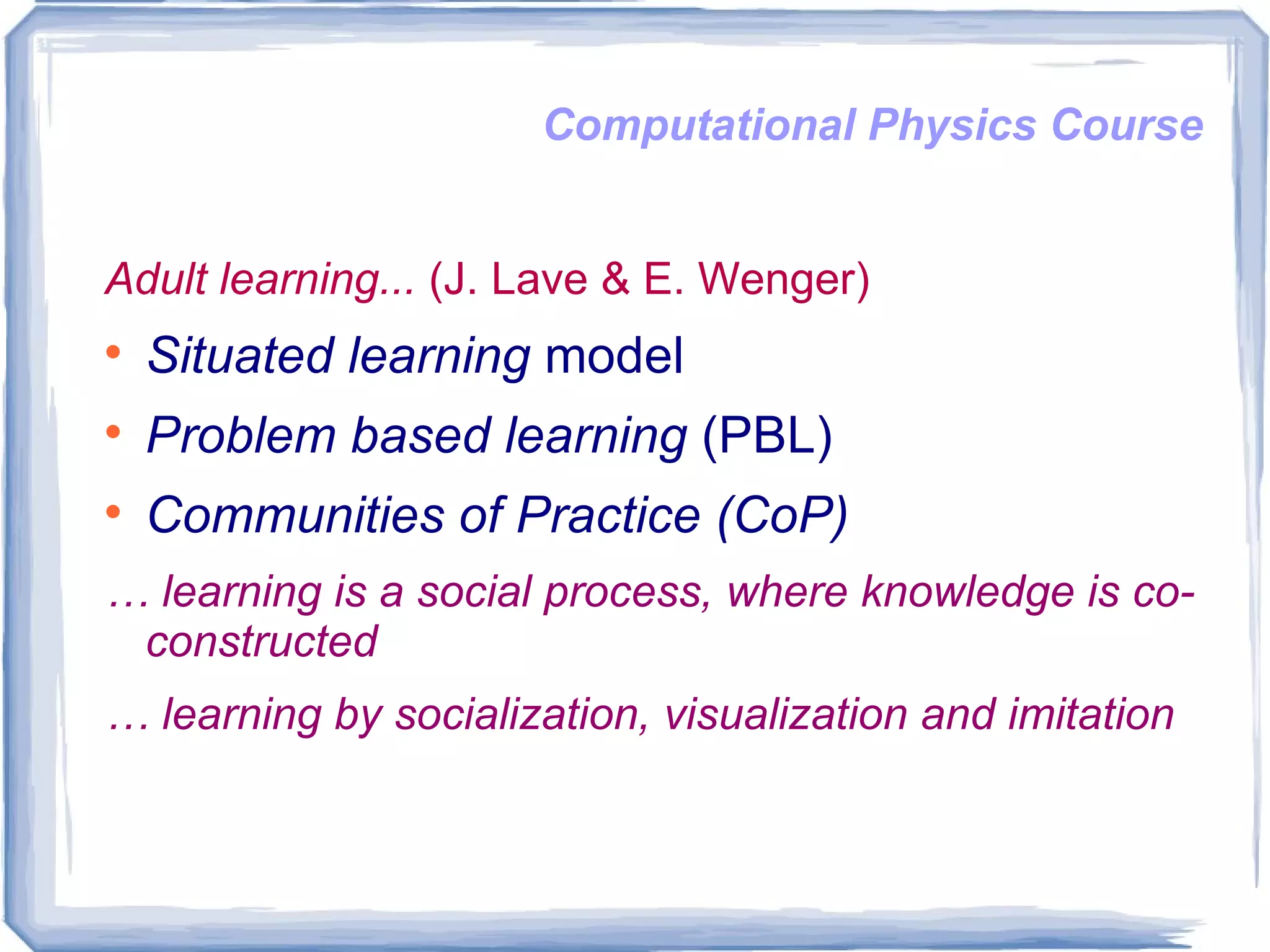
The document discusses an open and online computational physics course designed for intermediate undergraduate students, emphasizing a learner-centered, problem-based learning approach that incorporates adult learning principles. It highlights skill development in scientific computing, diverse programming environments, and the use of educational technologies like Linux-based tools and online resources. Student feedback indicated advantages such as autonomy in learning pace and the ability to explore problem-solving, while also noting the risk of accumulated work due to a lack of explicit instructor pressure.













![Computational Physics Course Computational Physics Course versions: Grou.ps: http://grou.ps/zendoscero/ Wikispaces.com: http://fisicacomputacional.wikispaces.com/ Pbworks.com: http://fisicacomputacional.pbworks.com/ Thank You! Questions and comments E-mail: [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/compphysicsuson-110815001458-phpapp02/75/Experience-in-learning-in-an-open-Computational-Physics-Course-at-undergraduate-level-16-2048.jpg)
