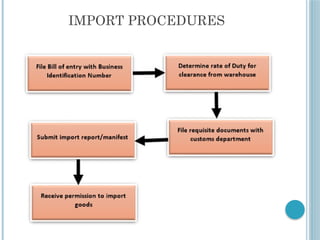
The document outlines export and import procedures and documentation, detailing basic processes for each, including market research, trade regulations, sales contracts, and customs clearance. It emphasizes the legal frameworks governing foreign trade and the various types of export sales contracts. Additionally, it highlights that import trade involves bringing goods into a country and is heavily regulated by national policies.