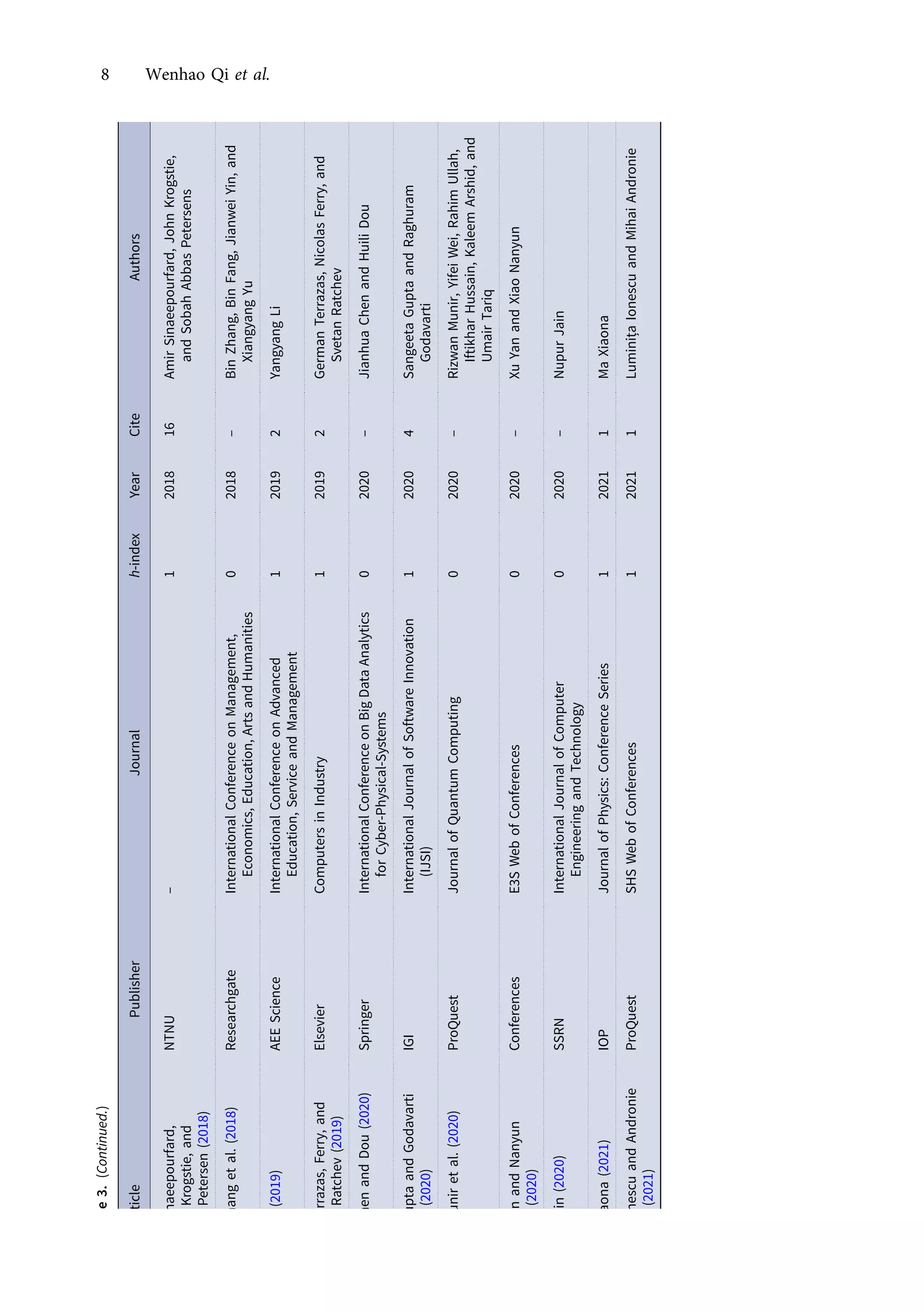
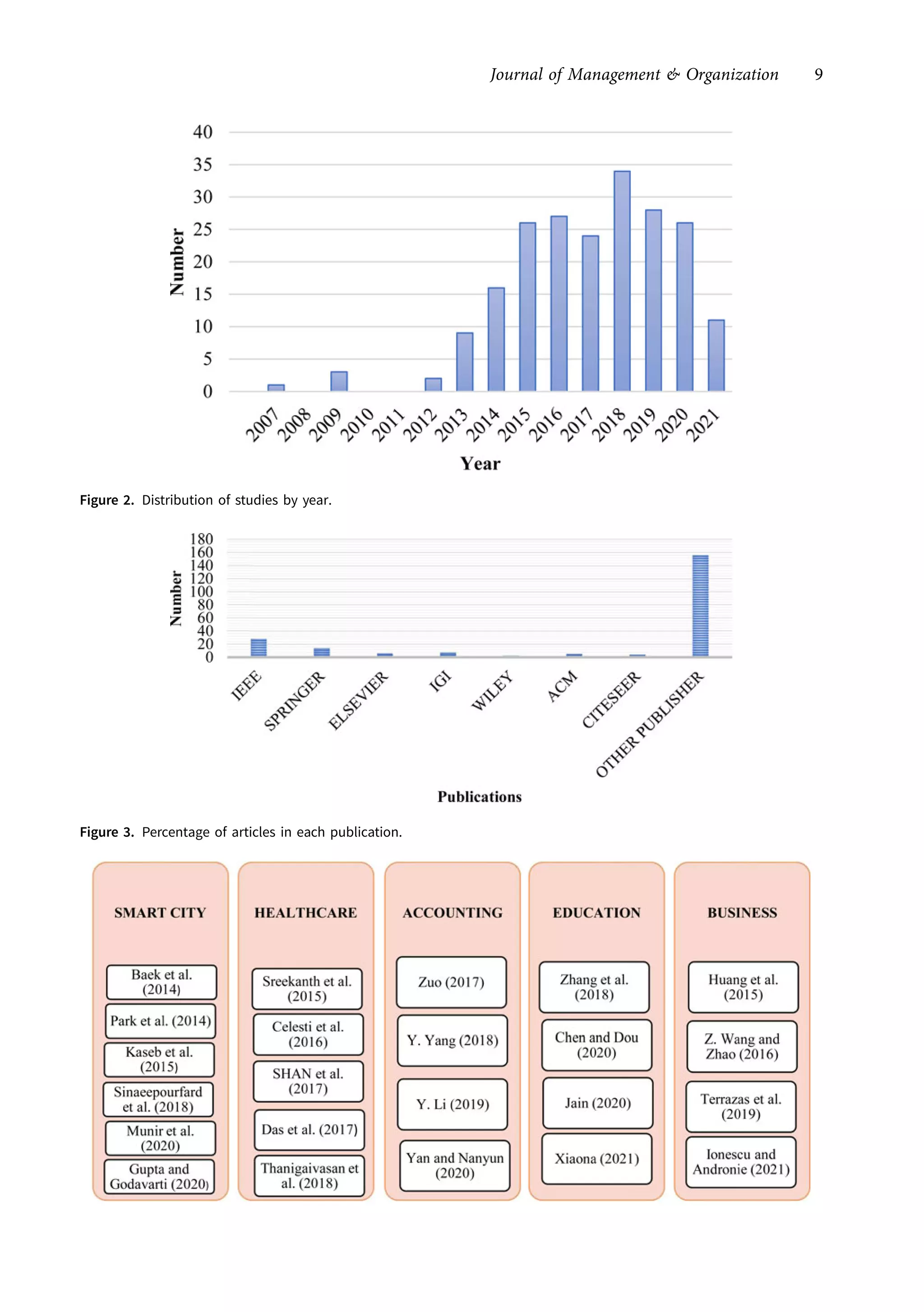
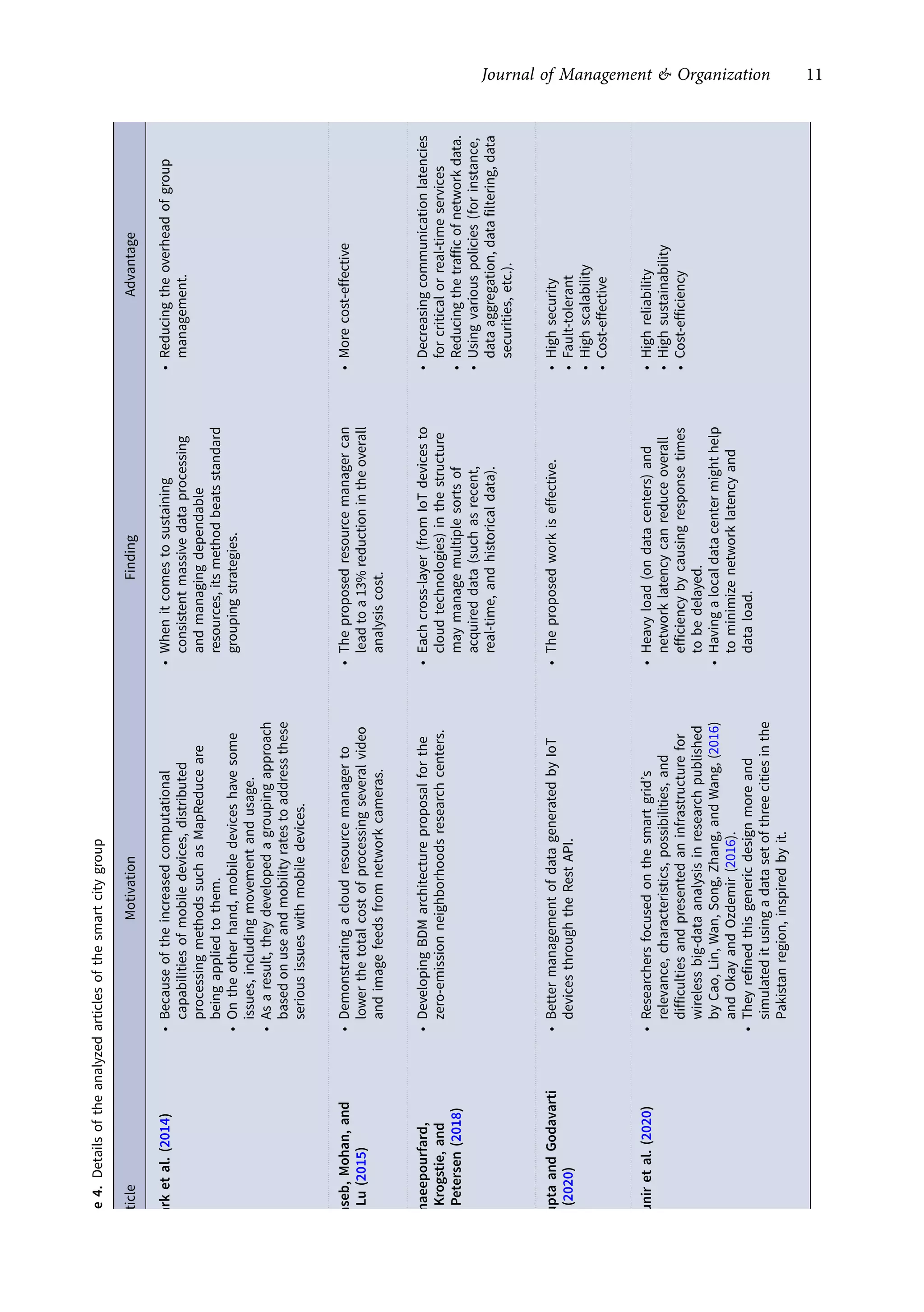
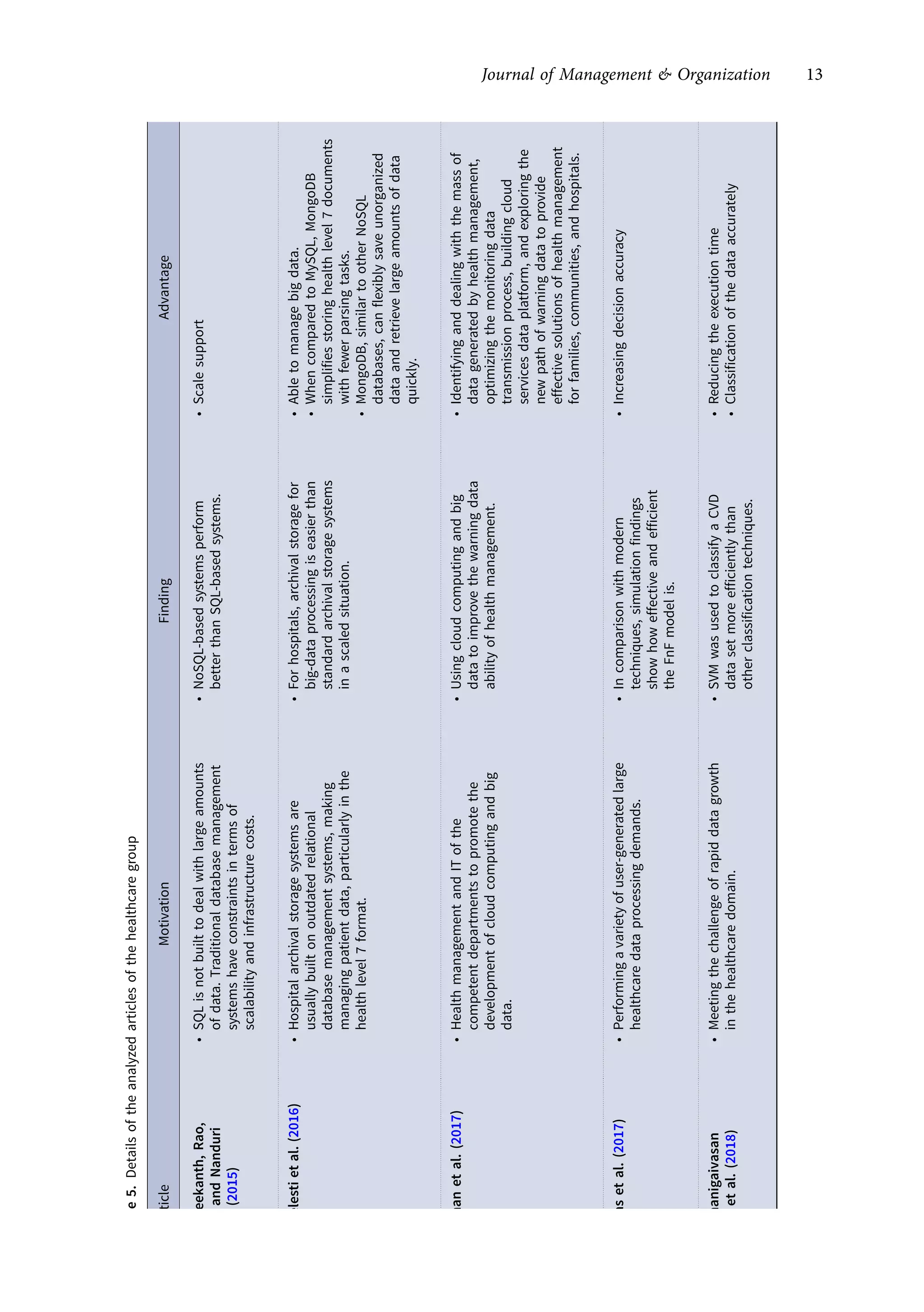
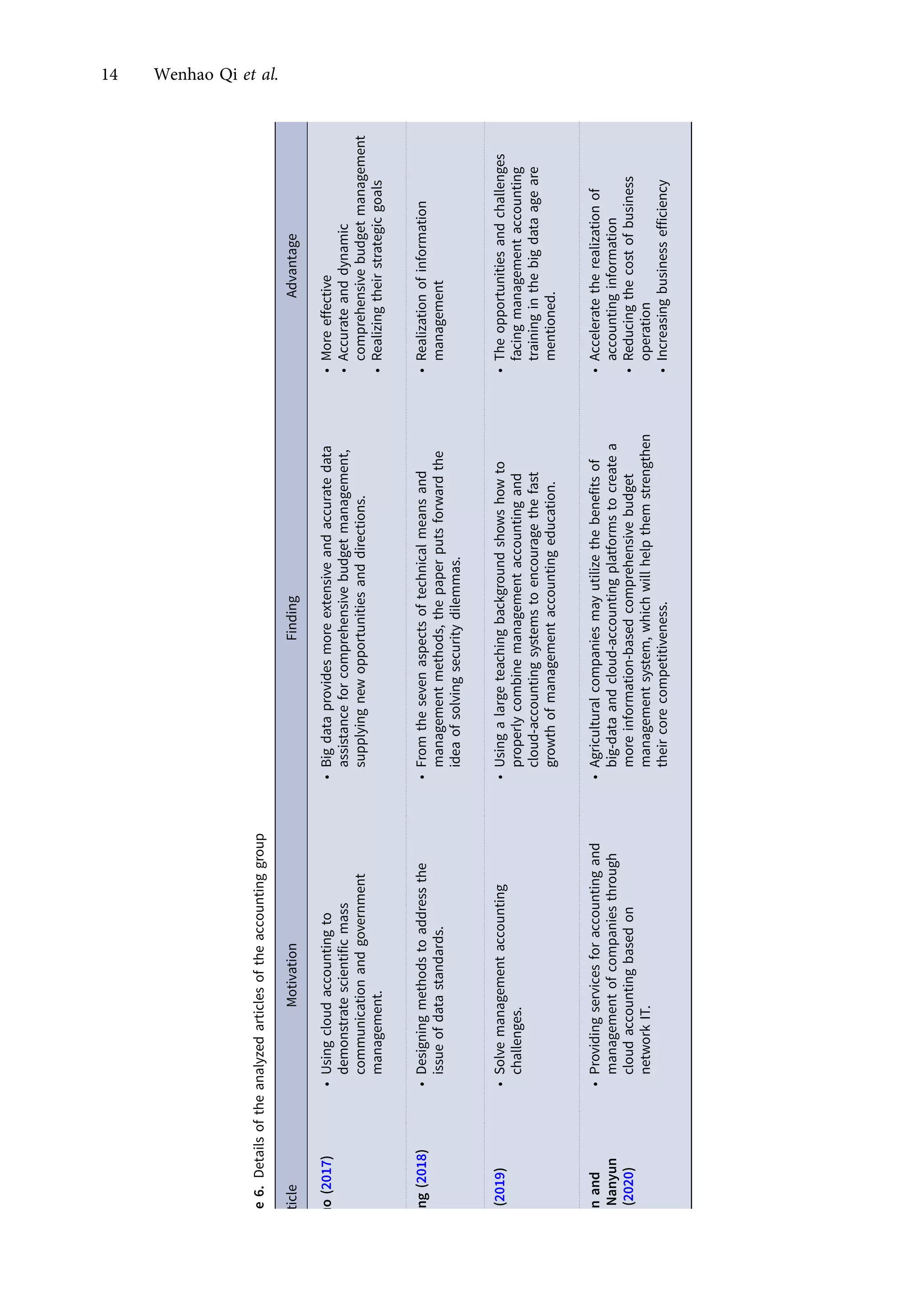
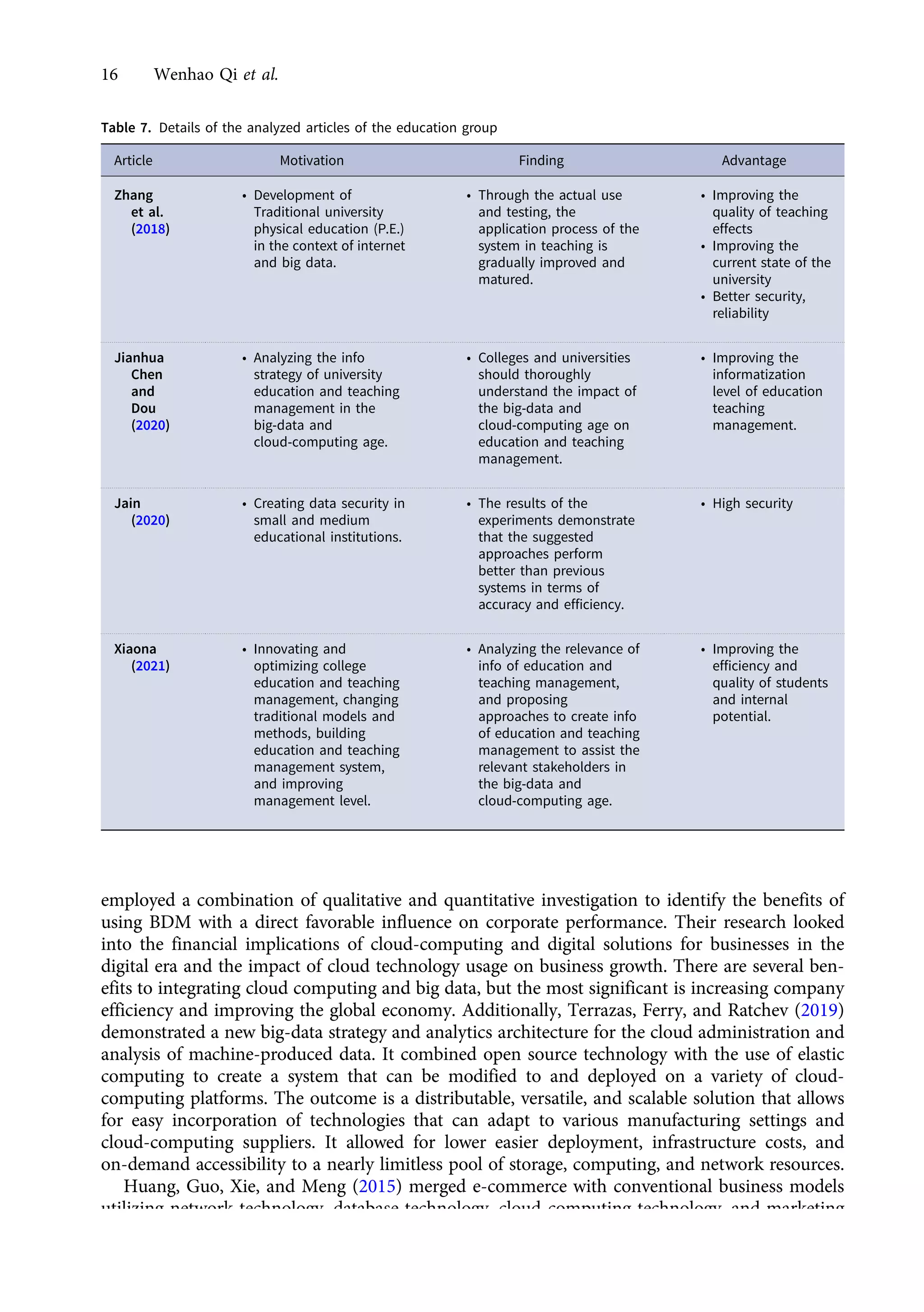
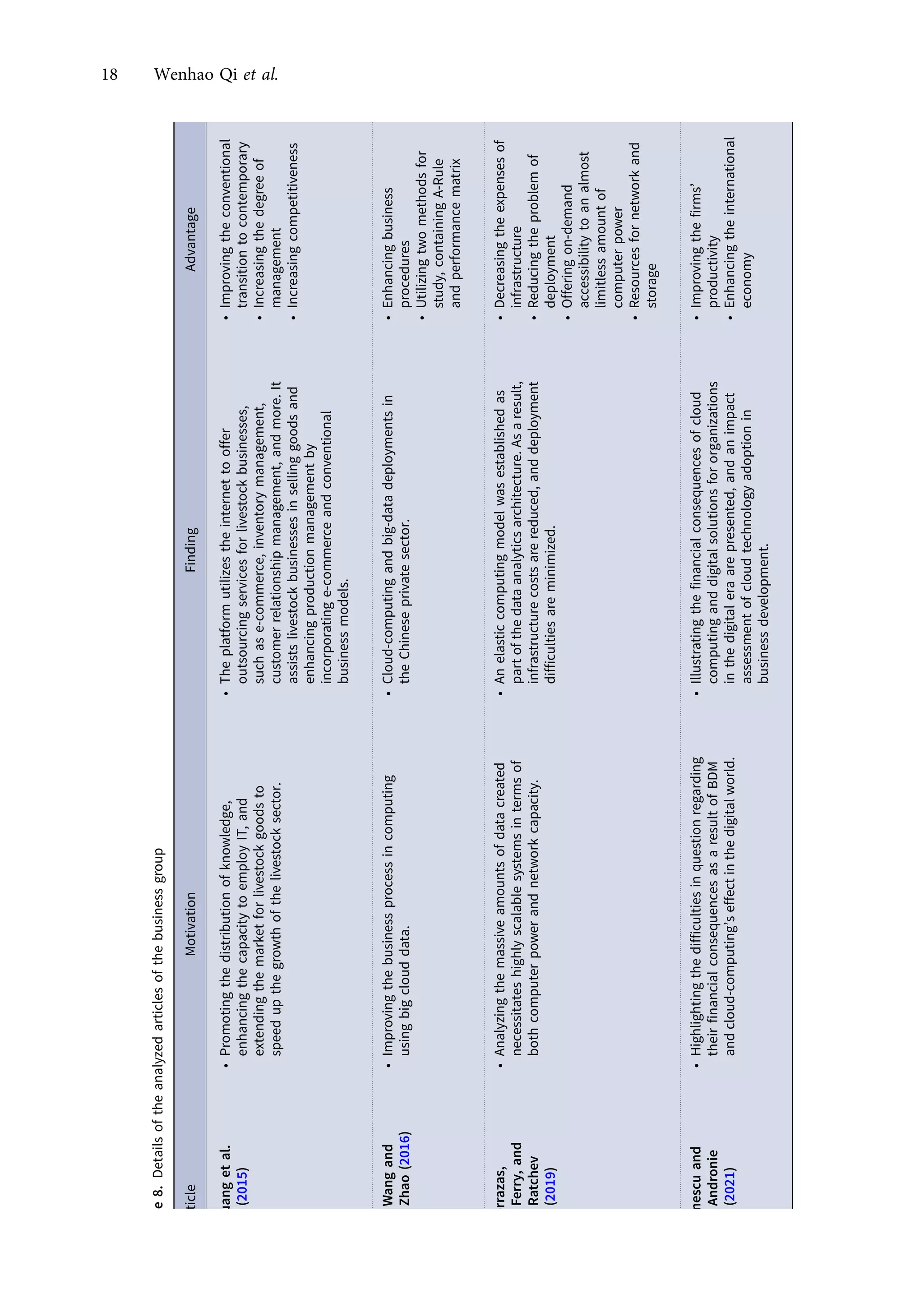
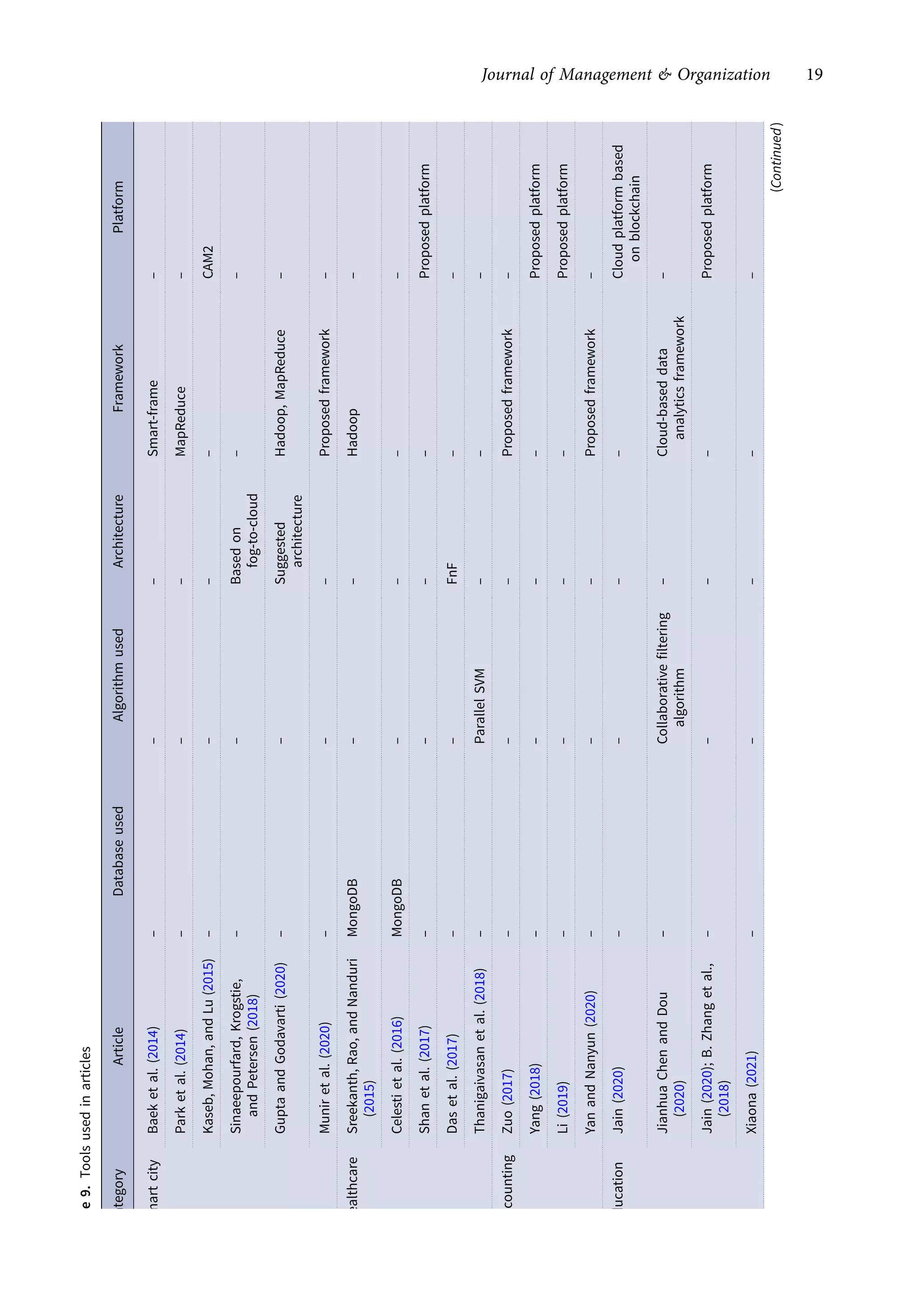
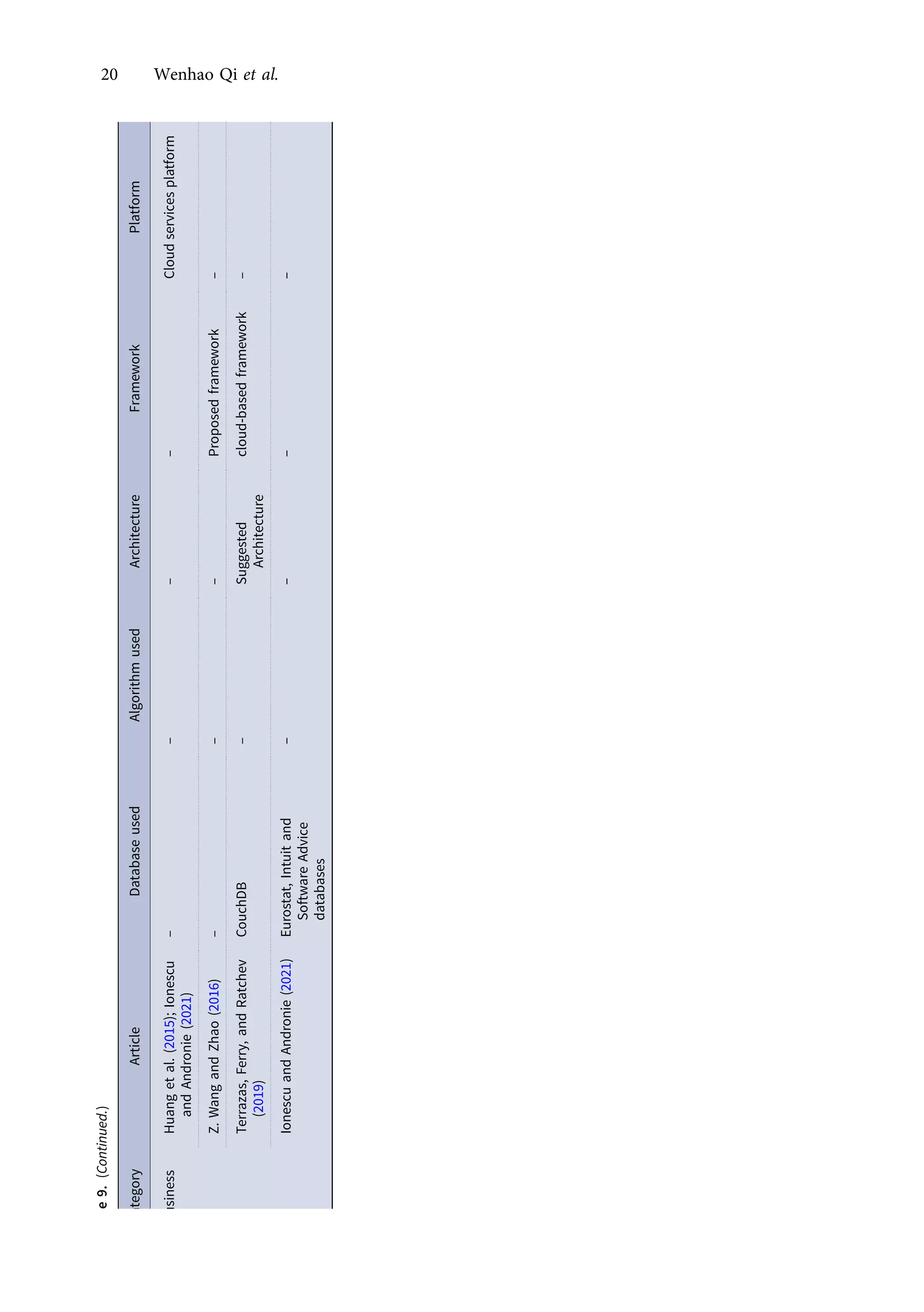
This research article explores the management of big data in modern businesses and organizations using cloud computing, highlighting its advantages, challenges, and impact on efficiency and trade. It emphasizes the need for effective big-data management (BDM) systems to handle vast data volumes generated by digital life, presenting a systematic review of existing literature. The authors identify gaps in current research and propose directions for future studies in this domain.