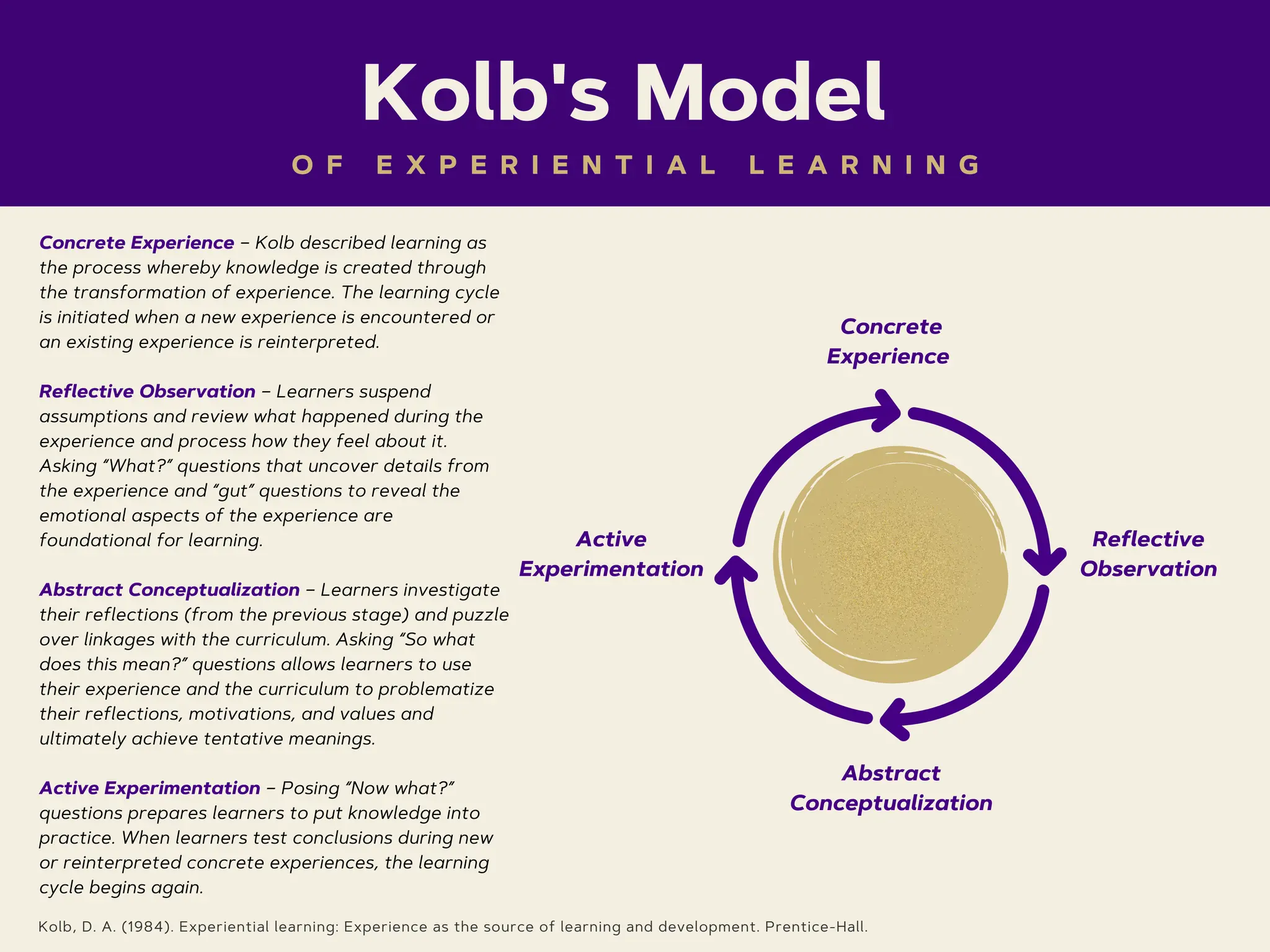
Kolb's model of experiential learning outlines a cycle that starts with concrete experience, where knowledge is created through transforming experiences. It progresses through reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation, with learners critically analyzing their experiences and applying newfound knowledge. This cyclical process reinforces learning as an ongoing development of understanding and practice.