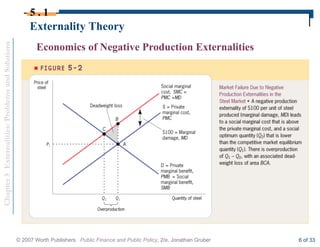
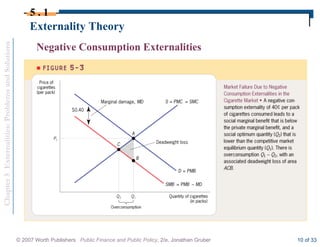
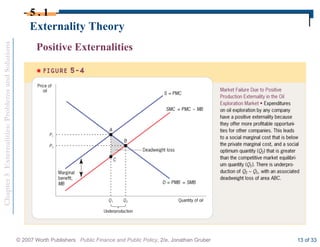
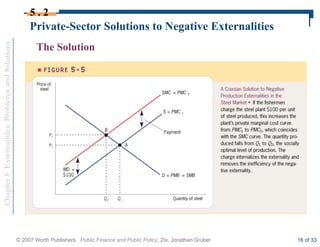
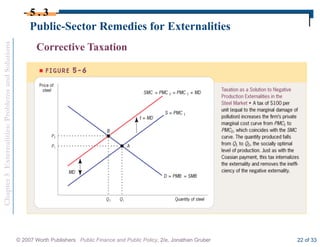
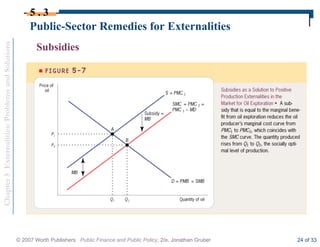
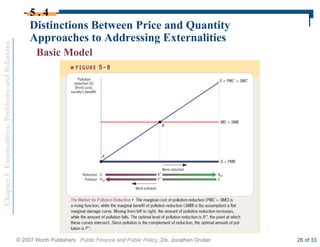
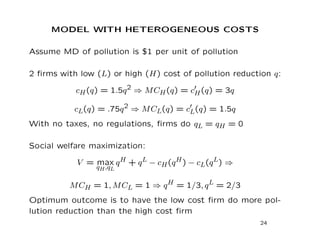
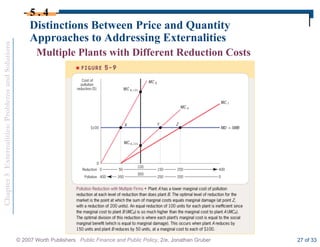
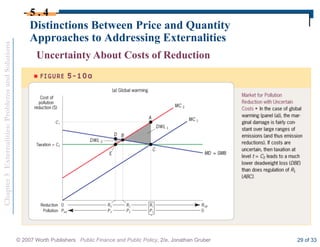
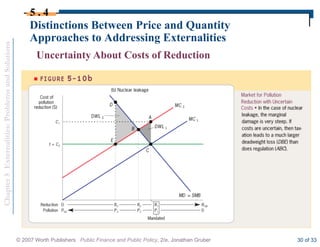
This document discusses externalities and potential solutions. It begins by defining externalities as costs or benefits imposed on third parties not involved in a transaction. Negative production externalities like pollution mean firms do not face all social costs of production, leading to overproduction. The Coase theorem holds that with well-defined property rights and no transaction costs, bargaining can achieve efficiency, but in practice this is difficult for large-scale externalities. Government remedies for externalities include corrective taxes equal to marginal damage or quantity regulations to limit production to efficient levels.